编程实现数据结构线性表基本操作
2018-03-26 17:15
585 查看
这个代码主要实现了
1 线性表的创建,插入,删除函数等
2 主函数调用上面的函数
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<malloc.h>
struct LinearList /*定义线性表结构*/
{
int *list; /* 存线性表元素 */
int size; /* 存线性表长度 */
int MaxSize; /* 存list数组元素个数 */
};
typedef struct LinearList LIST;
void InitList(LIST *L, int ms) /* 初始化线性表 */
{
if ((L->list = (int*)malloc(ms * sizeof(int))) == NULL) {
printf("内存申请错误!\n");
exit(1);
}
L->size = 0;// L->size=0;
L->MaxSize = ms;
}
int InsertList(LIST *L, int item, int rc)
/* item:记录值 rc:插入位置 */
{
int i;
if (L->size == L->MaxSize) /* 线性表已满 */
return -1;
if (rc < 0) /* 插入位置为 0 --> L->size */
rc = 0;
if (rc>L->size)
rc = L->size;
for (i = L->size - 1; i >= rc; i--) /* 将线性表元素后移 */
L->list[i + 1] = L->list[i];
L->list[rc] = item;
L->size++;
return 0;
}
void OutputList(LIST *L) /* 输出线性表元素 */
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i<L->size; i++)
printf("%d ", L->list[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int FindList(LIST *L, int item)/* 返回 >=0 为元素位置 -1 没找到 */
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < L->size; i++)
if (item == L->list[i]) /* 找到相同的元素,返回位置 */
return i;
return -1; /* 没找到 */
}
int DeleteList1(LIST *L, int item)
/* 删除指定元素值的线性表记录,返回>=0:删除成功 */
{
int i, n;
for (i = 0; i < L->size; i++)
if (item == L->list[i]) /* 找到相同的元素 */
break;
if (i < L->size) {
for (n = i; n < L->size - 1; n++)
L->list
= L->list[n + 1];
L->size--;
return i;
}
return -1;
}
int DeleteList2(LIST L, int rc) /* 删除指定位置的线性表记录 */
{
int i, n;
if (rc<0 || rc >= L.size)
return -1;
for (n = rc; n<L.size - 1; n++)
L.list
= L.list[n + 1];
L.list--;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
LIST L1;
int i, r;
InitList(&L1, 100);
printf("list addr=%p\tsize=%d\tMaxsize=%d\n");
while (1)
{
printf("请输入元素值,输入0结束插入操作:");
fflush(stdin);
scanf_s("%d", &i);
if (i == 0)
break;
printf("请输入插入位置:");
scanf_s("%d", &r);
InsertList(&L1, i, r - 1);
printf("线性表为:");
OutputList(&L1);
}
while (1)
{
printf("请输入查找元素值,输入0结束查找操作:");
fflush(stdin); /* 清空标准输入缓冲区 */
scanf("%d", &i);
if (i == 0)
break;
r = FindList(&L1, i);
if (r < 0)
printf("没找到\n");
else
printf("有符合条件的元素,位置为:%d\n", r + 1);
}
while (1)
{
printf("请输入删除元素值,输入0结束查找操作:");
fflush(stdin); /* 清空标准输入缓冲区 */
scanf("%d", &i);
if (i == 0)
break;
r = DeleteList1(&L1, i);
if (r < 0)
printf("没找到\n");
