dubbo原理系列3-consumer调用过程
2018-03-08 18:09
344 查看
dubbo客户端实际持有的是服务端的一个代理类,代理类中封装了对服务端接口的调用流程。
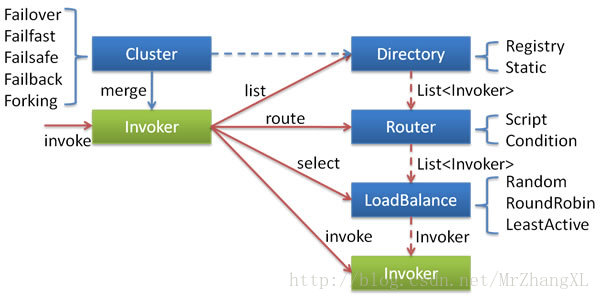
dubbo中有两个生产代理类工厂
- com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.javassist.JavassistProxyFactory 采用javassist修改字节码技术
- com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.jdk.JdkProxyFactory 采用jdk自带的动态代理技术
那么生成的代理类中包装的是什么呢???我们可以看看上述两个类的代码
JavassistProxyFactory.java代码片段
2
3
4
5
6
[/code]
JdkProxyFactory.java代码片段
2
3
4
5
6
[/code]
看到了么getProxy方法,第三个参数是InvokerInvocationHandler。
如果你熟悉jdk的动态代理的话,那么你一定知道每个代理类都要关联一个InvocationHandler,这个InvocationHandler接口只有一个invoke方法,也就是当触发被代理类的任意一个接口的时候,实际调用的是InvocationHandler实现类的invoke方法。
因此consumer调用的时候回先进入InvokerInvocationHandler类的invoke方法。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
InvokerInvocationHandler持有的是MockClusterInvoker
4000
MockClusterInvoker默认持有的是FailoverClusterInvoker,FailoverClusterInvoker继承了AbstractClusterInvoker,所以首先会进入AbstractClusterInvoker的invoke方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
AbstractClusterInvoker有7个子类,实现了抽象的doInvoke方法
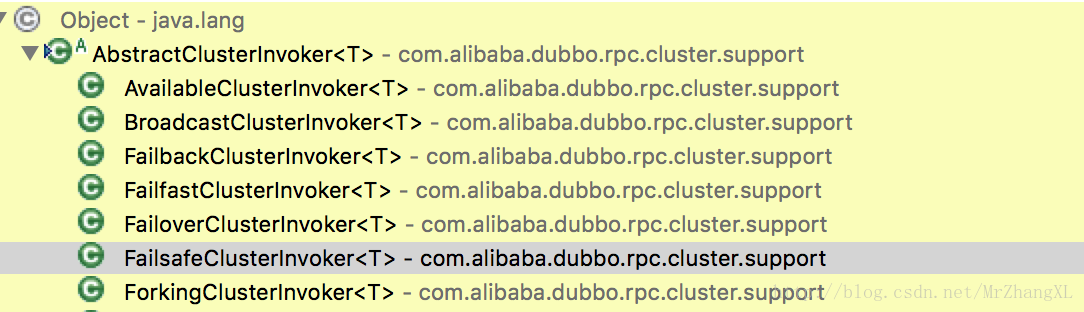
AvailableClusterInvoker
官方无记载,源码中直接调用后面逻辑,没有额外处理
BroadcastClusterInvoker
广播调用所有提供者,逐个调用,任意一台报错则报错。(2.1.0开始支持)
FailbackClusterInvoker
失败自动恢复,后台记录失败请求,定时重发,通常用于消息通知操作。
FailfastClusterInvoker
快速失败,只发起一次调用,失败立即报错,通常用于非幂等性的写操作。
FailoverClusterInvoker
失败转移,当出现失败,重试其它服务器,通常用于读操作,但重试会带来更长延迟。
FailsafeClusterInvoker
失败安全,出现异常时,直接忽略,通常用于写入审计日志等操作。
ForkingClusterInvoker
并行调用,只要一个成功即返回,通常用于实时性要求较高的操作,但需要浪费更多服务资源。
然后默认进入FailoverClusterInvoker的doInvoke方法。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
[/code]
select方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
[/code]
