Codeforces-936B:Sleepy Game(DP)
2018-03-07 12:50
543 查看
B. Sleepy Gametime limit per test2 secondsmemory limit per test256 megabytesinputstandard inputoutputstandard outputPetya and Vasya arranged a game. The game runs by the following rules. Players have a directed graph consisting of n vertices and medges. One of the vertices contains a chip. Initially the chip is located at vertex s. Players take turns moving the chip along some edge of the graph. Petya goes first. Player who can't move the chip loses. If the game lasts for 106 turns the draw is announced.Vasya was performing big laboratory work in "Spelling and parts of speech" at night before the game, so he fell asleep at the very beginning of the game. Petya decided to take the advantage of this situation and make both Petya's and Vasya's moves.Your task is to help Petya find out if he can win the game or at least draw a tie.InputThe first line of input contain two integers n and m — the number of vertices and the number of edges in the graph (2 ≤ n ≤ 105, 0 ≤ m ≤ 2·105).The next n lines contain the information about edges of the graph. i-th line (1 ≤ i ≤ n) contains nonnegative integer ci — number of vertices such that there is an edge from i to these vertices and ci distinct integers ai, j — indices of these vertices (1 ≤ ai, j ≤ n, ai, j ≠ i).It is guaranteed that the total sum of ci equals to m.The next line contains index of vertex s — the initial position of the chip (1 ≤ s ≤ n).OutputIf Petya can win print «Win» in the first line. In the next line print numbers v1, v2, ..., vk (1 ≤ k ≤ 106) — the sequence of vertices Petya should visit for the winning. Vertex v1 should coincide with s. For i = 1... k - 1 there should be an edge from vi to vi + 1 in the graph. There must be no possible move from vertex vk. The sequence should be such that Petya wins the game.If Petya can't win but can draw a tie, print «Draw» in the only line. Otherwise print «Lose».ExamplesinputCopy
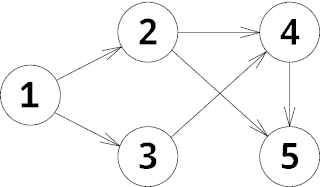
Initially the chip is located at vertex 1. In the first move Petya moves the chip to vertex 2, after that he moves it to vertex 4 for Vasya. After that he moves to vertex 5. Now it is Vasya's turn and there is no possible move, so Petya wins.In the second example the graph is the following:

Initially the chip is located at vertex 2. The only possible Petya's move is to go to vertex 1. After that he has to go to 3 for Vasya. Now it's Petya's turn but he has no possible move, so Petya loses.In the third example the graph is the following:
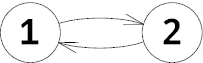
Petya can't win, but he can move along the cycle, so the players will draw a tie.思路:用v[k][0/1]表示在k点时后手/先手的状态,v[k][0/1]=0表示还未曾搜过,v[k][0/1]=1表示还在深搜中,v[k][0/1]=2表示已经搜索完。d[k][0/1]记录路径,d[k][0/1]=0表示路径不存在。
比赛时最后想起来在一些点可以通过走一遍由奇数个点组成的环来把v[k][0]变为v[k][1],即把先后手状态转换,但却不知如何处理,其实用二维v[k][0/1]就行了。#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX=1e6;
const int MOD=1e9+7;
typedef __int64 ll;
struct edg
{
int to,next;
}ed[MAX];
int head[MAX],d[MAX][2],v[MAX][2],tot=0,circle=0;
int son[MAX];
void add(int x,int y)
{
ed[tot].to=y;
ed[tot].next=head[x];
head[x]=tot++;
}
int dfs(int k,int step)
{
if(son[k]==0)return step==0; //没有后继
if(v[k][step]==2)return d[k][step];//已经访问过了
v[k][step]=1; //正在搜索中
for(int i=head[k];i!=-1;i=ed[i].next)
{
int nex=ed[i].to;
if(v[nex][step^1]==1)//碰到一个搜索中的节点,说明有环
{
circle=1;
continue;
}
if(dfs(nex,step^1))d[k][step]=nex;
}
v[k][step]=2; //搜索完毕
return d[k][step];
}
void DFS(int k,int step)
{
printf("%d ",k);
if(d[k][step])DFS(d[k][step],step^1);
}
int main()
{
memset(head,-1,sizeof head);
memset(v,0,sizeof v);
memset(d,0,sizeof d);
memset(son,0,sizeof son);
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d",&x);
son[i]=x;
while(x--)
{
scanf("%d",&y);
add(i,y);
}
}
int st;
scanf("%d",&st);
if(dfs(st,1))
{
puts("Win");
DFS(st,1);
}
else if(circle)puts("Draw");
else puts("Lose");
return 0;
}
5 6 2 2 3 2 4 5 1 4 1 5 0 1output
Win 1 2 4 5inputCopy
3 2 1 3 1 1 0 2output
LoseinputCopy
2 2 1 2 1 1 1output
DrawNoteIn the first example the graph is the following:

Initially the chip is located at vertex 1. In the first move Petya moves the chip to vertex 2, after that he moves it to vertex 4 for Vasya. After that he moves to vertex 5. Now it is Vasya's turn and there is no possible move, so Petya wins.In the second example the graph is the following:

Initially the chip is located at vertex 2. The only possible Petya's move is to go to vertex 1. After that he has to go to 3 for Vasya. Now it's Petya's turn but he has no possible move, so Petya loses.In the third example the graph is the following:

Petya can't win, but he can move along the cycle, so the players will draw a tie.思路:用v[k][0/1]表示在k点时后手/先手的状态,v[k][0/1]=0表示还未曾搜过,v[k][0/1]=1表示还在深搜中,v[k][0/1]=2表示已经搜索完。d[k][0/1]记录路径,d[k][0/1]=0表示路径不存在。
比赛时最后想起来在一些点可以通过走一遍由奇数个点组成的环来把v[k][0]变为v[k][1],即把先后手状态转换,但却不知如何处理,其实用二维v[k][0/1]就行了。#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX=1e6;
const int MOD=1e9+7;
typedef __int64 ll;
struct edg
{
int to,next;
}ed[MAX];
int head[MAX],d[MAX][2],v[MAX][2],tot=0,circle=0;
int son[MAX];
void add(int x,int y)
{
ed[tot].to=y;
ed[tot].next=head[x];
head[x]=tot++;
}
int dfs(int k,int step)
{
if(son[k]==0)return step==0; //没有后继
if(v[k][step]==2)return d[k][step];//已经访问过了
v[k][step]=1; //正在搜索中
for(int i=head[k];i!=-1;i=ed[i].next)
{
int nex=ed[i].to;
if(v[nex][step^1]==1)//碰到一个搜索中的节点,说明有环
{
circle=1;
continue;
}
if(dfs(nex,step^1))d[k][step]=nex;
}
v[k][step]=2; //搜索完毕
return d[k][step];
}
void DFS(int k,int step)
{
printf("%d ",k);
if(d[k][step])DFS(d[k][step],step^1);
}
int main()
{
memset(head,-1,sizeof head);
memset(v,0,sizeof v);
memset(d,0,sizeof d);
memset(son,0,sizeof son);
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d",&x);
son[i]=x;
while(x--)
{
scanf("%d",&y);
add(i,y);
}
}
int st;
scanf("%d",&st);
if(dfs(st,1))
{
puts("Win");
DFS(st,1);
}
else if(circle)puts("Draw");
else puts("Lose");
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- CodeForces - 937D Sleepy Game [dfs+DP]
- Codeforces 837D Round Subset【思维+Dp+滚动数组】
- Codeforces 148D - Bag of mice 概率dp
- Codeforces 467C George and Job(dp)
- Codeforces 513G1 513G2 Inversions problem [概率dp]
- Codeforces 513G2 Inversions problem (dp)
- 51nod 1232 完美数 / codeforces 55D 数位DP
- Codeforces 414A Mashmokh and ACM(dp)
- Codeforces 441E Valera and Number 概率DP
- Codeforces 61D--树形dp
- 【dp】codeforces 837D Round Subset
- Codeforces 149 D Coloring Brackets(区间dp,标记状态,dfs)
- CodeForces 149D-Coloring Brackets(区间dp 的好题)
- codeforces 229 D Towers 贪心+DP
- 【CodeForces 149D Coloring Barkets】【区间DP/递推】
- codeforces 580D. Kefa and Dishes(状压dp)
- codeforces 366C C. Dima and Salad(dp)
- codeforces 571B B. Minimization(dp)
- CodeForces 189D(最短路+dp)
- 【数位DP】 【CodeForces 55D】