else {
printf("有符合条件的元素,位置为:%d\n线性表为:", r + 1);
OutputList(&L1);
}
}
while (1)
{
printf("请输入删除元素位置,输入0结束查找操作:");
fflush(stdin); /* 清空标准输入缓冲区 */
scanf("%d", &r);
if (r == 0)
break;
i = r = DeleteList2(L1, r - 1);
if (i < 0)
printf("位置越界\n");
else {
printf("线性表为:");
OutputList(&L1);
}
}
return 0;
}
//书上代码
//#include<stdio.h>
//#include<stdlib.h>
//#include<malloc.h>
//struct LinearList /*定义线性表结构*/
//{
// int *list; /* 存线性表元素 */
// int size; /* 存线性表长度 */
// int MaxSize; /* 存list数组元素个数 */
//};
//typedef struct LinearList LIST;
//void InitList(LIST *L, int ms) /* 初始化线性表 */
//{
// if ((L->list = (int*)malloc(ms * sizeof(int))) == NULL) {
// printf("内存申请错误!\n");
// exit(1);
// }
// L->size = 0;
// L->MaxSize = ms;
//}
//
//int InsertList(LIST *L, int item, int rc)
///* item:记录值 rc:插入位置 */
//{
// int i;
// if (L->size = L->MaxSize) /* 线性表已满 */
// return -1;
// if (rc < 0) /* 插入位置为 0 --> L->size */
// rc = 0;
// if (rc>L->size)
// rc = L->size;
// for (i = L->size - 1; i >= rc; i--) /* 将线性表元素后移 */
// L->list[i + 1] = L->list[i];
// L->list[rc] = item;
// L->size++;
// return 0;
//}
//
//void OutputList(LIST *L) /* 输出线性表元素 */
//{
// int i;
// for (i = 0; i<L->size; i++)
// printf("%d ", L->list[i]);
// printf("\n");
//}
//
//int FindList(LIST *L, int item) /* 返回 >=0 为元素位置 -1 没找到 */
//{
// int i;
// for (i = 0; i < L->size; i++)
// if (item == L->list[i]) /* 找到相同的元素,返回位置 */
// return i;
// return -1; /* 没找到 */
//}
//
//int DeleteList1(LIST *L, int item)
///* 删除指定元素值的线性表记录,返回>=0:删除成功 */
//{
// int i, n;
// for (i = 0; i < L->size; i++)
// if (item == L->list[i]) /* 找到相同的元素 */
// break;
// if (i < L->size) {
// for (n = i; n < L->size - 1; n++)
// L->list
= L->list[n + 1];
// L->size--;
// return i;
// }
// return -1;
//}
//
//int DeleteList2(LIST L, int rc) /* 删除指定位置的线性表记录 */
//{
// /*编写删除指定位置的线性表记录子程序*/
//
// int DeleteList2(LIST * L, int rc)
// {
// int i, n;
// if (rc<0 || rc >= L->size)
// return -1;
// for (n = rc; n<L->size - 1; n++)
// L->list
= L->list[n + 1];
// L->list--;
// return 0;
// }
//}
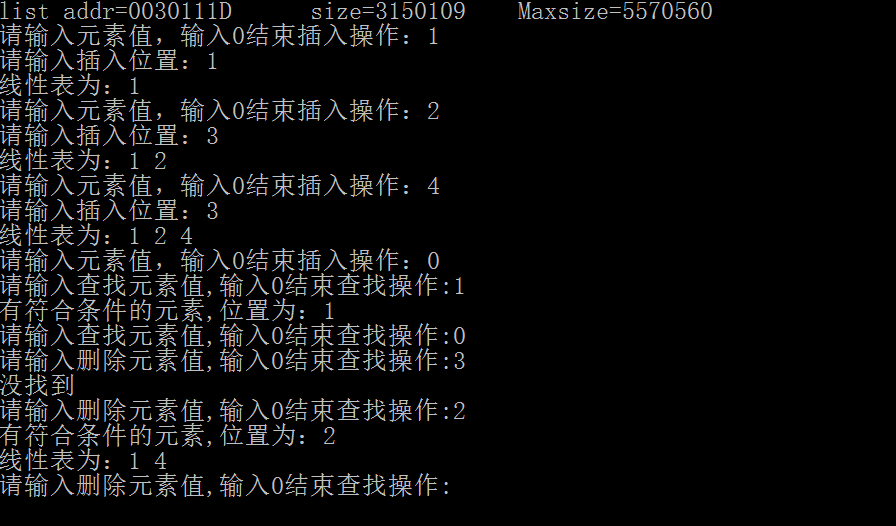
1 线性表的创建,插入,删除函数等
2 主函数调用上面的函数
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<malloc.h>
struct LinearList /*定义线性表结构*/
{
int *list; /* 存线性表元素 */
int size; /* 存线性表长度 */
int MaxSize; /* 存list数组元素个数 */
};
typedef struct LinearList LIST;