AbstractLoadBalance的select方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[/code]
doSelect
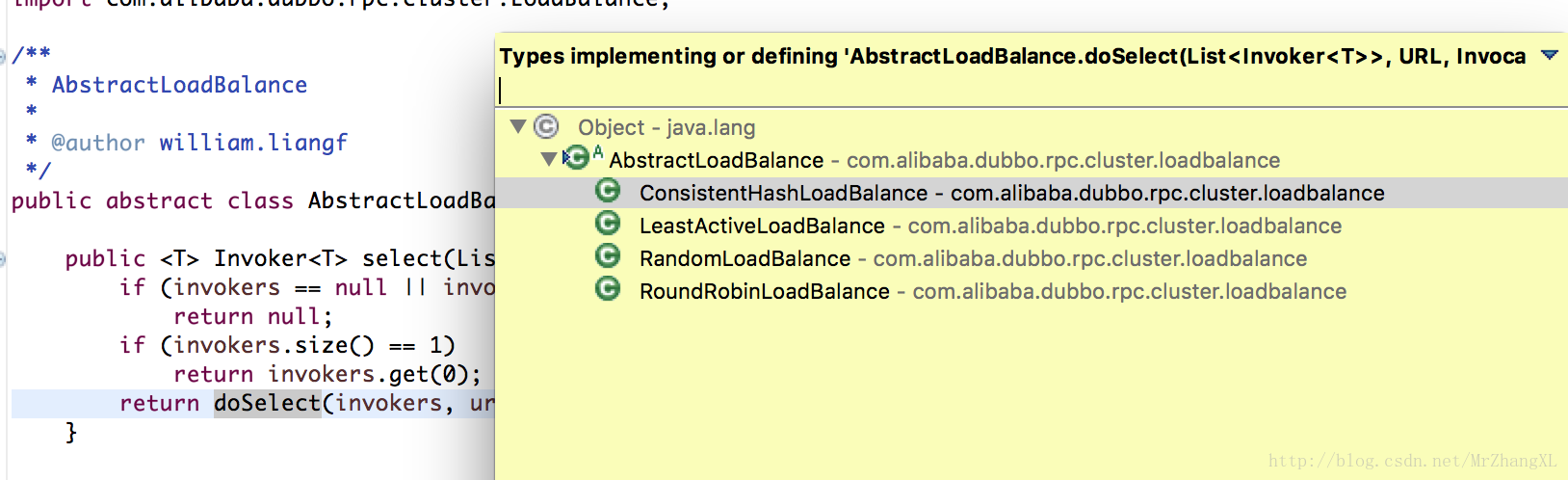
会有四种负载策略
ConsistentHashLoadBalance
1 致性Hash,相同参数的请求总是发到同一提供者。
2 当某一台提供者挂时,原本发往该提供者的请求,基于虚拟节点,平 摊到其它提供者,不会引起剧烈变动。
3 缺省只对第一个参数Hash,如果要修改,请配置
4 缺省用160份虚拟节点,如果要修改,请配置
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[/code]
LeastActiveLoadBalance
1 最少活跃调用数,相同活跃数的随机,活跃数指调用前后计数差。
2 使慢的提供者收到更少请求,因为越慢的提供者的调用前后计数差会越大。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
[/code]
RandomLoadBalance
1 随机,按权重设置随机概率。
2 在一个截面上碰撞的概率高,但调用量越大分布越均匀,而且按概率使用权重后也比较均匀,有利于动态调整提供者权重。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
RoundRobinLoadBalance
1 轮循,按公约后的权重设置轮循比率。
2 存在慢的提供者累积请求的问题,比如:第二台机器很慢,但没挂,当请求调到第二台时就卡在那,久而久之,所有请求都卡在调到第二台上。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
[/code]
参考资料:
http://dubbo.io/user-guide/demos/%E9%9B%86%E7%BE%A4%E5%AE%B9%E9%94%99.html
http://dubbo.io/user-guide/demos/%E8%B4%9F%E8%BD%BD%E5%9D%87%E8%A1%A1.html

客户端持有服务端代理类
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.proxy17@72217aa5dubbo中有两个生产代理类工厂
- com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.javassist.JavassistProxyFactory 采用javassist修改字节码技术
- com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.jdk.JdkProxyFactory 采用jdk自带的动态代理技术
那么生成的代理类中包装的是什么呢???我们可以看看上述两个类的代码
JavassistProxyFactory.java代码片段
public class JavassistProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory {
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
...
}12
3
4
5
6
[/code]
JdkProxyFactory.java代码片段
public class JdkProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory {
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), interfaces, new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
...
