您的位置:首页
『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其七:损失函数
2018-07-23 19:12
483 查看
Fork版本项目地址:SSD
定义

为第i个搜索框和对应的第j个ground truth box,相应的类别为p。目标函数定义为:

其中,N为匹配的搜索框。如果N=0,loss为零。

为预测框

和ground truth box

的Smooth L1 loss,

值通过cross validation设置为1。
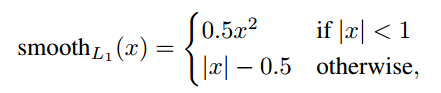

定义如下:
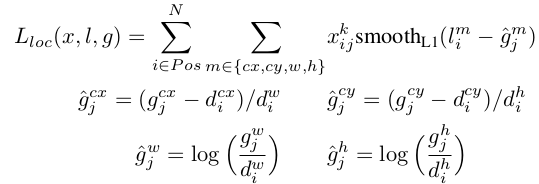
其中,

为预测框,

为ground truth。

为补偿(regress to offsets)后的默认框(

)的中心,

为默认框的宽和高。

定义为多累别softmax loss,公式如下:
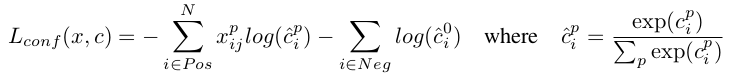
更为详细的字母说明如下:
i指代搜索框序号,j指代真实框序号,p指代类别序号,p=0表示背景,

中取1表示此时第i个搜索框和第j个类别框IOU大于阈值,此时真实框中对象类别为p。
cip表示第i个搜索框对应类别p的预测概率。

也就是说只要IOU到达阈值就认为这个搜索框是正样本(fpmask标记),注意,即使是第0类也可以(不过一般来说是不会有真实框框住背景并进行标注的), 然后看负样本,
此时的负样本(fnmask标记)同样的为{0,1},且和正样本互补,但是这样会导致负样本过多,所以建立nvalue用于筛选负样本,nvalue中fnmask为1的位置记为对应搜索框的第0类(背景)预测概率,否则记为1(fpmask标记位置),
在进一步处理中,我们希望负样本不要超过正样本数目的3倍,确保能够收敛(具体推导不明),由于知道这些负样本都属于背景(和真实框IOU不足),所以理论上其class 0预测值越大越好,我们取class 0预测值最小的3倍正样本数目的负样本,最大化其class 0预测值,达到最小化损失函数的目的。筛选后的负样本(fnmask标记)为原负样本中class 0预测值最小的目标数目的点。
对应两部分的损失函数计算。上面的公式中第一部分比第二部分多了个x,实际上是为了确定cp中p的取值,而第二部分不需要了,因为p恒为0。
no_classes为标签,只要保证fnmask中标记点(负样本)对应位置为0即可。对应的gclasses其实只要pnmask为1位置有真实分类标签即可,之所以额外划分出no_classes是因为gclasses在迭代生成时有可能给得分(IOU)不足够高的搜索框标注上类别信息,而在本函数一开始,我们就使用得分(IOU)对搜索框进行了二次筛选(在gclasses、gscores、glocalisations生成过程中会对IOU进行一次筛选),fpmask可能会将一些一次筛选中标记了gclasses(且不为0)的搜索框剔除,这对正样本没有影响(正样本位置一定是gclasses标记位置的子集),但是会影响负样本(新的认定为背景的搜索框在gclasses上有标记类别,同时也是说其gscore分数不够二次筛选的标准),所以需要为负样本标注新的类别标签。
调用函数如下:
一、损失函数介绍
SSD损失函数分为两个部分:对应搜索框的位置loss(loc)和类别置信度loss(conf)。(搜索框指网络生成的网格)定义
为第i个搜索框和对应的第j个ground truth box,相应的类别为p。目标函数定义为:
其中,N为匹配的搜索框。如果N=0,loss为零。
为预测框
和ground truth box
的Smooth L1 loss,
值通过cross validation设置为1。
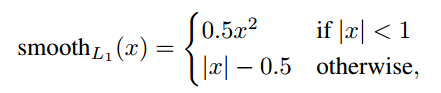
定义如下:
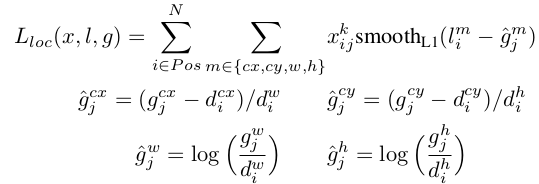
其中,
为预测框,
为ground truth。
为补偿(regress to offsets)后的默认框(
)的中心,
为默认框的宽和高。
定义为多累别softmax loss,公式如下:
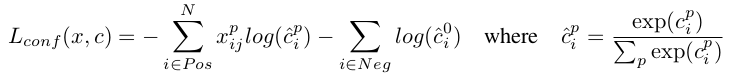
更为详细的字母说明如下:
i指代搜索框序号,j指代真实框序号,p指代类别序号,p=0表示背景,
中取1表示此时第i个搜索框和第j个类别框IOU大于阈值,此时真实框中对象类别为p。
cip表示第i个搜索框对应类别p的预测概率。

