课程设计-多种排序方式
2018-02-10 10:56
218 查看
各种排序方式的使用
一、排序的简单介绍
排序算法的稳定性:稳定性是指能保证排序前2个相等的数其在序列的前后位置顺序和排序后它们两个的前后位置顺序相同。例如,a1、a2的值相等,排序前 a1在a2位置前,排序后a1还是在a2位置前,则算法稳定。
下面举例时,都按从小到大排序。(1)直接插入排序 (Straight Insertion Sort)
时间复杂度 O(n^2) 空间复杂度 O(1) 稳定将要排序的元素放入结构体数组tmp[0...n-1]中,排序过程中,数组被分为子区间tmp[0...i-1]和tmp[i...n-1],其中前一个子区间是有序区;后一个子区间是无序区,i每加1时,要求tmp[i]插入到tmp[0...i-1]中适当的位置上,tmp[0...i]变为有序区。原始序列 4 7 3 9 6
第一步(4) (7 3 9 6)//第一个括号中序列为有序,第二个括号中无序
第二步(4 7) (3 9 6)//取无序区中第一个元素7,for循环有序区,查找合适的位置插入(此处可用二分查找优化)
第三步(3 4 7)(9 6)//取无序区中第一个元素3,for循环有序区,查找合适的位置插入
第四步(3 4 7 9)(6)//取无序区中第一个元素9,同上
第五步(3 4 6 7 9)排序完成(2)希尔排序(Shell's Sort)
时间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 空间复杂度 O(1) 不稳定
先取一个小于n的整数d1作为第一个增量,把文件的全部记录分组。所有距离为d1的倍数的记录放在同一个组中。先在各组内进行直接插入排序;然后,取第二个增量d2<d1重复上述的分组和排序(一般d2=d1/2),直至所取的增量 =1( < …<d2<d1),即所有记录放在同一组中进行直接插入排序为止。
下列图片中:
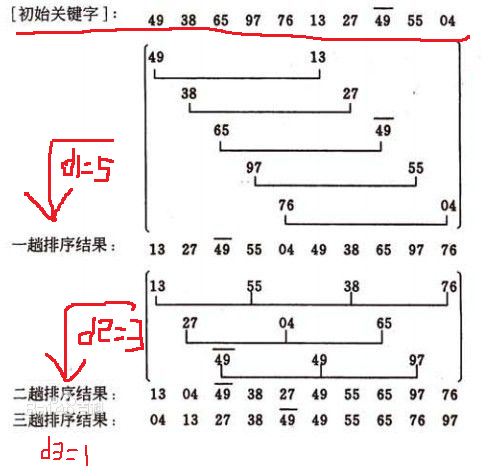
(3)冒泡排序
时间复杂度 O(n^2) 空间复杂度 O(1) 稳定
在tmp[0...n]中,通过无序区相邻元素间的交换,使得无序区的最大元素下沉至有序区。第一次排序中无序区的最大元素到达位置tmp[n-1]的位置,下一次排序中,tmp[n-2]的位置上会填入tmp[0...n-2]中的最大元素,以此类推,知道i=n-1时程序截止。原始序列 4 7 3 9 6
第一趟排序 4 3 7 6 9 //4比7小,故不交换位置。7比3大,则交换位置(4 3 7 9 6)。7比9小,故不交换位置。9比6大,则交换位置(4 3 7 6 9)。
第二趟排序 3 4 6 7 9 //4比3大,则交换位置(3 4 7 9 6)。4比7小,故不交换位置。7比6大,则交换位置(3 4 6 7 9)。
第三趟排序3 4 6 7 9 //3比4小,则交换位置。4比6小,则交换位置。
第四趟排序3 4 6 7 9 //3比4小,则交换位置。
第五趟排序3 4 6 7 9 //排序完成(4)快速排序(Quick Sort)时间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 空间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 不稳定
排序开始时,将第一个元素作为关键字,大于关键字的数字放在关键字后,小于关键字的数字放在关键字前(无序),则关键字归位,这种算法是以递归的方式写出来的。每次在排列完当前长度数组的关键字后,分别排列他的左区间和右区间,直到每个子区间内只剩一个关键字为止。有一点需要注意例如 6 2 7 3 8 9第一趟排序以后是3 2 7 6 8 9 并不是 2 3 6 7 8 9,这是由算法的代码决定的。在学习时,建议看着代码自己手动模拟一遍。可以看百度百科中的排列演示(5)直接选择排序时间复杂度 O(n^2) 空间复杂度 O(1) 不稳定
排序开始时,有数组tmp[0...n-1],其基本思想:第一次从R[0]~R[n-1]中选取最小值,与R[0]交换,第二次从R[1]~R[n-1]中选取最小值,与R[1]交换,....,第i次从R[i-1]~R[n-1]中选取最小值,与R[i-1]交换,.....,第n-1次从R[n-2]~R[n-1]中选取最小值,与R[n-2]交换, 总共通过n-1次,得到一个按排序码从小到大排列的有序序列·
第一趟排序
在待排序列式(4 7 3 9 6)中最小的是3,3与小标为0的元素交换,待排序列式(4 7 9 6)
第二趟排序
在待排序列式(4 7 9 6)中最小的是4,4与小标为1的元素交换,待排序列式(7 9 6)
第三趟排序
在待排序列式(7 9 6)中最小的是6,6与小标为2的元素交换,待排序列式(9 7)
第四趟排序
在待排序列式(9 7)中最小的是7,7与小标为3的元素交换,待排序列式(9)
