[置顶] 容器化RDS|计算存储分离架构下的“Split-Brain”
2018-02-26 18:30
585 查看
不管是架构选型还是生活,大多数时候都是在做trade off,获了计算存储分离带来的好处, 也意味着要忍受它带来的一些棘手问题。本文尝试结合Kubernetes,Docker,MySQL和计算存储分离架构,分享我们遇到的诸多问题之一 “Split-Brain” 。
2018年1月19号参加了阿里巴巴双十一数据库技术峰会,见到了好多老同事(各位研究员、资深专家),也了解到业界最新的数据库技术发展趋势:数据库容器化作为下一代数据库基础架构
基于编排架构管理容器化数据库
采用计算存储分离架构
这和我们在私有 RDS 上的技术选型不谋而合,尤其是计算存储分离架构。
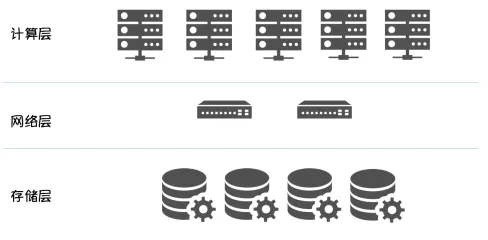
在我们看来, 其最大优势在于:计算资源 / 存储资源独立扩展,架构更清晰,部署更容易。
将有状态的数据下沉到存储层,Scheduler 调度时,无需感知计算节点的存储介质,只需调度到满足计算资源要求的 Node,数据库实例启动时,只需在分布式文件系统挂载mapping volume 即可,可以显著的提高数据库实例的部署密度和计算资源利用率。
以阿里巴巴为例,考虑到今时今日它的规模,如果能够实现数据库服务的离线(ODPS)/在线集群的混合部署,意义极其重大。关键问题在于,离线(ODPS)计算和在线计算对实时性要求不同,硬件配置也不同,尤其是本地存储介质:离线(ODPS)以机械磁盘为主
在线以 SSD / Flash 为主
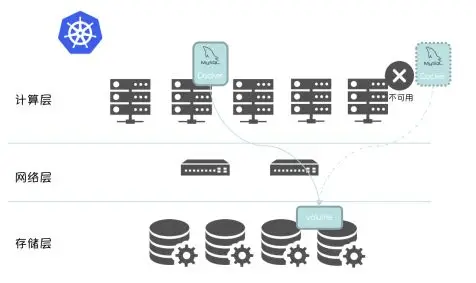
如果采用本地存储作为数据库实例的存储介质,试想一下,一个 Storage Qos 要求是 Flash 的数据库实例无法调度到离线计算集群,哪怕离线计算集群 CPU,Memory 有大量空闲。计算存储分离为实现离线(ODPS)/在线集群的混合部署提供了可能。结合 Kubernetes,Docker和 MySQL,进一步细化架构图, 如下图所示 :
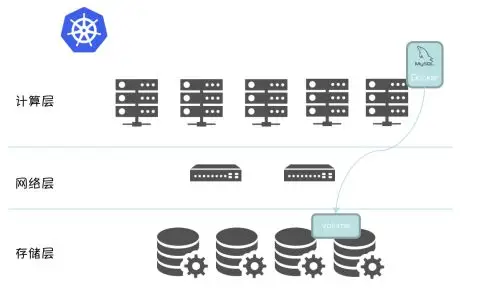
同时,这套架构也带给我们更加简单、通用,高效的 High Availability 方案。当集群中某个 Node不可用后,借助 Kubernetes 的原生组件Node Controller, Scheduler 和原生 API Statefulset 即可将数据库实例调度到其他可用节点,以实现数据库实例的高可用。
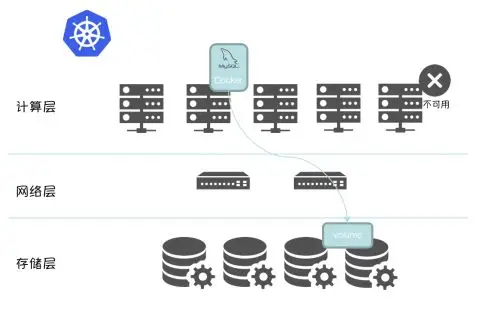
一切是多么的美好,是不是可以得到这个结论:借助 Kubernetes 的原生组件NodeController,Scheduler和原生API Statefulset, 加上计算存储分离架构,并将成熟的分布式文件系统集成到 Kubernetes 存储系统,就能提供私有RDS服务。之前我们也是这么想的,直到遇到 “Split-Brain” 问题(也即是本文的主题)。回到上面的 High Availability 方案。当集群中某个 Node不可用后,借助Kubernetes 的原生组件Node Controller,Scheduler 和原生 API Statefulset 即可将数据库实例调度到其他可用节点,以实现数据库实例的高可用。判定 Node 不可用将是后续触发 Failover 动作的关键。所以这里需要对节点状态的判定机制稍作展开:Kubelet 借助 API Server 定期(node-status-update-frequency)更新 etcd 中对应节点的心跳信息
Controller Manager 中的 Node Controller 组件定期(node-monitor-period)轮询 ETCD中节点的心跳信息
如果在周期 (node-monitor-grace-period) 内,心跳更新丢失, 该节点标记为 Unknown(ConditionUnknown)
如果在周期 (pod-eviction-timeout) 内,心跳更新持续丢失, Node Controller 将会触发集群层面的驱逐机制
Scheduler 将 Unknown 节点上的所有数据库实例调度到其他健康(Ready)节点
访问架构图如下所示:
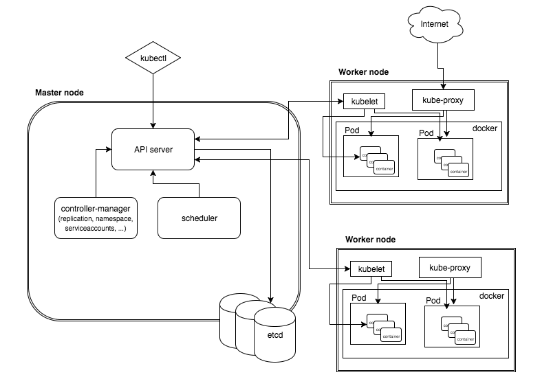
补充一句,借助 ETCD 集群的高可用强一致,得以保证 Kubernetes 集群元信息的一致性:ETCD基于 Raft 算法实现
Raft算法是一种基于消息传递(state machine replicated)且具有高度容错(fault tolerance)特性的一致性算法(consensusalgorithm)
Raft是大名鼎鼎的 Paxos 的简化版本
如果对于 Raft 算法的实现有兴趣,可以看看https://github.com/goraft/raft
所有感兴趣一致性算法的同学,都值得花精力学习。基于 goraft/raft,我实现了Network Partition Failures/Recovery TestCase,收获不小。看上去合理的机制会给我们带来两个问题,问题一:无法判定节点真实状态心跳更新是判断节点是否可用的依据。但是,心跳更新丢失是无法判定节点真实状态的 (Kubernetes 中将节点标记为 Condition Unknown 也说明了这点)。Node 可能仅仅是网络问题,CPU 繁忙,“假死”, Kubelet bug 等原因导致心跳更新丢失,但节点上的数据库实例还在运行中。问题二:缺乏有效的 Fence 机制在这个情况下,借助 Kubernetes 的原生组件 Node Controller,Scheduler 和原生 API Statefulset 实现的 Failover, 将数据库实例从 Unknown 节点驱逐到可用节点,但对原 Unknown节点不做任何操作。这种“软驱逐”,将会导致新旧两个数据库实例同时访问同一份数据文件。
发生 “Split-Brain” 导致 Data Corruption.数据丢失,损失无法弥补。下面是枯燥的故障复现,通过日志和代码分析驱逐的工作机制,总结 “Split-Brain” 过程。测试过程使用 Statefulset 创建 MySQL 单实例 gxr-oracle-statefulset (这是一个 Oracle DBA 取的名字,原谅他)
Scheduler 将 MySQL 单实例调度到集群中的节点 “k8s-node3”
通过 sysbench 对该实例制造极高的负载,k8s-node3” load 飙升,致“k8s-node3” 上的Kubelet 无法跟 API Server 通讯, 并开始报错
NodeController 启动驱逐
Statefulset 发起重建
Scheduler 将 MySQL 实例调度到 “k8s-node1” 上
新旧 MySQL 实例访问同一个 Volume
数据文件被写坏,旧MySQL实例都报错, 并无法启动
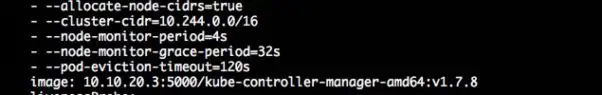
测试参数kube-controller-manager 启动参数
kubelet 启动参数

基于日志,个事件流如下:时间点 December 1st 2017,10:18:05.000 (最后一次更新成功应该是 10:17:42.000)节点 (k8s-node3) 启动数据库压力测试,以模拟该节点“假死”,kubelet 跟 API Server 出现心跳丢失。
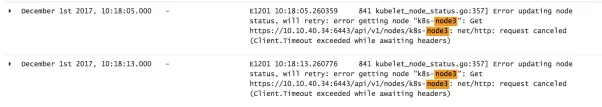
kubelet 日志报错,法通过 API Server 更新 k8s-node3 状态。Kubelet 细节如下:
通过 API Server 更新集群信息