二、分类损失函数
有了上图的分析,我们可以看具体实现了,首先我们看Lconf部分的计算,其分为最大化第一个累加符号和最大化第二个累加符号两个部分(这牵扯到另一个问题:Pos框和Neg框的选择,这一点我们在下面分析代码中会也提及,注意两者都是对搜索框进行的讨论),我们将分别讨论两部分的实现逻辑,根据代码来看,首先确定正样本框的掩码:dtype = logits.dtype pmask = gscores > match_threshold # (全部搜索框数目, 21),类别搜索框和真实框IOU大于阈值 fpmask = tf.cast(pmask, dtype) # 浮点型前景掩码(前景假定为含有对象的IOU足够的搜索框标号) n_positives = tf.reduce_sum(fpmask) # 前景总数
也就是说只要IOU到达阈值就认为这个搜索框是正样本(fpmask标记),注意,即使是第0类也可以(不过一般来说是不会有真实框框住背景并进行标注的), 然后看负样本,
no_classes = tf.cast(pmask, tf.int32) predictions = slim.softmax(logits) # 此时每一行的21个数转化为概率 nmask = tf.logical_and(tf.logical_not(pmask), gscores > -0.5) # IOU达不到阈值的类别搜索框位置记1 fnmask = tf.cast(nmask, dtype) nvalues = tf.where(nmask, predictions[:, 0], # 框内无物体标记为背景预测概率 1. - fnmask) # 框内有物体位置标记为1 nvalues_flat = tf.reshape(nvalues, [-1])
此时的负样本(fnmask标记)同样的为{0,1},且和正样本互补,但是这样会导致负样本过多,所以建立nvalue用于筛选负样本,nvalue中fnmask为1的位置记为对应搜索框的第0类(背景)预测概率,否则记为1(fpmask标记位置),
# 在nmask中剔除n_neg个最不可能背景点(对应的class0概率最低) max_neg_entries = tf.cast(tf.reduce_sum(fnmask), tf.int32) # 3 × 前景掩码数量 + batch_size n_neg = tf.cast(negative_ratio * n_positives, tf.int32) + batch_size n_neg = tf.minimum(n_neg, max_neg_entries) val, idxes = tf.nn.top_k(-nvalues_flat, k=n_neg) # 最不可能为背景的n_neg个点 max_hard_pred = -val[-1] # Final negative mask. nmask = tf.logical_and(nmask, nvalues < max_hard_pred) # 不是前景,又最不像背景的n_neg个点 fnmask = tf.cast(nmask, dtype)
在进一步处理中,我们希望负样本不要超过正样本数目的3倍,确保能够收敛(具体推导不明),由于知道这些负样本都属于背景(和真实框IOU不足),所以理论上其class 0预测值越大越好,我们取class 0预测值最小的3倍正样本数目的负样本,最大化其class 0预测值,达到最小化损失函数的目的。筛选后的负样本(fnmask标记)为原负样本中class 0预测值最小的目标数目的点。
# Add cross-entropy loss.
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy_pos'):
loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,
labels=gclasses) # 0-20
loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * fpmask), batch_size, name='value')
tf.losses.add_loss(loss)
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy_neg'):
loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,
labels=no_classes) # {0,1}
loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * fnmask), batch_size, name='value')
tf.losses.add_loss(loss)对应两部分的损失函数计算。上面的公式中第一部分比第二部分多了个x,实际上是为了确定cp中p的取值,而第二部分不需要了,因为p恒为0。
no_classes为标签,只要保证fnmask中标记点(负样本)对应位置为0即可。对应的gclasses其实只要pnmask为1位置有真实分类标签即可,之所以额外划分出no_classes是因为gclasses在迭代生成时有可能给得分(IOU)不足够高的搜索框标注上类别信息,而在本函数一开始,我们就使用得分(IOU)对搜索框进行了二次筛选(在gclasses、gscores、glocalisations生成过程中会对IOU进行一次筛选),fpmask可能会将一些一次筛选中标记了gclasses(且不为0)的搜索框剔除,这对正样本没有影响(正样本位置一定是gclasses标记位置的子集),但是会影响负样本(新的认定为背景的搜索框在gclasses上有标记类别,同时也是说其gscore分数不够二次筛选的标准),所以需要为负样本标注新的类别标签。