void InitList(LIST *L, int ms) /* 初始化线性表 */
{
if ((L->list = (int*)malloc(ms * sizeof(int))) == NULL) {
printf("内存申请错误!\n");
exit(1);
}
L->size = 0;// L->size=0;
L->MaxSize = ms;
}
int InsertList(LIST *L, int item, int rc)
/* item:记录值 rc:插入位置 */
{
int i;
if (L->size == L->MaxSize) /* 线性表已满 */
return -1;
if (rc < 0) /* 插入位置为 0 --> L->size */
rc = 0;
if (rc>L->size)
rc = L->size;
for (i = L->size - 1; i >= rc; i--) /* 将线性表元素后移 */
L->list[i + 1] = L->list[i];
L->list[rc] = item;
L->size++;
return 0;
}
void OutputList(LIST *L) /* 输出线性表元素 */
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i<L->size; i++)
printf("%d ", L->list[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int FindList(LIST *L, int item)/* 返回 >=0 为元素位置 -1 没找到 */
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < L->size; i++)
if (item == L->list[i]) /* 找到相同的元素,返回位置 */
return i;
return -1; /* 没找到 */
}
int DeleteList1(LIST *L, int item)
/* 删除指定元素值的线性表记录,返回>=0:删除成功 */
{
int i, n;
for (i = 0; i < L->size; i++)
if (item == L->list[i]) /* 找到相同的元素 */
break;
if (i < L->size) {
for (n = i; n < L->size - 1; n++)
L->list
= L->list[n + 1];
L->size--;
return i;
}
return -1;
}
int DeleteList2(LIST L, int rc) /* 删除指定位置的线性表记录 */
{
int i, n;
if (rc<0 || rc >= L.size)
return -1;
for (n = rc; n<L.size - 1; n++)
L.list
= L.list[n + 1];
L.list--;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
LIST L1;
int i, r;
InitList(&L1, 100);
printf("list addr=%p\tsize=%d\tMaxsize=%d\n");
while (1)
{
printf("请输入元素值,输入0结束插入操作:");
fflush(stdin);
scanf_s("%d", &i);
if (i == 0)
break;
printf("请输入插入位置:");
scanf_s("%d", &r);
InsertList(&L1, i, r - 1);
printf("线性表为:");
OutputList(&L1);
}
while (1)
{
printf("请输入查找元素值,输入0结束查找操作:");
fflush(stdin); /* 清空标准输入缓冲区 */
scanf("%d", &i);
if (i == 0)
break;
r = FindList(&L1, i);
if (r < 0)
printf("没找到\n");
else
printf("有符合条件的元素,位置为:%d\n", r + 1);
}
while (1)
{
printf("请输入删除元素值,输入0结束查找操作:");
fflush(stdin); /* 清空标准输入缓冲区 */
scanf("%d", &i);
if (i == 0)
break;
r = DeleteList1(&L1, i);
if (r < 0)
printf("没找到\n");
else {
printf("有符合条件的元素,位置为:%d\n线性表为:", r + 1);
OutputList(&L1);
}
}
while (1)
{
printf("请输入删除元素位置,输入0结束查找操作:");
fflush(stdin); /* 清空标准输入缓冲区 */
scanf("%d", &r);
if (r == 0)
break;
i = r = DeleteList2(L1, r - 1);
if (i < 0)
printf("位置越界\n");
else {
printf("线性表为:");