if kl.kubeClient != nil { //Start syncing node status immediately, this may set up things the runtime needsto run. gowait.Until(kl.syncNodeStatus, kl.nodeStatusUpdateFrequency, wait.NeverStop)}
定期(node Status Update Frequency)更新对应节点状态
nodeStatusUpdateFrequency 默认时间为 10 秒, 测试时设置的是8sobj.NodeStatusUpdateFrequency =metav1.Duration{Duration: 10 * time.Second}
更新如下信息:
func (kl *Kubelet) defaultNodeStatusFuncs()[]func(*v1.Node) error { //initial set of node status update handlers, can be modified by Option's withoutError := func(f func(*v1.Node)) func(*v1.Node) error { return func(n *v1.Node) error { f(n) return nil } } return []func(*v1.Node) error{ kl.setNodeAddress, withoutError(kl.setNodeStatusInfo), withoutError(kl.setNodeOODCondition), withoutError(kl.setNodeMemoryPressureCondition), withoutError(kl.setNodeDiskPressureCondition), withoutError(kl.setNodeReadyCondition), withoutError(kl.setNodeVolumesInUseStatus), withoutError(kl.recordNodeSchedulableEvent), }}
通过 kubectl 可以获得节点的信息:

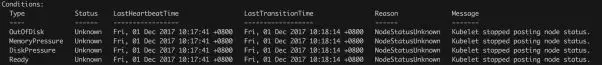
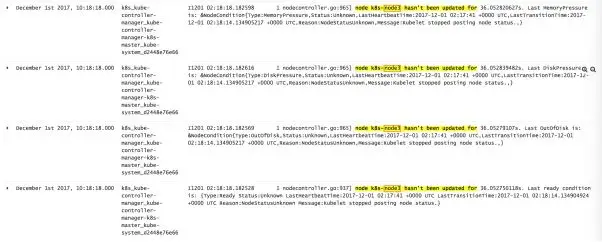
时间点 December 1st 2017, 10:18:14.000
· NodeController 发现 k8s-node3 的状态有32s 没有发生更新。 ○ ready/ outofdisk / diskpressure / memorypressue condition




将该节点状态更新为 UNKNOWN:
每隔 NodeMonitorPeriod 继续节点状态是否有更新:
定期(NodeMonitorPeriod)查看一次节点状态
// Incorporate the results of node statuspushed from kubelet to master.go wait.Until(func() { iferr := nc.monitorNodeStatus(); err != nil { glog.Errorf("Error monitoring node status: %v", err) }}, nc.nodeMonitorPeriod, wait.NeverStop)
NodeMonitorPeriod默认 5秒, 测试时4s
NodeMonitorPeriod: metav1.Duration{Duration: 5 * time.Second},
当超过 NodeMonitorGracePeriod 时间后, 节点状态没有更新将节点状态设置成 unknown
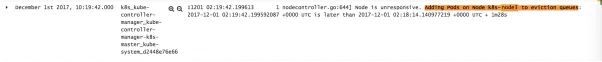
ifnc.now().After(savedNodeStatus.probeTimestamp.Add(gracePeriod)) { //NodeReady condition was last set longer ago than gracePeriod, so update it toUnknown //(regardless of its current value) in the master. ifcurrentReadyCondition == nil { glog.V(2).Infof("node %v is never updated by kubelet",node.Name) node.Status.Conditions = append(node.Status.Conditions,v1.NodeCondition{ Type: v1.NodeReady, Status: v1.ConditionUnknown, Reason: "NodeStatusNeverUpdated", Message: fmt.Sprintf("Kubelet never posted node status."), LastHeartbeatTime: node.CreationTimestamp, LastTransitionTime: nc.now(), }) }else { glog.V(4).Infof("node %v hasn't been updated for %+v. Last readycondition is: %+v", node.Name, nc.now().Time.Sub(savedNodeStatus.probeTimestamp.Time),observedReadyCondition) if observedReadyCondition.Status != v1.ConditionUnknown { currentReadyCondition.Status = v1.ConditionUnknown currentReadyCondition.Reason = "NodeStatusUnknown" currentReadyCondition.Message = "Kubelet stopped posting nodestatus." // LastProbeTime is the last time we heard from kubelet. currentReadyCondition.LastHeartbeatTime =observedReadyCondition.LastHeartbeatTime currentReadyCondition.LastTransitionTime = nc.now() } }时间点 December 1st 2017, 10:19:42.000刚好过去 podEvictionTimeout , 将该节点添加到驱逐队列中:
在podEvictionTimeout 后,为该节点上 pods 需要开始驱逐