第五趟排序
排序完成
(6)堆排序时间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 空间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 不稳定
堆分为大根堆和小根堆。大根堆的要求是每个节点的值都不大于其父节点的值,即A[PARENT[i]] >= A[i]。
小根堆的要求是任一非终端节点的值均不大于其左子节点和右子节点的值,即A[PARENT[i]] <= A[i]。用大根堆排序的基本思想,先将初始文件R[1..n]建成一个大根堆,此堆为初始的无序区,再将关键字最大的记录R[1](即堆顶)和无序区的最后一个记录R
交换,由此得到新的无序区R[1..n-1]和有序区R
,且满足R[1..n-1].keys≤R
.key,由于交换后新的根R[1]可能违反堆性质,故应将当前无序区 R[1..n-1]调整为堆。然后再次将R[1..n-1]中关键字最大的记录R[1]和该区间的最后一个记录R[n-1]交换,由此得到新的无序区 R[1..n-2]和有序区R[n-1..n],且仍满足关系R[1..n-2].keys≤R[n-1..n].keys,同样要将R[1..n-2] 调整为堆。……直到无序区只有一个元素为止。
(7)归并排序时间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 空间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 稳定
归并排序是分治法思想运用的一个典范。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。其主要算法操作:首先,将n个元素分成两个含n/2元素的子序列,然后用归并排序将两个子序列递归排序(最后可以将整个原序列分解成n个子序列),最后合并两个已排序好的序列。原始序列 4 3 7 9 6
排列下划线的数字
第一趟排序 3 4 7 9 6
第二趟排序 3 4 6 7 9
(8)二叉排序树时间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 空间复杂度 O(n) 稳定
二叉排序树具有下列性质:(1)若左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;(2)若右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;(3)左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树;(4)没有键值相等的节点。查找基本原理:若根结点的关键字值等于查找的关键字,成功。否则,若小于根结点的关键字值,递归查左子树。若大于根结点的关键字值,递归查右子树。若子树为空,查找不成功。
二、文件打开方式
fopen,fclose
TXT文件的打开方式。待排序的内容在user.txt。user.txt中存放了120万余条用户编号(user_id)、密码(password)的记录。每行一条记录,user_id和password中间为TAB分隔(即C语言中的\t)。user_id的范围为:1~1,230,000
三、代码
Shell's Sort别 名缩小增量排序类 型插入排序时间复杂度O(n^1.3)空间复杂度O(1)Shell's Sort
一、排序的简单介绍
排序算法的稳定性:稳定性是指能保证排序前2个相等的数其在序列的前后位置顺序和排序后它们两个的前后位置顺序相同。例如,a1、a2的值相等,排序前 a1在a2位置前,排序后a1还是在a2位置前,则算法稳定。
下面举例时,都按从小到大排序。(1)直接插入排序 (Straight Insertion Sort)
时间复杂度 O(n^2) 空间复杂度 O(1) 稳定将要排序的元素放入结构体数组tmp[0...n-1]中,排序过程中,数组被分为子区间tmp[0...i-1]和tmp[i...n-1],其中前一个子区间是有序区;后一个子区间是无序区,i每加1时,要求tmp[i]插入到tmp[0...i-1]中适当的位置上,tmp[0...i]变为有序区。原始序列 4 7 3 9 6
第一步(4) (7 3 9 6)//第一个括号中序列为有序,第二个括号中无序
第二步(4 7) (3 9 6)//取无序区中第一个元素7,for循环有序区,查找合适的位置插入(此处可用二分查找优化)
第三步(3 4 7)(9 6)//取无序区中第一个元素3,for循环有序区,查找合适的位置插入
第四步(3 4 7 9)(6)//取无序区中第一个元素9,同上
第五步(3 4 6 7 9)排序完成(2)希尔排序(Shell's Sort)