}12
3
4
5
6
[/code]
看到了么getProxy方法,第三个参数是InvokerInvocationHandler。
如果你熟悉jdk的动态代理的话,那么你一定知道每个代理类都要关联一个InvocationHandler,这个InvocationHandler接口只有一个invoke方法,也就是当触发被代理类的任意一个接口的时候,实际调用的是InvocationHandler实现类的invoke方法。
因此consumer调用的时候回先进入InvokerInvocationHandler类的invoke方法。
dubbo中的InvokerInvocationHandler
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.InvokerInvocationHandlerpublic class InvokerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final Invoker<?> invoker;
public InvokerInvocationHandler(Invoker<?> handler){
this.invoker = handler;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return method.invoke(invoker, args);
}
if ("toString".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.toString();
}
if ("hashCode".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.hashCode();
}
if ("equals".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 1) {
return invoker.equals(args[0]);
}
return invoker.invoke(new RpcInvocation(method, args)).recreate();
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
InvokerInvocationHandler持有的是MockClusterInvoker
MockClusterInvoker
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.wrapper.MockClusterInvoker
4000
MockClusterInvoker默认持有的是FailoverClusterInvoker,FailoverClusterInvoker继承了AbstractClusterInvoker,所以首先会进入AbstractClusterInvoker的invoke方法
AbstractClusterInvoker
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
checkWheatherDestoried();
LoadBalance loadbalance;
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation);
if (invokers != null && invokers.size() > 0) {
loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(invokers.get(0).getUrl()
.getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(),Constants.LOADBALANCE_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE));
} else {
loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE);
}
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
AbstractClusterInvoker有7个子类,实现了抽象的doInvoke方法

AvailableClusterInvoker
官方无记载,源码中直接调用后面逻辑,没有额外处理
BroadcastClusterInvoker
广播调用所有提供者,逐个调用,任意一台报错则报错。(2.1.0开始支持)
FailbackClusterInvoker
失败自动恢复,后台记录失败请求,定时重发,通常用于消息通知操作。
FailfastClusterInvoker
快速失败,只发起一次调用,失败立即报错,通常用于非幂等性的写操作。
FailoverClusterInvoker
失败转移,当出现失败,重试其它服务器,通常用于读操作,但重试会带来更长延迟。
FailsafeClusterInvoker
失败安全,出现异常时,直接忽略,通常用于写入审计日志等操作。
ForkingClusterInvoker
并行调用,只要一个成功即返回,通常用于实时性要求较高的操作,但需要浪费更多服务资源。
然后默认进入FailoverClusterInvoker的doInvoke方法。
FailoverClusterInvoker
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.FailoverClusterInvokerpublic Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
List<Invoker<T>> copyinvokers = invokers;
checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation);
int len = getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.RETRIES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_RETRIES) + 1;
if (len <= 0) {
len = 1;
}
// retry loop.
RpcException le = null; // last exception.
List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyinvokers.size()); // invoked invokers.
Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
//重试时,进行重新选择,避免重试时invoker列表已发生变化.
//注意:如果列表发生了变化,那么invoked判断会失效,因为invoker示例已经改变
if (i > 0) {
checkWheatherDestoried();
copyinvokers = list(invocation);
//重新检查一下
checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation);
}
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyinvokers, invoked);
invoked.add(invoker);
RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List)invoked);
try {
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Although retry the method " + invocation.getMethodName()
+ " in the service " + getInterface().getName()
+ " was successful by the provider " + invoker.getUrl().getAddress()
+ ", but there have been failed providers " + providers
+ " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyinvokers.size()
+ ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress()
+ " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ " using the dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: "
+ le.getMessage(), le);
}
return result;
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) { // biz exception.
throw e;
}
le = e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
le = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress());
}
}
throw new RpcException(le != null ? le.getCode() : 0, "Failed to invoke the method "
+ invocation.getMethodName() + " in the service " + getInterface().getName()
+ ". Tried " + len + " times of the providers " + providers
+ " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyinvokers.size()
+ ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress()
+ " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using the dubbo version "
+ Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: "
+ (le != null ? le.getMessage() : ""), le != null && le.getCause() != null ? le.getCause() : le);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
[/code]
select方法
/**
* 使用loadbalance选择invoker.</br>
* a)先lb选择,如果在selected列表中 或者 不可用且做检验时,进入下一步(重选),否则直接返回</br>
* b)重选验证规则:selected > available .保证重选出的结果尽量不在select中,并且是可用的
*
* @param availablecheck 如果设置true,在选择的时候先选invoker.available == true
* @param selected 已选过的invoker.注意:输入保证不重复
*
*/
protected Invoker<T> select(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
if (invokers == null || invokers.size() == 0)
return null;
String methodName = invocation == null ? "" : invocation.getMethodName();
boolean sticky = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName,Constants.CLUSTER_STICKY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CLUSTER_STICKY) ;
{
//ignore overloaded method
if ( stickyInvoker != null && !invokers.contains(stickyInvoker) ){
stickyInvoker = null;
}
//ignore cucurrent problem
if (sticky && stickyInvoker != null && (selected == null || !selected.contains(stickyInvoker))){
if (availablecheck && stickyInvoker.isAvailable()){
return stickyInvoker;
}
}
}
Invoker<T> invoker = doselect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected);
if (sticky){
stickyInvoker = invoker;
}
return invoker;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
[/code]
private Invoker<T> doselect(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcExceptio
11285
n {
if (invokers == null || invokers.size() == 0)
return null;
if (invokers.size() == 1)
return invokers.get(0);
// 如果只有两个invoker,退化成轮循
if (invokers.size() == 2 && selected != null && selected.size() > 0) {
return selected.get(0) == invokers.get(0) ? invokers.get(1) : invokers.get(0);
}
Invoker<T> invoker = loadbalance.select(invokers, getUrl(), invocation);
//如果 selected中包含(优先判断) 或者 不可用&&availablecheck=true 则重试.