if observedReadyCondition.Status ==v1.ConditionUnknown { ifnc.useTaintBasedEvictions { // We want to update the taint straight away if Node is already taintedwith the UnreachableTaint if taintutils.TaintExists(node.Spec.Taints, NotReadyTaintTemplate) { taintToAdd := *UnreachableTaintTemplate if !util.SwapNodeControllerTaint(nc.kubeClient,[]*v1.Taint{&taintToAdd}, []*v1.Taint{NotReadyTaintTemplate}, node) { glog.Errorf("Failed to instantly swap UnreachableTaint toNotReadyTaint. Will try again in the next cycle.") } } else if nc.markNodeForTainting(node) { glog.V(2).Infof("Node %v is unresponsive as of %v. Adding it to theTaint queue.", node.Name, decisionTimestamp, ) } }else { ifdecisionTimestamp.After(nc.nodeStatusMap[node.Name].probeTimestamp.Add(nc.podEvictionTimeout)){ if nc.evictPods(node) { glog.V(2).Infof("Node is unresponsive. Adding Pods on Node %s toeviction queues: %v is later than %v + %v", node.Name, decisionTimestamp, nc.nodeStatusMap[node.Name].readyTransitionTimestamp, nc.podEvictionTimeout-gracePeriod, ) } } }}
放到驱逐数组中
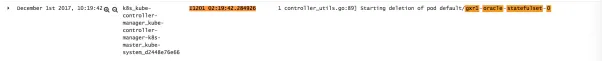
// evictPods queues an eviction for theprovided node name, and returns false if the node is already// queued for eviction.func (nc *Controller) evictPods(node*v1.Node) bool { nc.evictorLock.Lock() defer nc.evictorLock.Unlock() return nc.zonePodEvictor[utilnode.GetZoneKey(node)].Add(node.Name,string(node.UID))}时间点 December 1st 2017, 10:19:42.000 开始驱逐:


驱逐 goroutine
if nc.useTaintBasedEvictions { //Handling taint based evictions. Because we don't want a dedicated logic inTaintManager for NC-originated //taints and we normally don't rate limit evictions caused by taints, we need torate limit adding taints. gowait.Until(nc.doNoExecuteTaintingPass, scheduler.NodeEvictionPeriod,wait.NeverStop)} else { //Managing eviction of nodes: //When we delete pods off a node, if the node was not empty at the time we then //queue an eviction watcher. If we hit an error, retry deletion. gowait.Until(nc.doEvictionPass, scheduler.NodeEvictionPeriod, wait.NeverStop)}
通过删除 pods 的方式驱逐
func (nc *Controller) doEvictionPass() { nc.evictorLock.Lock() defer nc.evictorLock.Unlock() fork := range nc.zonePodEvictor { // Function should return 'false' and a time after which it should beretried, or 'true' if it shouldn't (it succeeded). nc.zonePodEvictor[k].Try(func(value scheduler.TimedValue) (bool,time.Duration) { node, err := nc.nodeLister.Get(value.Value) if apierrors.IsNotFound(err) { glog.Warningf("Node %v no longer present in nodeLister!",value.Value) } else if err != nil { glog.Warningf("Failed to get Node %v from the nodeLister: %v",value.Value, err) } else { zone := utilnode.GetZoneKey(node) evictionsNumber.WithLabelValues(zone).Inc() } nodeUID, _ := value.UID.(string) remaining, err := util.DeletePods(nc.kubeClient, nc.recorder,value.Value, nodeUID, nc.daemonSetStore) if err != nil { utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to evict node %q:%v", value.Value, err)) return false, 0 } if remaining { glog.Infof("Pods awaiting deletion due to Controllereviction") } return true, 0 }) }}时间点 December 1st 2017, 10:19:42.000 statefulsetcontroller 发现 default/gxr1-oracle-statefulset 状态异常

时间点 December 1st 2017, 10:19:42.000 scheduler 将 pod 调度到 k8s-node1

这样旧的 MySQL 实例在 k8s-node3 上,ubernetes 又将新的实例调度到 k8s-node1.两个数据库实例写同一份数据文件, data corruption. 两个节点都无法启动。老实例启动报错,日志为:2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] mysqld(mysqld 5.7.19-log) starting as process 963 ...2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:PUNCH HOLE support available2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Mutexes and rw_locks use GCC atomic builtins2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Uses event mutexes2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: GCCbuiltin __atomic_thread_fence() is used for memory barrier2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Compressed tables use zlib 