OutputList(&L1);
}
}
return 0;
}
//书上代码
//#include<stdio.h>
//#include<stdlib.h>
//#include<malloc.h>
//struct LinearList /*定义线性表结构*/
//{
// int *list; /* 存线性表元素 */
// int size; /* 存线性表长度 */
// int MaxSize; /* 存list数组元素个数 */
//};
//typedef struct LinearList LIST;
//void InitList(LIST *L, int ms) /* 初始化线性表 */
//{
// if ((L->list = (int*)malloc(ms * sizeof(int))) == NULL) {
// printf("内存申请错误!\n");
// exit(1);
// }
// L->size = 0;
// L->MaxSize = ms;
//}
//
//int InsertList(LIST *L, int item, int rc)
///* item:记录值 rc:插入位置 */
//{
// int i;
// if (L->size = L->MaxSize) /* 线性表已满 */
// return -1;
// if (rc < 0) /* 插入位置为 0 --> L->size */
// rc = 0;
// if (rc>L->size)
// rc = L->size;
// for (i = L->size - 1; i >= rc; i--) /* 将线性表元素后移 */
// L->list[i + 1] = L->list[i];
// L->list[rc] = item;
// L->size++;
// return 0;
//}
//
//void OutputList(LIST *L) /* 输出线性表元素 */
//{
// int i;
// for (i = 0; i<L->size; i++)
// printf("%d ", L->list[i]);
// printf("\n");
//}
//
//int FindList(LIST *L, int item) /* 返回 >=0 为元素位置 -1 没找到 */
//{
// int i;
// for (i = 0; i < L->size; i++)
// if (item == L->list[i]) /* 找到相同的元素,返回位置 */
// return i;
// return -1; /* 没找到 */
//}
//
//int DeleteList1(LIST *L, int item)
///* 删除指定元素值的线性表记录,返回>=0:删除成功 */
//{
// int i, n;
// for (i = 0; i < L->size; i++)
// if (item == L->list[i]) /* 找到相同的元素 */
// break;
// if (i < L->size) {
// for (n = i; n < L->size - 1; n++)
// L->list
= L->list[n + 1];
// L->size--;
// return i;
// }
// return -1;
//}
//
//int DeleteList2(LIST L, int rc) /* 删除指定位置的线性表记录 */
//{
// /*编写删除指定位置的线性表记录子程序*/
//
// int DeleteList2(LIST * L, int rc)
// {
// int i, n;
// if (rc<0 || rc >= L->size)
// return -1;
// for (n = rc; n<L->size - 1; n++)
// L->list
= L->list[n + 1];
// L->list--;
// return 0;
// }
//}

相关文章推荐
- hrbustoj 1545:基础数据结构——顺序表(2)(数据结构,顺序表的实现及基本操作,入门题)
- 【数据结构】双向循环线性表的基本操作--C++/C实现
- 【数据结构】二叉搜索树的插入,删除,查找等基本操作的实现
- 【C++数据结构】几种单链表的模类板实现及基本操作
- javascript实现数据结构: 树和二叉树,二叉树的遍历和基本操作
- 第二十六课 实现线性表基本操作的函数 【项目1-4】
- 数据结构-顺序线性表基本操作实现
- 数据结构-循环队列的基本实现操作
- 第四周《C语言及程序设计》实践项目26 实现线性表基本操作的函数
- 数据结构:二叉树的基本操作(JAVA实现)
- 间接寻址储存的线性表—基本操作实现
- 编程实现单链表的创建等基本操作
- javascript实现数据结构: 树和二叉树,二叉树的遍历和基本操作
- 数据结构--串的操作基本实现程序代…
- 编程实现顺序表的基本操作
- 算法与数据结构-栈的基本操作C语言实现
- 数据结构--线性表 算法函数的实现(实现线性表的插入操作)
- C语言及程序设计提高例程-26 实现线性表基本操作的函数
- 数据结构-共享栈的基本操作实现
- 数据结构第四次作业(二叉树的基本操作实现)