if( (selected != null && selected.contains(invoker))
||(!invoker.isAvailable() && getUrl()!=null && availablecheck)){
try{
Invoker<T> rinvoker = reselect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected, availablecheck);
if(rinvoker != null){
invoker = rinvoker;
}else{
//看下第一次选的位置,如果不是最后,选+1位置.
int index = invokers.indexOf(invoker);
try{
//最后在避免碰撞
invoker = index <invokers.size()-1?invokers.get(index+1) :invoker;
}catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn(e.getMessage()+" may because invokers list dynamic change, ignore.",e);
}
}
}catch (Throwable t){
logger.error("clustor relselect fail reason is :"+t.getMessage() +" if can not slove ,you can set cluster.availablecheck=false in url",t);
}
}
return invoker;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
[/code]
AbstractLoadBalance的select方法
public <T> Invoker<T> select(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
if (invokers == null || invokers.size() == 0)
return null;
if (invokers.size() == 1)
return invokers.get(0);
return doSelect(invokers, url, invocation);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
[/code]
doSelect

会有四种负载策略
ConsistentHashLoadBalance
1 致性Hash,相同参数的请求总是发到同一提供者。
2 当某一台提供者挂时,原本发往该提供者的请求,基于虚拟节点,平 摊到其它提供者,不会引起剧烈变动。
3 缺省只对第一个参数Hash,如果要修改,请配置
4 缺省用160份虚拟节点,如果要修改,请配置
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
int identityHashCode = System.identityHashCode(invokers);
ConsistentHashSelector<T> selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
if (selector == null || selector.getIdentityHashCode() != identityHashCode) {
selectors.put(key, new ConsistentHashSelector<T>(invokers, invocation.getMethodName(), identityHashCode));
selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
}
return selector.select(invocation);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[/code]
LeastActiveLoadBalance
1 最少活跃调用数,相同活跃数的随机,活跃数指调用前后计数差。
2 使慢的提供者收到更少请求,因为越慢的提供者的调用前后计数差会越大。
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
int length = invokers.size(); // 总个数
int leastActive = -1; // 最小的活跃数
int leastCount = 0; // 相同最小活跃数的个数
int[] leastIndexs = new int[length]; // 相同最小活跃数的下标
int totalWeight = 0; // 总权重
int firstWeight = 0; // 第一个权重,用于于计算是否相同
boolean sameWeight = true; // 是否所有权重相同
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Invoker<T> invoker = invokers.get(i);
int active = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive(); // 活跃数
int weight = invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.WEIGHT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_WEIGHT); // 权重
if (leastActive == -1 || active < leastActive) { // 发现更小的活跃数,重新开始
leastActive = active; // 记录最小活跃数
leastCount = 1; // 重新统计相同最小活跃数的个数
leastIndexs[0] = i; // 重新记录最小活跃数下标
totalWeight = weight; // 重新累计总权重
firstWeight = weight; // 记录第一个权重
sameWeight = true; // 还原权重相同标识
} else if (active == leastActive) { // 累计相同最小的活跃数
leastIndexs[leastCount ++] = i; // 累计相同最小活跃数下标
totalWeight += weight; // 累计总权重
// 判断所有权重是否一样
if (sameWeight && i > 0
&& weight != firstWeight) {
sameWeight = false;
}
}
}
// assert(leastCount > 0)
if (leastCount == 1) {
// 如果只有一个最小则直接返回
return invokers.get(leastIndexs[0]);
}
if (! sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) {
// 如果权重不相同且权重大于0则按总权重数随机
int offsetWeight = random.nextInt(totalWeight);
// 并确定随机值落在哪个片断上
for (int i = 0; i < leastCount; i++) {
int leastIndex = leastIndexs[i];
offsetWeight -= getWeight(invokers.get(leastIndex), invocation);
