SpringBoot使用笔记
2018-03-25 09:01
399 查看
SpringBoot使用笔记
其实也是参考官方的:http://spring.io/guides/gs/rest-service/ ,在官方代码基础上加入了很多实用的东西,比如运行环境启动命令等等。官方文档:http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/
SpringBoot并不神秘,其最大的好处是可以帮你省略引用一堆jar包,需要神秘jar它自动帮你引用,集成tomcat,集成配置等待好处太多,总之就是更方便开发而已。
还是自己体验下比较好。
1.建立java应用程序
起一个Maven的java应用程序,注意不要再起Web应用程序了:
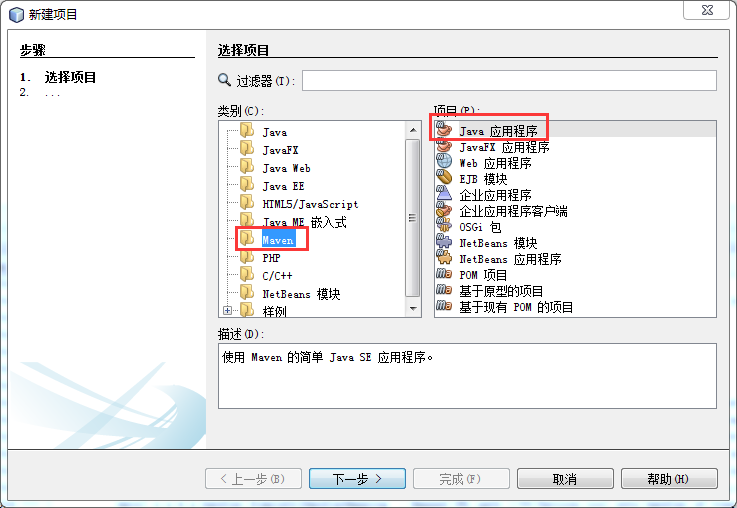
2.maven配置文件
pom.xml:
[html] view
plain copy
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.xxx</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-hello</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.4.3.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jayway.jsonpath</groupId>
<artifactId>json-path</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
3.新建类文件
[java] view
plain copy
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
[html] view
plain copy
public class Greeting {
private final long id;
private final String content;
public Greeting(long id, String content) {
this.id = id;
this.content = content;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
}
[html] view