时间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 空间复杂度 O(1) 不稳定
先取一个小于n的整数d1作为第一个增量,把文件的全部记录分组。所有距离为d1的倍数的记录放在同一个组中。先在各组内进行直接插入排序;然后,取第二个增量d2<d1重复上述的分组和排序(一般d2=d1/2),直至所取的增量 =1( < …<d2<d1),即所有记录放在同一组中进行直接插入排序为止。
下列图片中:

(3)冒泡排序
时间复杂度 O(n^2) 空间复杂度 O(1) 稳定
在tmp[0...n]中,通过无序区相邻元素间的交换,使得无序区的最大元素下沉至有序区。第一次排序中无序区的最大元素到达位置tmp[n-1]的位置,下一次排序中,tmp[n-2]的位置上会填入tmp[0...n-2]中的最大元素,以此类推,知道i=n-1时程序截止。原始序列 4 7 3 9 6
第一趟排序 4 3 7 6 9 //4比7小,故不交换位置。7比3大,则交换位置(4 3 7 9 6)。7比9小,故不交换位置。9比6大,则交换位置(4 3 7 6 9)。
第二趟排序 3 4 6 7 9 //4比3大,则交换位置(3 4 7 9 6)。4比7小,故不交换位置。7比6大,则交换位置(3 4 6 7 9)。
第三趟排序3 4 6 7 9 //3比4小,则交换位置。4比6小,则交换位置。
第四趟排序3 4 6 7 9 //3比4小,则交换位置。
第五趟排序3 4 6 7 9 //排序完成(4)快速排序(Quick Sort)时间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 空间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 不稳定
排序开始时,将第一个元素作为关键字,大于关键字的数字放在关键字后,小于关键字的数字放在关键字前(无序),则关键字归位,这种算法是以递归的方式写出来的。每次在排列完当前长度数组的关键字后,分别排列他的左区间和右区间,直到每个子区间内只剩一个关键字为止。有一点需要注意例如 6 2 7 3 8 9第一趟排序以后是3 2 7 6 8 9 并不是 2 3 6 7 8 9,这是由算法的代码决定的。在学习时,建议看着代码自己手动模拟一遍。可以看百度百科中的排列演示(5)直接选择排序时间复杂度 O(n^2) 空间复杂度 O(1) 不稳定
排序开始时,有数组tmp[0...n-1],其基本思想:第一次从R[0]~R[n-1]中选取最小值,与R[0]交换,第二次从R[1]~R[n-1]中选取最小值,与R[1]交换,....,第i次从R[i-1]~R[n-1]中选取最小值,与R[i-1]交换,.....,第n-1次从R[n-2]~R[n-1]中选取最小值,与R[n-2]交换, 总共通过n-1次,得到一个按排序码从小到大排列的有序序列·
| 下标 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 原始序列 | 4 | 7 | 3 | 9 | 6 |
在待排序列式(4 7 3 9 6)中最小的是3,3与小标为0的元素交换,待排序列式(4 7 9 6)
| 下标 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 原始序列 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 9 | 6 |
在待排序列式(4 7 9 6)中最小的是4,4与小标为1的元素交换,待排序列式(7 9 6)
| 下标 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 原始序列 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 9 | 6 |
在待排序列式(7 9 6)中最小的是6,6与小标为2的元素交换,待排序列式(9 7)
| 下标 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 原始序列 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 7 |
在待排序列式(9 7)中最小的是7,7与小标为3的元素交换,待排序列式(9)
| 下标 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 原始序列 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 9 |
排序完成
| 下标 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 原始序列 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 9 |
