Makes And The Product
2018-03-04 19:53
211 查看
After returning from the army Makes received a gift — an array a consisting of npositive integer numbers. He hadn't been solving problems for a long time, so he became interested
to answer a particular question: how many triples of indices (i, j, k) (i < j < k), such that ai·aj·ak is
minimum possible, are there in the array? Help him with it!
Input
The first line of input contains a positive integer number n (3 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of elements in array a. The second line contains n positive
integer numbers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the elements of a given array.
Output
Print one number — the quantity of triples (i, j, k) such that i, j and k are pairwise distinct and ai·aj·ak is
minimum possible.
Example
Input
Output
Input
Output
Input
Output
Note
In the first example Makes always chooses three ones out of four, and the number of ways to choose them is 4.
In the second example a triple of numbers (1, 2, 3) is chosen (numbers, not indices). Since there are two ways to choose an element 3, then the answer is 2.
In the third example a triple of numbers (1, 1, 2) is chosen, and there's only one way to choose indices.
有三种情况:
1.最小数字的个数n1>=3,则只需计算
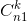
2.n1<3,第二小的数字个数n2>=3-n1,则只需计算
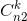
3.n1,n2<3,第三小的数字个数n3>=3-n2-n1,则只需计算
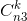
注意结果会超过int
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
struct list
{
int num,amount;
list() { }
list(int a,int b):num(a),amount(b) { }
friend bool operator < (struct list c,struct list d)
{
return c.num>d.num;
}
};
long long C(int a,int b)
{
if(b>a-b)
b=a-b;
if(b==0)
return 1;
long long up=1,down=1;
int i=b;
while(i--)
up*=a--;
for(i=1;i<=b;i++)
down*=i;
return up/down;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin >> n)
{
map<int,int> mp;
priority_queue<list> q;
while(n--)
{
int a;
cin >> a;
mp[a]++;
}
map<int,int>::iterator it;
for(it=mp.begin();it!=mp.end();it++)
q.push(list(it->first,it->second));
if(q.top().amount>=3)
{
cout << C(q.top().amount,3) << endl;
continue;
}
else
{
int num=q.top().amount;
q.pop();
if(q.top().amount>=3-num)
{
cout << C(q.top().amount,3-num) << endl;
continue;
}
else
{
num+=q.top().amount;
q.pop();
cout << C(q.top().amount,3-num) << endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
to answer a particular question: how many triples of indices (i, j, k) (i < j < k), such that ai·aj·ak is
minimum possible, are there in the array? Help him with it!
Input
The first line of input contains a positive integer number n (3 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of elements in array a. The second line contains n positive
integer numbers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the elements of a given array.
Output
Print one number — the quantity of triples (i, j, k) such that i, j and k are pairwise distinct and ai·aj·ak is
minimum possible.
Example
Input
4 1 1 1 1
Output
4
Input
5
1 3 2 3 4
Output
2
Input
6
1 3 3 1 3 2
Output
1
Note
In the first example Makes always chooses three ones out of four, and the number of ways to choose them is 4.
In the second example a triple of numbers (1, 2, 3) is chosen (numbers, not indices). Since there are two ways to choose an element 3, then the answer is 2.
In the third example a triple of numbers (1, 1, 2) is chosen, and there's only one way to choose indices.
有三种情况:
1.最小数字的个数n1>=3,则只需计算
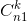
2.n1<3,第二小的数字个数n2>=3-n1,则只需计算
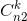
3.n1,n2<3,第三小的数字个数n3>=3-n2-n1,则只需计算
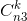
注意结果会超过int
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
struct list
{
int num,amount;
list() { }
list(int a,int b):num(a),amount(b) { }
friend bool operator < (struct list c,struct list d)
{
return c.num>d.num;
}
};
long long C(int a,int b)
{
if(b>a-b)
b=a-b;
if(b==0)
return 1;
long long up=1,down=1;
int i=b;
while(i--)
up*=a--;
for(i=1;i<=b;i++)
down*=i;
return up/down;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin >> n)
{
map<int,int> mp;
priority_queue<list> q;
while(n--)
{
int a;
cin >> a;
mp[a]++;
}
map<int,int>::iterator it;
for(it=mp.begin();it!=mp.end();it++)
q.push(list(it->first,it->second));
if(q.top().amount>=3)
{
cout << C(q.top().amount,3) << endl;
continue;
}
else
{
int num=q.top().amount;
q.pop();
if(q.top().amount>=3-num)
{
cout << C(q.top().amount,3-num) << endl;
continue;
}
else
{
num+=q.top().amount;
q.pop();
cout << C(q.top().amount,3-num) << endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- B. Makes And The Product
- Educational Codeforces Round 23 B - Makes And The Product
- codeforce817B Makes And The Product (排序)
- Educational Codeforces Round 23 B. Makes And The Product
- Educational Codeforces Round 23#B. Makes And The Product
- CodeForces 817 B.Makes And The Product(水~)
- codeforces817b Makes And The Product
- android studio 发布app出错:please select the product flavors to build and sign
- Geometric regularity criterion for NSE: the cross product of velocity and vorticity 1: $u\times \om$
- [论文笔记] Leveraging the crowd as a source of innovation Does crowdsourcing represent a new model for product and service innovation? (SIGMIS-CPR, 2012)
- Six Sigma and the Product Development Cycle
- Geometric regularity criterion for NSE: the cross product of velocity and vorticity 2: $u\times \om\cdot \n\times \om$
- 解决安装photoshop提示”please uninstall and reinstall the product“
- Win8.1/win10安装photoshop软件提示please uninstall and reinstall the product如何解决
- Platform Road Map for the MATLAB and Simulink Product Families
- walk around by The provided App differs from another App with the same version and product ID
- 解决PS启动时的问题---Please uninstall and reinstall the product.
- android studio 发布app出错:please select the product flavors to build and sign
- Geometric regularity criterion for NSE: the cross product of velocity and vorticity 3: $u\times \f{\om}{|\om|}\cdot \f{\vLm^\be u}{|\vLm^\be u|}$
- Determine whether the product of a and b is even or odd.