三、定位损失函数
定位损失函数形式简单一点,# Add localization loss: smooth L1, L2, ...
with tf.name_scope('localization'):
# Weights Tensor: positive mask + random negative.
weights = tf.expand_dims(alpha * fpmask, axis=-1)
loss = custom_layers.abs_smooth(localisations - glocalisations)
loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * weights), batch_size, name='value')
tf.losses.add_loss(loss)调用函数如下:
def abs_smooth(x): """Smoothed absolute function. Useful to compute an L1 smooth error. Define as: x^2 / 2 if abs(x) < 1 abs(x) - 0.5 if abs(x) > 1 We use here a differentiable definition using min(x) and abs(x). Clearly not optimal, but good enough for our purpose! """ absx = tf.abs(x) minx = tf.minimum(absx, 1) r = 0.5 * ((absx - 1) * minx + absx) return r
四、损失函数全览
def ssd_losses(logits, localisations, # 预测类别,位置
gclasses, glocalisations, gscores, # ground truth类别,位置,得分
match_threshold=0.5,
negative_ratio=3.,
alpha=1.,
label_smoothing=0.,
device='/cpu:0',
scope=None):
with tf.name_scope(scope, 'ssd_losses'):
# 提取类别数和batch_size
lshape = tfe.get_shape(logits[0], 5) # tensor_shape函数可以取代
num_classes = lshape[-1]
batch_size = lshape[0]
# Flatten out all vectors!
flogits = []
fgclasses = []
fgscores = []
flocalisations = []
fglocalisations = []
for i in range(len(logits)): # 按照ssd特征层循环
flogits.append(tf.reshape(logits[i], [-1, num_classes]))
fgclasses.append(tf.reshape(gclasses[i], [-1]))
fgscores.append(tf.reshape(gscores[i], [-1]))
flocalisations.append(tf.reshape(localisations[i], [-1, 4]))
fglocalisations.append(tf.reshape(glocalisations[i], [-1, 4]))
# And concat the crap!
logits = tf.concat(flogits, axis=0) # 全部的搜索框,对应的21类别的输出
gclasses = tf.concat(fgclasses, axis=0) # 全部的搜索框,真实的类别数字
gscores = tf.concat(fgscores, axis=0) # 全部的搜索框,和真实框的IOU
localisations = tf.concat(flocalisations, axis=0)
glocalisations = tf.concat(fglocalisations, axis=0)
"""[<tf.Tensor 'ssd_losses/concat:0' shape=(279424, 21) dtype=float32>,
<tf.Tensor 'ssd_losses/concat_1:0' shape=(279424,) dtype=int64>,
<tf.Tensor 'ssd_losses/concat_2:0' shape=(279424,) dtype=float32>,
<tf.Tensor 'ssd_losses/concat_3:0' shape=(279424, 4) dtype=float32>,
<tf.Tensor 'ssd_losses/concat_4:0' shape=(279424, 4) dtype=float32>]
"""
dtype = logits.dtype
pmask = gscores > match_threshold # (全部搜索框数目, 21),类别搜索框和真实框IOU大于阈值
fpmask = tf.cast(pmask, dtype) # 浮点型前景掩码(前景假定为含有对象的IOU足够的搜索框标号)
n_positives = tf.reduce_sum(fpmask) # 前景总数
# Hard negative mining...
no_classes = tf.cast(pmask, tf.int32)
predictions = slim.softmax(logits) # 此时每一行的21个数转化为概率