plain copy
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class GreetingController {
private static final String template = "Hello, %s!";
private final AtomicLong counter = new AtomicLong();
@RequestMapping("/greeting")
public Greeting greeting(@RequestParam(value="name", defaultValue="World") String name) {
return new Greeting(counter.incrementAndGet(),
String.format(template, name));
}
}
4.运行项目
注意:SpringBoot已经集成了tomcat所以无需再安装了,默认是8080不要和现有的tomcat冲突
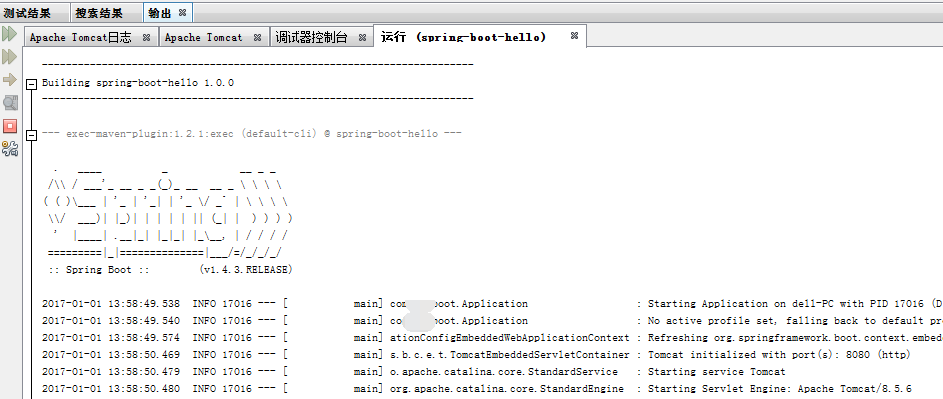
成功启动会提示:FrameworkServlet 'dispatcherServlet': initialization completed in 10 ms
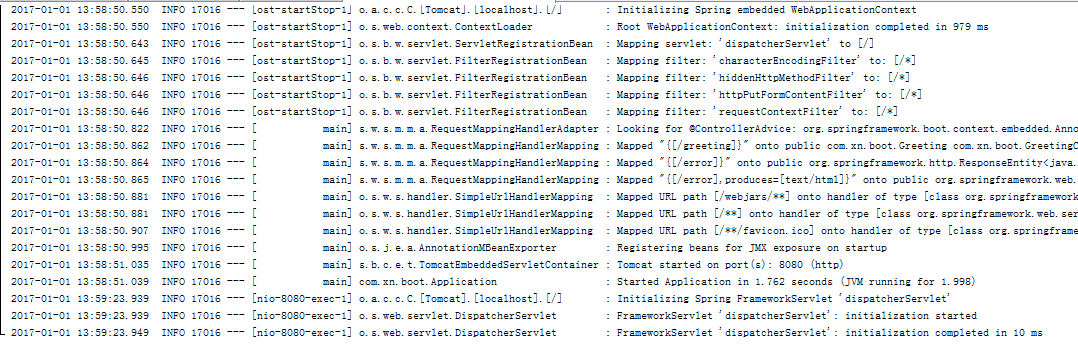
5.验证
http://localhost:8080/greeting
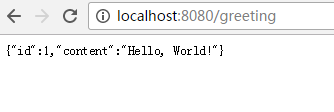
6.集成依赖文件
我们去看下系统依赖文件,发现springmvc都自动被引入,如果不适用springboot就需要一个个去单独引用。
7.命令行下启动
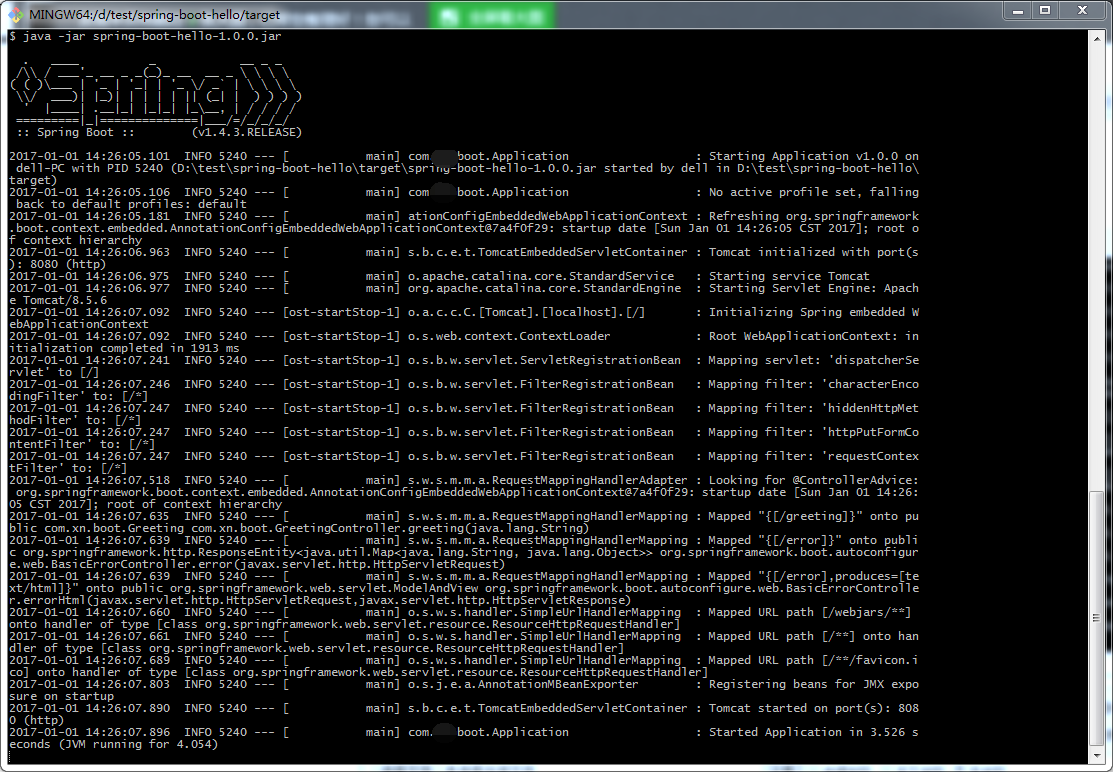
实际项目中肯定是到命令行下启动
Windows下
# java -jar spring-boot-hello-1.0.0.jar
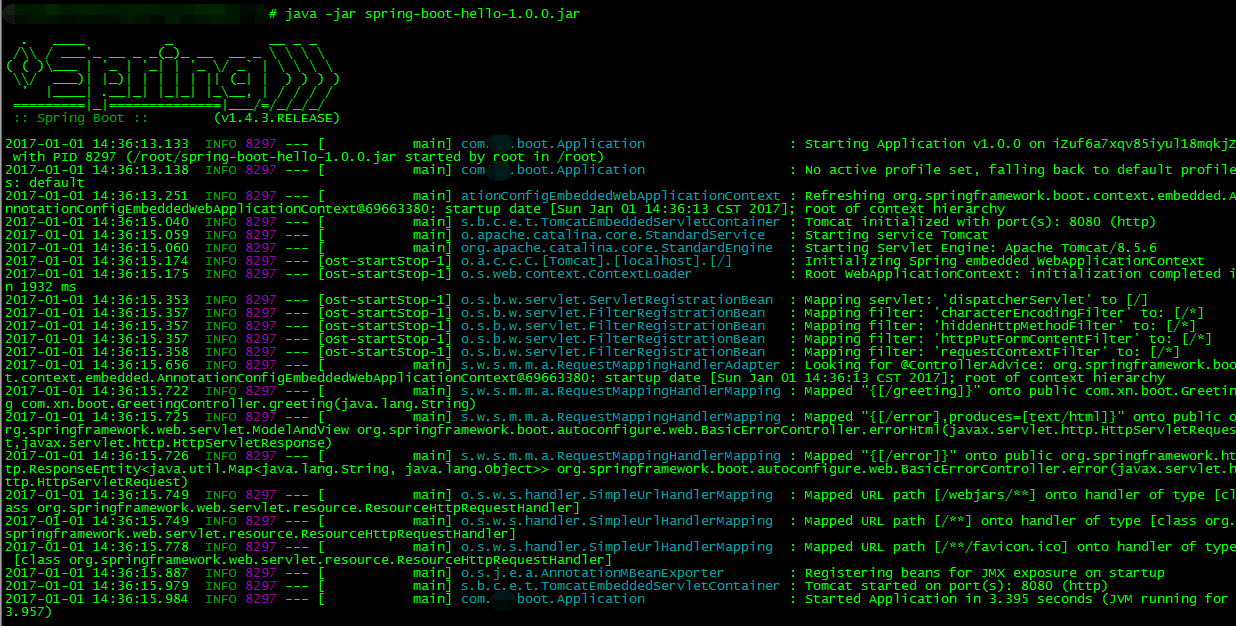
Linux下
实际是需要再后台运行的加个&符号,比如这样
# nohup java -jar spring-boot-hello-1.0.0.jar >/dev/null 2>&1 &
定制化JVM启动参数
