深度学习: mAP (Mean Average Precision)
2018-03-07 09:44
591 查看
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/jningwei/article/details/78955536
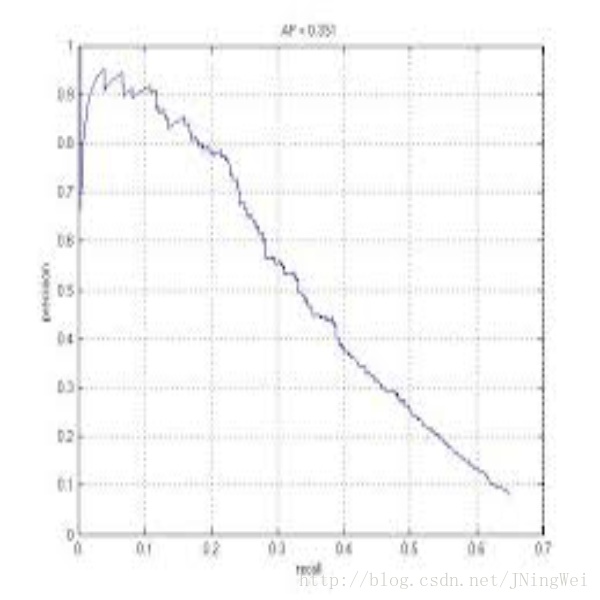
一般来说,precision 和 recall 是 鱼与熊掌 的关系。下图即是 PR曲线:
如何衡量一个模型的性能,单纯用 precision 和 recall 都不科学。于是人们想到,哎嘛为何不把 PR曲线下的面积 当做衡量尺度呢?于是就有了 AP值 这一概念。这里的 average,等于是对 precision 进行 取平均 。
是对多个验证集个体 求 平均AP值 。如下图:
深度学习: mAP (Mean Average Precision)
版权声明:转载请注明出处 http://blog.csdn.net/JNingWei/article/details/78955536mAP
概念P
precision,即 准确率 。R
recall,即 召回率 。PR曲线
即 以 precision 和 recall 作为 横纵轴坐标 的二维曲线。一般来说,precision 和 recall 是 鱼与熊掌 的关系。下图即是 PR曲线:

AP值
Average Precision,即 平均精确度 。如何衡量一个模型的性能,单纯用 precision 和 recall 都不科学。于是人们想到,哎嘛为何不把 PR曲线下的面积 当做衡量尺度呢?于是就有了 AP值 这一概念。这里的 average,等于是对 precision 进行 取平均 。
mAP值
Mean Average Precision,即 平均AP值 。是对多个验证集个体 求 平均AP值 。如下图:

mAP 计算
公式
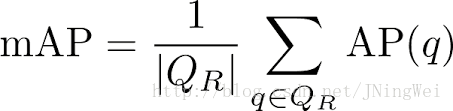
Code
def compute_ap(gt_boxes, gt_class_ids, pred_boxes, pred_class_ids, pred_scores, iou_threshold=0.5): """Compute Average Precision at a set IoU threshold (default 0.5). Returns: mAP: Mean Average Precision precisions: List of precisions at different class score thresholds. recalls: List of recall values at different class score thresholds. overlaps: [pred_boxes, gt_boxes] IoU overlaps. """ # Trim zero padding and sort predictions by score from high to low gt_boxes = trim_zeros(gt_boxes) pred_boxes = trim_zeros(pred_boxes) pred_scores = pred_scores[:pred_boxes.shape[0]] indices = np.argsort(pred_scores)[::-1] pred_boxes = pred_boxes[indices] pred_class_ids = pred_class_ids[indices] pred_scores = pred_scores[indices] # Compute IoU overlaps [pred_boxes, gt_boxes] overlaps = compute_overlaps(pred_boxes, gt_boxes) # Loop through ground truth boxes and find matching predictions match_count = 0 pred_match = np.zeros([pred_boxes.shape[0]]) gt_match = np.zeros([gt_boxes.shape[0]]) for i in range(len(pred_boxes)): # Find best matching ground truth box sorted_ixs = np.argsort(overlaps[i])[::-1] for j in sorted_ixs: # If ground truth box is already matched, go to next one if gt_match[j] == 1: continue # If we reach IoU smaller than the threshold, end the loop iou = overlaps[i, j] if iou < iou_threshold: break # Do we have a match? if pred_class_ids[i] == gt_class_ids[j]: match_count += 1 gt_match[j] = 1 pred_match[i] = 1 break # Compute precision and recall at each prediction box step precisions = np.cumsum(pred_match) / (np.arange(len(pred_match)) + 1) recalls = np.cumsum(pred_match).astype(np.float32) / len(gt_match) # Pad with start and end values to simplify the math precisions = np.concatenate([[0], precisions, [0]]) recalls = np.concatenate([[0], recalls, [1]]) # Ensure precision values decrease but don't increase. This way, the # precision value at each recall threshold is the maximum it can be # for all following recall thresholds, as specified by the VOC paper. for i in range(len(precisions) - 2, -1, -1): precisions[i] = np.maximum(precisions[i], precisions[i + 1]) # Compute mean AP over recall range indices = np.where(recalls[:-1] != recalls[1:])[0] + 1 mAP = np.sum((recalls[indices] - recalls[indices - 1]) * precisions[indices]) return mAP, precisions, recalls, overlaps
相关文章推荐
- 深度学习: mAP (Mean Average Precision)
- Mean Average Precision(MAP)平均精度均值
- MAP(Mean Average Precision)
- 一个评测指标就是MAP(Mean Average Precision)平均精度均值。
- MAP(Mean Average Precision)
- Mean Average Precision(MAP)
- mAP(mean average precision)
- Precision、Recall and Mean Average Precision(MAP)
- mean average precision(MAP)
- Mean Average Precision(MAP)平均精度均值
- 目标检测模型的性能评估--MAP(Mean Average Precision)
- MAP(Mean Average Precision):
- mean average precision(MAP)在计算机视觉中的计算和应用
- 目标检测模型中的性能评估——MAP(Mean Average Precision)
- MAP(Mean Average Precision)
- Mean Average Precision(MAP)
- mean average precision 定义以及计算
- Mean Average Precision vs Mean Reciprocal Rank
- Mean Average Precision
- 【YOLO学习】召回率(Recall),精确率(Precision),平均正确率(Average_precision(AP) ),交除并(Intersection-over-Union(IoU))
