HashMap环形链表
2018-07-08 19:57
330 查看
一、环形链表的形成分析
那么,在HashMap中,到底是怎样形成环形链表的?这个问题,得从HashMap的resize扩容问题说起!备注:本博客中所示源码,均为java 7版本
HashMap的扩容原理:
/** * The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two. */ static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; /** * The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified * by either of the constructors with arguments. * MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30. */ static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; /** * The load factor used when none specified in constructor. */ static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
当HashMap中的元素个数超过数组大小(数组总大小length,不是数组中个数size)*loadFactor时,就会进行数组扩容,loadFactor的默认值为0.75,这是一个折中的取值。也就是说,默认情况下,数组大小为16,那么当HashMap中元素个数超过16*0.75=12(这个值就是代码中的threshold值,也叫做临界值)的时候,就把数组的大小扩展为 2*16=32,即扩大一倍,然后重新计算每个元素在数组中的位置,而这是一个非常消耗性能的操作,所以如果我们已经预知HashMap中元素的个数,那么预设元素的个数能够有效的提高HashMap的性能。
再看源码中,关于扩容resize()的实现:
/**
* Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a
* larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in this map reaches its threshold.
*
* If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not
* resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE.
* This has the effect of preventing future calls.
*
* @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two;
* must be greater than current capacity unless current
* capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value
* is irrelevant).
*/
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
boolean oldAltHashing = useAltHashing;
useAltHashing |= sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(newCapacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
boolean rehash = oldAltHashing ^ useAltHashing;
transfer(newTable, rehash);
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}备注:请注意这句话: newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two; must be greater than current capacity unless current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value is irrelevant)
在这里面,又调用了一个函数transfer函数:
/**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}总得来说,就是拷贝旧的数据元素,从新新建一个更大容量的空间,然后进行数据复制!
那么关于环形链表的形成,则主要在这扩容的过程。当多个线程同时对这个HashMap进行put操作,而察觉到内存容量不够,需要进行扩容时,多个线程会同时执行resize操作,而这就出现问题了,问题的原因分析如下:
首先,在HashMap扩容时,会改变链表中的元素的顺序,将元素从链表头部插入。PS:说是为了避免尾部遍历,这一部分不是本博客的主要介绍内容,后面再说。
而环形链表就在这一时刻发生,以下模拟2个线程同时扩容。假设,当前hashmap的空间为2(临界值为1),hashcode分别为0和1,在散列地址0处有元素A和B,这时候要添加元素C,C经过hash运算,得到散列地址为1,这时候由于超过了临界值,空间不够,需要调用resize方法进行扩容,那么在多线程条件下,会出现条件竞争,模拟过程如下:
(额,我画图的功底一向不好,见谅见谅)
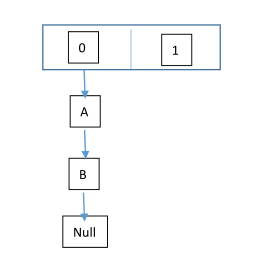
线程一:读取到当前的hashmap情况,在准备扩容时,线程二介入
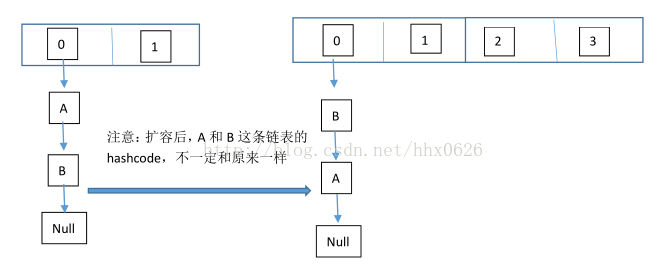
线程二:读取hashmap,进行扩容
线程一:继续执行
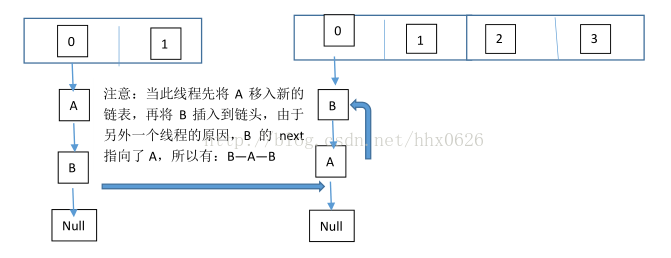
这个过程为,先将A复制到新的hash表中,然后接着复制B到链头(A的前边:B.next=A),本来B.next=null,到此也就结束了(跟线程二一样的过程),但是,由于线程二扩容的原因,将B.next=A,所以,这里继续复制A,让A.next=B,由此,环形链表出现:B.next=A; A.next=B
相关文章推荐
- 【java基础 12】HashMap中是如何形成环形链表的?
- 【java基础 12】HashMap中是如何形成环形链表的?
- 【java基础 13】两种方法判断hashmap中是否形成环形链表
- 【java基础 13】两种方法判断hashmap中是否形成环形链表
- 关于HashMap多线程下环形链表的总结
- hashmap环形链表
- 使用环形链表解决约瑟夫(丢手帕)问题
- 找到环形链表的入口点
- 在一个环形的无重复元素的排序单向链表中插入一个元素
- 判断链表是否存在环形链表
- 环形链表(用双向链表实现)
- 数据结构:环形链表
- 反射获取HashMap内部table字段及其node链表,打印全部数据
- 用c语言创建双向环形链表
- 【环形链表】丢手帕问题
- 环形链表 有m个人围成一圈,开始报数,报道n,退出,问最后剩下的是几号。
- 码农小汪-剑指Offer之34 -两个链表的第一个公共结点 hashMap
- 环形链表插值
- 链表中环形的入口
- Java HashMap中链表结构是如何产生的