# nohup java -Xms1024m -Xmx1024m -Xss1024K -XX:PermSize=64m -XX:MaxPermSize=128m -jar spring-boot-hello-1.0.0.jar >/dev/null 2>&1 &
8.Tomcat下运行
其实完全没必要再到tomcat下再去运行了,如果真的还需要这样可以打war包即可。
[html] view
plain copy
<artifactId>spring-boot-hello</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
改为
[html] view
plain copy
<artifactId>spring-boot-hello</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
需要注意的是jdk需要1.8以上版本,Tomcat需要8.0以上版本
9.Spring Boot配置
如果你需要修改配置,可以在resources文件夹下创建一个application.properties或者application.yml文件,这个文件会被发布到classpath。
比如修改默认的tomcat端口为80
application.properties
[html] view
plain copy
server.port: 80
server.tomcat.uri-encoding: UTF-8
application.yml
[html] view
plain copy
server:
port: 80
tomcat:
uri-encoding: UTF-8
再重新运行tomcat就是80端口了:
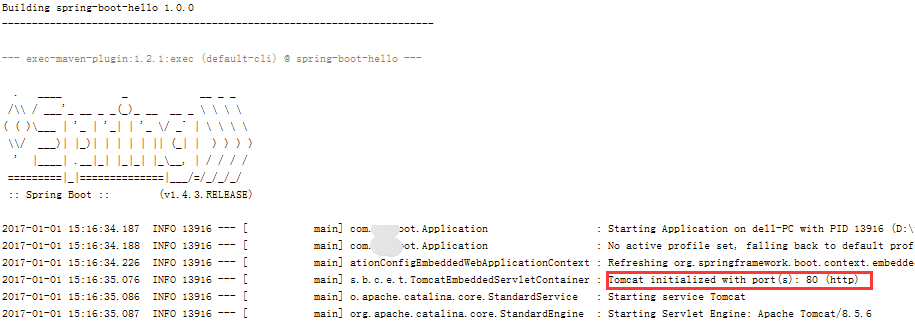
更多配置参考:http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/common-application-properties.html
另外:推荐一本书《深入实践Spring Boot》
10.spring boot多环境配置
一般会有开发环境,测试环境,正式环境,甚至于预发布环境。
配置文件不管理好,如果这个靠手工去做非常不靠谱,很容易出错。
Spring boot可以配置多个配置文件,自动切换。
application-online.properties
[html] view
plain copy
server.port: 80
server.tomcat.uri-encoding: UTF-8
application-test.properties
