Java线程实现
2018-05-18 17:57
330 查看
在Java中,开启一个线程的唯一方式是,是通过Thread的start()方法,并且在线程中执行的Runnable的run()方法。
先看下Thread的部分源码
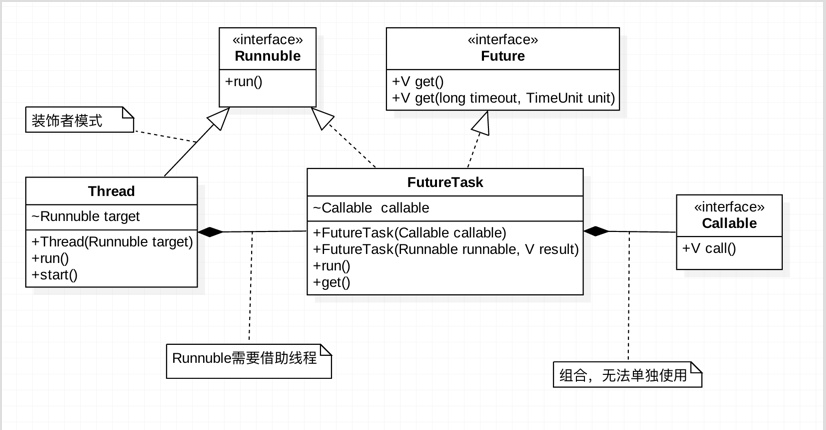
call()函数返回的类型就是创建Callable传进来的V类型。
下面看下FutureTask的源码
创建Thread需要Runnable对象,所以要使用Callable,需要通过FutureTask来创建。FutureTask会在run()方法中调用Callable的call()方法。
通过get方法来获取结果,get()是个阻塞方法,直到结果返回,或者中断发生。还可以通过get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)方法控制等待结果的最大时间。
创建FutureTask,还可以通过Runnable对象,系统会转换成Callable对象。
先看下Thread的部分源码
public class Thread implements Runnable {
Runnable target;
public Thread(Runnable runnable) {
target = Runnable;
//省略其他初始化线程的任务
}
public void start() {
nativeCreate(this, stackSize, daemon);//native方法开启多线程,并调用run方法
}
public void run() {
if (target != null) {
target.run();
}
}
}1. 实例化Runnable接口
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}public class ThreadClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new RunnaleImpl());
thread.start();
}
static class RunnaleImpl implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(threadName + " is running");
}
}
}Thread-0 is running
2. 继承Thread类
public class ThreadClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new ThreadImpl();
thread.start();
}
static class ThreadImpl extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(threadName + " is running");
}
}
}Thread-0 is running
重点:启动线程,必须通过调用start()方法,不能直接调用run()方法。start()方法会调用native的方法,利用操作系统给线程分配资源。
通过下面的示例代码可以看出,直接调用run()方法,线程还是主线程。
public class ThreadClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new ThreadImpl();
thread.run();
}
static class ThreadImpl extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(threadName + " is running");
}
}
}main is running
3. 使用Callable和Future
在JDK1.5后增加了Callable接口,用来实现线程的方式。
call()函数返回的类型就是创建Callable传进来的V类型。
/**
* A task that returns a result and may throw an exception.
* Implementors define a single method with no arguments called
* {@code call}.
*
* <p>The {@code Callable} interface is similar to {@link
* java.lang.Runnable}, in that both are designed for classes whose
* instances are potentially executed by another thread. A
* {@code Runnable}, however, does not return a result and cannot
* throw a checked exception.
*
* <p>The {@link Executors} class contains utility methods to
* convert from other common forms to {@code Callable} classes.
*
* @see Executor
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
* @param <V> the result type of method {@code call}
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Callable<V> {
/**
* Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.
*
* @return computed result
* @throws Exception if unable to compute a result
*/
V call() throws Exception;
}下面看下FutureTask的源码
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> {
public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!U.compareAndSwapObject(this, RUNNER, null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
}创建Thread需要Runnable对象,所以要使用Callable,需要通过FutureTask来创建。FutureTask会在run()方法中调用Callable的call()方法。
public class ThreadClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Callable callable = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(threadName + " is running");
return threadName + " is finish";
}
};
FutureTask future = new FutureTask(callable);
Thread thread = new Thread(future);
thread.start();
try {
System.out.println((String)future.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}通过get方法来获取结果,get()是个阻塞方法,直到结果返回,或者中断发生。还可以通过get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)方法控制等待结果的最大时间。
创建FutureTask,还可以通过Runnable对象,系统会转换成Callable对象。
public class ThreadClient {
/**
* Creates a {@code FutureTask} that will, upon running, execute the
* given {@code Runnable}, and arrange that {@code get} will return the
* given result on successful completion.
*
* @param runnable the runnable task
* @param result the result to return on successful completion. If
* you don't need a particular result, consider using
* constructions of the form:
* {@code Future<?> f = new FutureTask<Void>(runnable, null)}
* @throws NullPointerException if the runnable is null
*/
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {
this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
}4. 可以配合Executor来生成线程
public class ThreadClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Callable callable = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(threadName + " is running");
return threadName + " is finish";
}
};
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Future future = executor.submit(callable);
executor.shutdown();
try {
System.out.println((String)future.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Callable使用场景示例
多线程下载文件时,需要等每个线程下载的文件片下载完毕后,最终合成一个文件。这时就可以使用Callable来处理,减少对每个线程的监听。public class DownloadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
DownloadCallable callable1 = new DownloadCallable("file_part1");
DownloadCallable callable2 = new DownloadCallable("file_part2");
Future future1 = executor.submit(callable1);
Future future2 = executor.submit(callable2);
// 所有线程都提交后,要关闭,即停止,不再接受线程任务
executor.shutdown();
// get()方法是线程阻塞的,会一直等待直到线程执行完。
// 但isDone()不是,isDone()是瞬间状态,当方法执行时,判断线程是否执行完。
if ((Boolean)future1.get() && (Boolean)future2.get()) {
long stop = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("all file finish download time " + (stop - start));
}
}
}
class DownloadCallable implements Callable {
String fileName;
public DownloadCallable(String name) {
this.fileName = name;
}
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("start download " + fileName);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
long stop = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("finish download " + fileName + " time " + (stop - start));
return true;
}
}start download file_part1 start download file_part2 finish download file_part2 time 190 finish download file_part1 time 295 all file finish download time 304
相关文章推荐
- 关于Java线程的实现
- 用JAVA实现线程等待提示框
- java中使用线程实现Timer(定时器)原理和源码
- java中使用线程实现Timer(定时器)原理和源码
- java中使用线程实现Timer(定时器)原理和源码
- java中使用线程实现Timer(定时器)原理和源码
- 用JAVA实现线程等待提示框
- java中使用线程实现Timer(定时器)原理和源码
- Java:使用wait()与notify()实现线程间协作
- java中使用线程实现Timer(定时器)原理和源码
- 用JAVA实现线程等待提示框
- 用JAVA实现线程等待提示框
- 彻底明白Java的多线程-实现多线程及线程的同步
- java中使用线程实现Timer(定时器)原理和源码
- java中使用线程实现Timer(定时器)原理和源码
- 用JAVA实现线程等待提示框
- java线程 超时控制的实现
- java中使用线程实现Timer(定时器)原理和源码
- Java 中利用管道实现线程间的通讯
- java中使用线程实现Timer(定时器)原理和源码