1.2.32017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Using Linux native AIO2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Number of pools: 12017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Using CPU crc32 instructions2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Initializing buffer pool, total size = 3.25G, instances = 2, chunk size = 128M2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Completed initialization of buffer pool2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Ifthe mysqld execution user is authorized, page cleaner thread priority can bechanged. See the man page of setpriority().2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Highest supported file format is Barracuda.2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Logscan progressed past the checkpoint lsn 4068223232017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Doing recovery: scanned up to log sequence number 4068231902017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Database was not shutdown normally!2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Starting crash recovery.2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Starting an apply batch of log records to the database...InnoDB: Progress in percent: 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 992017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Apply batch completed2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Last MySQL binlog file position 0 428730, file name mysql-bin.0000042017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Removed temporary tablespace data file: "ibtmp1"2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Creating shared tablespace for temporary tables2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Setting file './ibtmp1' size to 12 MB. Physically writing the file full; Pleasewait ...2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:File './ibtmp1' size is now 12 MB.2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: 96redo rollback segment(s) found. 96 redo rollback segment(s) are active.2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: 32non-redo rollback segment(s) are active.2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Waiting for purge to start2017-12-01 10:19:47 0x7fcb08928700 InnoDB: Assertion failure in thread140509998909184 in file trx0purge.cc line 168InnoDB: Failing assertion:purge_sys->iter.trx_no <= purge_sys->rseg->last_trx_noInnoDB: We intentionally generate a memorytrap.InnoDB: Submit a detailed bug report tohttp://bugs.mysql.com.InnoDB: If you get repeated assertionfailures or crashes, evenInnoDB: immediately after the mysqld startup,there may beInnoDB: corruption in the InnoDBtablespace. Please refer toInnoDB:http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/forcing-innodb-recovery.htmlInnoDB: about forcing recovery.10:19:47 5669 - mysqld got signal 6 ;以上问题通过 WOQU RDS Operator 提供的 Fence 机制已经得到有效解决。Kubernetes 使我们站在巨人的肩膀上,从各大互联网公司的技术发展看,将编排和容器技术应用到持久化 workload 也是显见的趋势之一。但是,借用 Portworx CEO 的 Murli Thirumale 对 Kubenretes 的预测:Kubernetes 相当复杂。Kubernetes 被拥趸们冠以”优雅”的头衔,但优雅并不意味着简单。弦论是优雅的,但是理解它需要付出极大的努力。Kubernetes一样,使用 Kubernetes 构建和运行应用程序并不是一个简单的命题。Kubernetes iscomplicated. Kubernetes is oftendescribed as elegant by enthusiasts. But its elegance doesn’t make itsimple. String theory is elegant, butunderstanding it with anything except the most imprecise analogies takes a lotof effort. Kubernetes is the same. Using Kubernetes to build and run anapplication is not a straightforward proposition.