[html] view
plain copy
server.port: 8080
server.tomcat.uri-encoding: UTF-8
application.properties里激活需要的环境即可
[html] view
plain copy
spring.profiles.active=test
也可以通过命令行方式启动
将程序打包之后 通过 java -jar xx.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev的方式启动
参考: SpringBoot学习笔记(2)
Spring Boot的一些配置
相关文章推荐
- 详解spring boot Websocket使用笔记
- springboot 学习笔记【3】Spring Boot中使用Spring-data-jpa
- SpringBoot学习笔记之Servlet使用
- springboot基本使用笔记----读取文件
- SpringBoot学习笔记-使用jdbcTemplate访问mysql
- IDEA+MAVEN+spring boot使用springloaded笔记
- springboot 学习笔记【4】Spring Boot中使用Spring-data-jpa
- SpringBoot使用Shiro验证登录笔记
- SpringBoot入坑笔记之spring-boot-starter-web 配置文件的使用
- SpringBoot学习笔记之JDBC使用
- spring boot Websocket(使用笔记)
- Spring Boot学习笔记-SQL数据库使用
- spring boot Websocket(使用笔记)
- SpringBoot学习笔记(7) SpringBoot整合Dubbo(使用yml配置)
- Spring Boot整合Dubbo使用及开发笔记
- SpringBoot笔记3---如何读写数据库之使用CrudRepository中提供的方法来读写数据库
- Spring Boot 学习笔记【6】使用FreeMarker与BootStrap开发Web
- java鬼混笔记:springboot之thymeleaf 2:字符串Strings常见的使用方法
- SpringBoot学习笔记(7) SpringBoot整合Dubbo(使用yml配置)
- 01.Spring Cloud学习笔记之使用IDEA+Spring Boot快速构建Rest服务