if (offsetWeight <= 0)
return invokers.get(leastIndex);
}
}
// 如果权重相同或权重为0则均等随机
return invokers.get(leastIndexs[random.nextInt(leastCount)]);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
[/code]
RandomLoadBalance
1 随机,按权重设置随机概率。
2 在一个截面上碰撞的概率高,但调用量越大分布越均匀,而且按概率使用权重后也比较均匀,有利于动态调整提供者权重。
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
int length = invokers.size(); // 总个数
int totalWeight = 0; // 总权重
boolean sameWeight = true; // 权重是否都一样
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
totalWeight += weight; // 累计总权重
if (sameWeight && i > 0
&& weight != getWeight(invokers.get(i - 1), invocation)) {
sameWeight = false; // 计算所有权重是否一样
}
}
if (totalWeight > 0 && ! sameWeight) {
// 如果权重不相同且权重大于0则按总权重数随机
int offset = random.nextInt(totalWeight);
// 并确定随机值落在哪个片断上
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
offset -= getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
if (offset < 0) {
return invokers.get(i);
}
}
}
// 如果权重相同或权重为0则均等随机
return invokers.get(random.nextInt(length));
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
RoundRobinLoadBalance
1 轮循,按公约后的权重设置轮循比率。
2 存在慢的提供者累积请求的问题,比如:第二台机器很慢,但没挂,当请求调到第二台时就卡在那,久而久之,所有请求都卡在调到第二台上。
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
int length = invokers.size(); // 总个数
int maxWeight = 0; // 最大权重
int minWeight = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 最小权重
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
maxWeight = Math.max(maxWeight, weight); // 累计最大权重
minWeight = Math.min(minWeight, weight); // 累计最小权重
}
if (maxWeight > 0 && minWeight < maxWeight) { // 权重不一样
AtomicPositiveInteger weightSequence = weightSequences.get(key);
if (weightSequence == null) {
weightSequences.putIfAbsent(key, new AtomicPositiveInteger());
weightSequence = weightSequences.get(key);
}
int currentWeight = weightSequence.getAndIncrement() % maxWeight;
List<Invoker<T>> weightInvokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>();
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) { // 筛选权重大于当前权重基数的Invoker
if (getWeight(invoker, invocation) > currentWeight) {
weightInvokers.add(invoker);
}
}
int weightLength = weightInvokers.size();
if (weightLength == 1) {
return weightInvokers.get(0);
} else if (weightLength > 1) {
invokers = weightInvokers;
length = invokers.size();
}
}
AtomicPositiveInteger sequence = sequences.get(key);
if (sequence == null) {
sequences.putIfAbsent(key, new AtomicPositiveInteger());
sequence = sequences.get(key);
}
// 取模轮循
return invokers.get(sequence.getAndIncrement() % length);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
[/code]
参考资料:
http://dubbo.io/user-guide/demos/%E9%9B%86%E7%BE%A4%E5%AE%B9%E9%94%99.html
http://dubbo.io/user-guide/demos/%E8%B4%9F%E8%BD%BD%E5%9D%87%E8%A1%A1.html
<link rel="stylesheet" href="http://csdnimg.cn/release/phoenix/production/markdown_views-68a8aad09e.css"> </div>
相关文章推荐
- dubbo原理系列3-consumer调用过程
- dubbo原理系列1-服务端暴露过程
- dubbo客户端(consumer层)大概调用过程
- dubbo原理系列2-reference代理生成过程
- dubbo原理系列1-服务端暴露过程
- dubbo原理系列2-reference代理生成过程
- C++基础知识:c 函数调用过程原理及函数栈帧分析
- 自定义View Measure过程 - 最易懂的自定义View原理系列(2)
- Dubbo学习过程、使用经验分享及实现原理简单介绍
- Java基础系列12:使用CallableStatement接口调用数据库中的存储过程
- Alibaba Dubbo框架同步调用原理分析-2
- dubbo请求调用过程分析
- 自定义View Layout过程 - 最易懂的自定义View原理系列(3)
- 存储过程系列之存储过程具体操作过程及sql数据库调用
- c函数调用过程原理及函数栈帧分析
- dubbo组成原理-service服务调用
- alibaba远程调用框架dubbo原理
- alibaba远程调用框架dubbo原理
- 自定义View Layout过程 - 最易懂的自定义View原理系列(3)
- dubbo远程调用过程中,把参数bean转换成了HashMap