2018年1月19号参加了阿里巴巴双十一数据库技术峰会,见到了好多老同事(各位研究员、资深专家),也了解到业界最新的数据库技术发展趋势:数据库容器化作为下一代数据库基础架构
基于编排架构管理容器化数据库
采用计算存储分离架构
这和我们在私有 RDS 上的技术选型不谋而合,尤其是计算存储分离架构。
在我们看来, 其最大优势在于:计算资源 / 存储资源独立扩展,架构更清晰,部署更容易。
将有状态的数据下沉到存储层,Scheduler 调度时,无需感知计算节点的存储介质,只需调度到满足计算资源要求的 Node,数据库实例启动时,只需在分布式文件系统挂载mapping volume 即可,可以显著的提高数据库实例的部署密度和计算资源利用率。
以阿里巴巴为例,考虑到今时今日它的规模,如果能够实现数据库服务的离线(ODPS)/在线集群的混合部署,意义极其重大。关键问题在于,离线(ODPS)计算和在线计算对实时性要求不同,硬件配置也不同,尤其是本地存储介质:离线(ODPS)以机械磁盘为主
在线以 SSD / Flash 为主
如果采用本地存储作为数据库实例的存储介质,试想一下,一个 Storage Qos 要求是 Flash 的数据库实例无法调度到离线计算集群,哪怕离线计算集群 CPU,Memory 有大量空闲。计算存储分离为实现离线(ODPS)/在线集群的混合部署提供了可能。结合 Kubernetes,Docker和 MySQL,进一步细化架构图, 如下图所示 :
同时,这套架构也带给我们更加简单、通用,高效的 High Availability 方案。当集群中某个 Node不可用后,借助 Kubernetes 的原生组件Node Controller, Scheduler 和原生 API Statefulset 即可将数据库实例调度到其他可用节点,以实现数据库实例的高可用。
一切是多么的美好,是不是可以得到这个结论:借助 Kubernetes 的原生组件NodeController,Scheduler和原生API Statefulset, 加上计算存储分离架构,并将成熟的分布式文件系统集成到 Kubernetes 存储系统,就能提供私有RDS服务。之前我们也是这么想的,直到遇到 “Split-Brain” 问题(也即是本文的主题)。回到上面的 High Availability 方案。当集群中某个 Node不可用后,借助Kubernetes 的原生组件Node Controller,Scheduler 和原生 API Statefulset 即可将数据库实例调度到其他可用节点,以实现数据库实例的高可用。判定 Node 不可用将是后续触发 Failover 动作的关键。所以这里需要对节点状态的判定机制稍作展开:Kubelet 借助 API Server 定期(node-status-update-frequency)更新 etcd 中对应节点的心跳信息
Controller Manager 中的 Node Controller 组件定期(node-monitor-period)轮询 ETCD中节点的心跳信息
如果在周期 (node-monitor-grace-period) 内,心跳更新丢失, 该节点标记为 Unknown(ConditionUnknown)
如果在周期 (pod-eviction-timeout) 内,心跳更新持续丢失, Node Controller 将会触发集群层面的驱逐机制
Scheduler 将 Unknown 节点上的所有数据库实例调度到其他健康(Ready)节点
访问架构图如下所示:
补充一句,借助 ETCD 集群的高可用强一致,得以保证 Kubernetes 集群元信息的一致性:ETCD基于 Raft 算法实现
Raft算法是一种基于消息传递(state machine replicated)且具有高度容错(fault tolerance)特性的一致性算法(consensusalgorithm)
Raft是大名鼎鼎的 Paxos 的简化版本
如果对于 Raft 算法的实现有兴趣,可以看看https://github.com/goraft/raft
所有感兴趣一致性算法的同学,都值得花精力学习。基于 goraft/raft,我实现了Network Partition Failures/Recovery TestCase,收获不小。看上去合理的机制会给我们带来两个问题,问题一:无法判定节点真实状态心跳更新是判断节点是否可用的依据。但是,心跳更新丢失是无法判定节点真实状态的 (Kubernetes 中将节点标记为 Condition Unknown 也说明了这点)。Node 可能仅仅是网络问题,CPU 繁忙,“假死”, Kubelet bug 等原因导致心跳更新丢失,但节点上的数据库实例还在运行中。问题二:缺乏有效的 Fence 机制在这个情况下,借助 Kubernetes 的原生组件 Node Controller,Scheduler 和原生 API Statefulset 实现的 Failover, 将数据库实例从 Unknown 节点驱逐到可用节点,但对原 Unknown节点不做任何操作。这种“软驱逐”,将会导致新旧两个数据库实例同时访问同一份数据文件。
发生 “Split-Brain” 导致 Data Corruption.数据丢失,损失无法弥补。下面是枯燥的故障复现,通过日志和代码分析驱逐的工作机制,总结 “Split-Brain” 过程。测试过程使用 Statefulset 创建 MySQL 单实例 gxr-oracle-statefulset (这是一个 Oracle DBA 取的名字,原谅他)
Scheduler 将 MySQL 单实例调度到集群中的节点 “k8s-node3”
通过 sysbench 对该实例制造极高的负载,k8s-node3” load 飙升,致“k8s-node3” 上的Kubelet 无法跟 API Server 通讯, 并开始报错
NodeController 启动驱逐
Statefulset 发起重建
Scheduler 将 MySQL 实例调度到 “k8s-node1” 上
新旧 MySQL 实例访问同一个 Volume
数据文件被写坏,旧MySQL实例都报错, 并无法启动
测试参数kube-controller-manager 启动参数
kubelet 启动参数
基于日志,个事件流如下:时间点 December 1st 2017,10:18:05.000 (最后一次更新成功应该是 10:17:42.000)节点 (k8s-node3) 启动数据库压力测试,以模拟该节点“假死”,kubelet 跟 API Server 出现心跳丢失。
kubelet 日志报错,法通过 API Server 更新 k8s-node3 状态。Kubelet 细节如下:
通过 API Server 更新集群信息
if kl.kubeClient != nil { //Start syncing node status immediately, this may set up things the runtime needsto run. gowait.Until(kl.syncNodeStatus, kl.nodeStatusUpdateFrequency, wait.NeverStop)}
定期(node Status Update Frequency)更新对应节点状态
nodeStatusUpdateFrequency 默认时间为 10 秒, 测试时设置的是8sobj.NodeStatusUpdateFrequency =metav1.Duration{Duration: 10 * time.Second}
更新如下信息:
func (kl *Kubelet) defaultNodeStatusFuncs()[]func(*v1.Node) error { //initial set of node status update handlers, can be modified by Option's withoutError := func(f func(*v1.Node)) func(*v1.Node) error { return func(n *v1.Node) error { f(n) return nil } } return []func(*v1.Node) error{ kl.setNodeAddress, withoutError(kl.setNodeStatusInfo), withoutError(kl.setNodeOODCondition), withoutError(kl.setNodeMemoryPressureCondition), withoutError(kl.setNodeDiskPressureCondition), withoutError(kl.setNodeReadyCondition), withoutError(kl.setNodeVolumesInUseStatus), withoutError(kl.recordNodeSchedulableEvent), }}
通过 kubectl 可以获得节点的信息:
时间点 December 1st 2017, 10:18:14.000
· NodeController 发现 k8s-node3 的状态有32s 没有发生更新。 ○ ready/ outofdisk / diskpressure / memorypressue condition
将该节点状态更新为 UNKNOWN:
每隔 NodeMonitorPeriod 继续节点状态是否有更新:
定期(NodeMonitorPeriod)查看一次节点状态
// Incorporate the results of node statuspushed from kubelet to master.go wait.Until(func() { iferr := nc.monitorNodeStatus(); err != nil { glog.Errorf("Error monitoring node status: %v", err) }}, nc.nodeMonitorPeriod, wait.NeverStop)
NodeMonitorPeriod默认 5秒, 测试时4s
NodeMonitorPeriod: metav1.Duration{Duration: 5 * time.Second},
当超过 NodeMonitorGracePeriod 时间后, 节点状态没有更新将节点状态设置成 unknown
ifnc.now().After(savedNodeStatus.probeTimestamp.Add(gracePeriod)) { //NodeReady condition was last set longer ago than gracePeriod, so update it toUnknown //(regardless of its current value) in the master. ifcurrentReadyCondition == nil { glog.V(2).Infof("node %v is never updated by kubelet",node.Name) node.Status.Conditions = append(node.Status.Conditions,v1.NodeCondition{ Type: v1.NodeReady, Status: v1.ConditionUnknown, Reason: "NodeStatusNeverUpdated", Message: fmt.Sprintf("Kubelet never posted node status."), LastHeartbeatTime: node.CreationTimestamp, LastTransitionTime: nc.now(), }) }else { glog.V(4).Infof("node %v hasn't been updated for %+v. Last readycondition is: %+v", node.Name, nc.now().Time.Sub(savedNodeStatus.probeTimestamp.Time),observedReadyCondition) if observedReadyCondition.Status != v1.ConditionUnknown { currentReadyCondition.Status = v1.ConditionUnknown currentReadyCondition.Reason = "NodeStatusUnknown" currentReadyCondition.Message = "Kubelet stopped posting nodestatus." // LastProbeTime is the last time we heard from kubelet. currentReadyCondition.LastHeartbeatTime =observedReadyCondition.LastHeartbeatTime currentReadyCondition.LastTransitionTime = nc.now() } }时间点 December 1st 2017, 10:19:42.000刚好过去 podEvictionTimeout , 将该节点添加到驱逐队列中:
在podEvictionTimeout 后,为该节点上 pods 需要开始驱逐
if observedReadyCondition.Status ==v1.ConditionUnknown { ifnc.useTaintBasedEvictions { // We want to update the taint straight away if Node is already taintedwith the UnreachableTaint if taintutils.TaintExists(node.Spec.Taints, NotReadyTaintTemplate) { taintToAdd := *UnreachableTaintTemplate if !util.SwapNodeControllerTaint(nc.kubeClient,[]*v1.Taint{&taintToAdd}, []*v1.Taint{NotReadyTaintTemplate}, node) { glog.Errorf("Failed to instantly swap UnreachableTaint toNotReadyTaint. Will try again in the next cycle.") } } else if nc.markNodeForTainting(node) { glog.V(2).Infof("Node %v is unresponsive as of %v. Adding it to theTaint queue.", node.Name, decisionTimestamp, ) } }else { ifdecisionTimestamp.After(nc.nodeStatusMap[node.Name].probeTimestamp.Add(nc.podEvictionTimeout)){ if nc.evictPods(node) { glog.V(2).Infof("Node is unresponsive. Adding Pods on Node %s toeviction queues: %v is later than %v + %v", node.Name, decisionTimestamp, nc.nodeStatusMap[node.Name].readyTransitionTimestamp, nc.podEvictionTimeout-gracePeriod, ) } } }}