nmask = tf.logical_and(tf.logical_not(pmask),
gscores > -0.5) # IOU达不到阈值的类别搜索框位置记1
fnmask = tf.cast(nmask, dtype)
nvalues = tf.where(nmask,
predictions[:, 0], # 框内无物体标记为背景预测概率
1. - fnmask) # 框内有物体位置标记为1
nvalues_flat = tf.reshape(nvalues, [-1])
# Number of negative entries to select.
# 在nmask中剔除n_neg个最不可能背景点(对应的class0概率最低)
max_neg_entries = tf.cast(tf.reduce_sum(fnmask), tf.int32)
# 3 × 前景掩码数量 + batch_size
n_neg = tf.cast(negative_ratio * n_positives, tf.int32) + batch_size
n_neg = tf.minimum(n_neg, max_neg_entries)
val, idxes = tf.nn.top_k(-nvalues_flat, k=n_neg) # 最不可能为背景的n_neg个点
max_hard_pred = -val[-1]
# Final negative mask.
nmask = tf.logical_and(nmask, nvalues < max_hard_pred) # 不是前景,又最不像背景的n_neg个点
fnmask = tf.cast(nmask, dtype)
# Add cross-entropy loss.
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy_pos'):
loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,
labels=gclasses) # 0-20
loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * fpmask), batch_size, name='value')
tf.losses.add_loss(loss)
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy_neg'):
loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,
labels=no_classes) # {0,1}
loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * fnmask), batch_size, name='value')
tf.losses.add_loss(loss)
# Add localization loss: smooth L1, L2, ...
with tf.name_scope('localization'):
# Weights Tensor: positive mask + random negative.
weights = tf.expand_dims(alpha * fpmask, axis=-1)
loss = custom_layers.abs_smooth(localisations - glocalisations)
loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * weights), batch_size, name='value')
tf.losses.add_loss(loss)
相关文章推荐
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其三:搜索网格生成
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其六:标注格式整理
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其五:TFR数据读取&数据预处理
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其二:基于VGG的SSD网络前向架构
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其八:网络训练
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其一:项目介绍导读
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其四:数据介绍及TFR文件生成
- TensorFlow 深度学习框架(4)-- 损失函数
- 学习Tensorflow,使用源码安装
- TensorFlow学习笔记之源码分析(1)----最近算法nearest_neighbor
- TensorFlow 深度学习框架(4)-- 损失函数
- TensorFlow 深度学习框架(4)-- 损失函数
- 学习Tensorflow,使用源码安装
- TensorFlow 深度学习框架(4)-- 损失函数
- TensorFlow 深度学习框架(4)-- 损失函数
- TensorFlow 深度学习框架(4)-- 损失函数
- TensorFlow 深度学习框架(4)-- 损失函数
- TensorFlow 深度学习框架(4)-- 损失函数
- TensorFlow学习笔记之源码分析(3)---- retrain.py
- RNN入门详解及TensorFlow源码实现--深度学习笔记