放到驱逐数组中
// evictPods queues an eviction for theprovided node name, and returns false if the node is already// queued for eviction.func (nc *Controller) evictPods(node*v1.Node) bool { nc.evictorLock.Lock() defer nc.evictorLock.Unlock() return nc.zonePodEvictor[utilnode.GetZoneKey(node)].Add(node.Name,string(node.UID))}时间点 December 1st 2017, 10:19:42.000 开始驱逐:
驱逐 goroutine
if nc.useTaintBasedEvictions { //Handling taint based evictions. Because we don't want a dedicated logic inTaintManager for NC-originated //taints and we normally don't rate limit evictions caused by taints, we need torate limit adding taints. gowait.Until(nc.doNoExecuteTaintingPass, scheduler.NodeEvictionPeriod,wait.NeverStop)} else { //Managing eviction of nodes: //When we delete pods off a node, if the node was not empty at the time we then //queue an eviction watcher. If we hit an error, retry deletion. gowait.Until(nc.doEvictionPass, scheduler.NodeEvictionPeriod, wait.NeverStop)}
通过删除 pods 的方式驱逐
func (nc *Controller) doEvictionPass() { nc.evictorLock.Lock() defer nc.evictorLock.Unlock() fork := range nc.zonePodEvictor { // Function should return 'false' and a time after which it should beretried, or 'true' if it shouldn't (it succeeded). nc.zonePodEvictor[k].Try(func(value scheduler.TimedValue) (bool,time.Duration) { node, err := nc.nodeLister.Get(value.Value) if apierrors.IsNotFound(err) { glog.Warningf("Node %v no longer present in nodeLister!",value.Value) } else if err != nil { glog.Warningf("Failed to get Node %v from the nodeLister: %v",value.Value, err) } else { zone := utilnode.GetZoneKey(node) evictionsNumber.WithLabelValues(zone).Inc() } nodeUID, _ := value.UID.(string) remaining, err := util.DeletePods(nc.kubeClient, nc.recorder,value.Value, nodeUID, nc.daemonSetStore) if err != nil { utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to evict node %q:%v", value.Value, err)) return false, 0 } if remaining { glog.Infof("Pods awaiting deletion due to Controllereviction") } return true, 0 }) }}时间点 December 1st 2017, 10:19:42.000 statefulsetcontroller 发现 default/gxr1-oracle-statefulset 状态异常
时间点 December 1st 2017, 10:19:42.000 scheduler 将 pod 调度到 k8s-node1
这样旧的 MySQL 实例在 k8s-node3 上,ubernetes 又将新的实例调度到 k8s-node1.两个数据库实例写同一份数据文件, data corruption. 两个节点都无法启动。老实例启动报错,日志为:2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] mysqld(mysqld 5.7.19-log) starting as process 963 ...2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:PUNCH HOLE support available2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Mutexes and rw_locks use GCC atomic builtins2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Uses event mutexes2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: GCCbuiltin __atomic_thread_fence() is used for memory barrier2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Compressed tables use zlib 1.2.32017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Using Linux native AIO2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Number of pools: 12017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Using CPU crc32 instructions2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Initializing buffer pool, total size = 3.25G, instances = 2, chunk size = 128M2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Completed initialization of buffer pool2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Ifthe mysqld execution user is authorized, page cleaner thread priority can bechanged. See the man page of setpriority().2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Highest supported file format is Barracuda.2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Logscan progressed past the checkpoint lsn 4068223232017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Doing recovery: scanned up to log sequence number 4068231902017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Database was not shutdown normally!2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB:Starting crash recovery.2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Starting an apply batch of log records to the database...InnoDB: Progress in percent: 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 992017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Apply batch completed2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Last MySQL binlog file position 0 428730, file name mysql-bin.0000042017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Removed temporary tablespace data file: "ibtmp1"2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Creating shared tablespace for temporary tables2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Setting file './ibtmp1' size to 12 MB. Physically writing the file full; Pleasewait ...2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:File './ibtmp1' size is now 12 MB.2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: 96redo rollback segment(s) found. 96 redo rollback segment(s) are active.2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: 32non-redo rollback segment(s) are active.2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB:Waiting for purge to start2017-12-01 10:19:47 0x7fcb08928700 InnoDB: Assertion failure in thread140509998909184 in file trx0purge.cc line 168InnoDB: Failing assertion:purge_sys->iter.trx_no <= purge_sys->rseg->last_trx_noInnoDB: We intentionally generate a memorytrap.InnoDB: Submit a detailed bug report tohttp://bugs.mysql.com.InnoDB: If you get repeated assertionfailures or crashes, evenInnoDB: immediately after the mysqld startup,there may beInnoDB: corruption in the InnoDBtablespace. Please refer toInnoDB:http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/forcing-innodb-recovery.htmlInnoDB: about forcing recovery.10:19:47 5669 - mysqld got signal 6 ;以上问题通过 WOQU RDS Operator 提供的 Fence 机制已经得到有效解决。Kubernetes 使我们站在巨人的肩膀上,从各大互联网公司的技术发展看,将编排和容器技术应用到持久化 workload 也是显见的趋势之一。但是,借用 Portworx CEO 的 Murli Thirumale 对 Kubenretes 的预测:Kubernetes 相当复杂。Kubernetes 被拥趸们冠以”优雅”的头衔,但优雅并不意味着简单。弦论是优雅的,但是理解它需要付出极大的努力。Kubernetes一样,使用 Kubernetes 构建和运行应用程序并不是一个简单的命题。Kubernetes iscomplicated. Kubernetes is oftendescribed as elegant by enthusiasts. But its elegance doesn’t make itsimple. String theory is elegant, butunderstanding it with anything except the most imprecise analogies takes a lotof effort. Kubernetes is the same. Using Kubernetes to build and run anapplication is not a straightforward proposition.
相关文章推荐
- 容器化RDS—计算存储分离架构下的“Split-Brain”
- 容器化RDS——计算存储分离架构下的“Split-Brain”
- 容器化RDS|计算存储分离架构下的IO优化
- 容器化RDS|计算存储分离架构下的 IO 优化
- 容器化RDS|计算存储分离架构下的 IO 优化
- 容器化RDS|计算存储分离架构下的 IO 优化
- 容器化RDS|计算存储分离架构下的 IO 优化
- 容器化RDS|计算存储分离架构下的IO优化
- [置顶] 容器化RDS:计算存储分离还是本地存储?
- 容器化RDS|计算存储分离 or 本地存储?
- 2017双11核心技术揭秘—阿里数据库计算存储分离与离在线混布
- 计算密集型分布式内存存储和运算平台架构
- 计算密集型分布式内存存储和运算平台架构
- 容器化RDS:计算存储分离还是本地存储?
- 2017双11技术揭秘—阿里数据库计算存储分离与离在线混布
- 计算与存储分离实践—swift消息系统
- 存储与计算分离:OSS构建表_+_计算引擎对接
- 6月2日云栖精选夜读:存储与计算分离:OSS构建表_+_计算引擎对接
- [置顶] Hadoop实战演练:搜索数据分析----计算结果存储到Mysql(3)