堆分为大根堆和小根堆。大根堆的要求是每个节点的值都不大于其父节点的值,即A[PARENT[i]] >= A[i]。
小根堆的要求是任一非终端节点的值均不大于其左子节点和右子节点的值,即A[PARENT[i]] <= A[i]。用大根堆排序的基本思想,先将初始文件R[1..n]建成一个大根堆,此堆为初始的无序区,再将关键字最大的记录R[1](即堆顶)和无序区的最后一个记录R
交换,由此得到新的无序区R[1..n-1]和有序区R
,且满足R[1..n-1].keys≤R
.key,由于交换后新的根R[1]可能违反堆性质,故应将当前无序区 R[1..n-1]调整为堆。然后再次将R[1..n-1]中关键字最大的记录R[1]和该区间的最后一个记录R[n-1]交换,由此得到新的无序区 R[1..n-2]和有序区R[n-1..n],且仍满足关系R[1..n-2].keys≤R[n-1..n].keys,同样要将R[1..n-2] 调整为堆。……直到无序区只有一个元素为止。
(7)归并排序时间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 空间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 稳定
归并排序是分治法思想运用的一个典范。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。其主要算法操作:首先,将n个元素分成两个含n/2元素的子序列,然后用归并排序将两个子序列递归排序(最后可以将整个原序列分解成n个子序列),最后合并两个已排序好的序列。原始序列 4 3 7 9 6
排列下划线的数字
第一趟排序 3 4 7 9 6
第二趟排序 3 4 6 7 9
(8)二叉排序树时间复杂度 O(nlog_{2}) 空间复杂度 O(n) 稳定
二叉排序树具有下列性质:(1)若左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;(2)若右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;(3)左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树;(4)没有键值相等的节点。查找基本原理:若根结点的关键字值等于查找的关键字,成功。否则,若小于根结点的关键字值,递归查左子树。若大于根结点的关键字值,递归查右子树。若子树为空,查找不成功。
二、文件打开方式
fopen,fclose
TXT文件的打开方式。待排序的内容在user.txt。user.txt中存放了120万余条用户编号(user_id)、密码(password)的记录。每行一条记录,user_id和password中间为TAB分隔(即C语言中的\t)。user_id的范围为:1~1,230,000
三、代码
#include <map>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef struct node
{
char pass[15];
int count;
}Node;//这个是用于(2)里面对密码的排序
struct no {
int num;
char pw[15];
struct no *next;
};//用于给(3)存储user_id
struct no *Crea();
struct no *Insert(struct no *head, struct no *p);
void Des(struct no *head);
void Print(struct no *head);
void find(struct no *head);
//以上为(3)用到的函数,提前声明先
typedef struct ser
{
int user_num;
char pw[15];
struct ser *lchild,*rchild;
}*User;//这个是用于(4)里面的二叉排序树的
struct ppp
{
int id;
char pw[15];
}user_ID[1230000];
void quick_sort(Node s[], int l, int r)
{
if (l < r)
{
int i = l, j = r;
Node x = s[l];
while (i < j)
{
while(i < j && s[j].count < x.count)
j--;
if(i < j)
s[i++] = s[j];
while(i < j && s[i].count > x.count)
i++;
if(i < j)
s[j--] = s[i];
}//退出while
s[i] = x;
quick_sort(s, l, i - 1);
quick_sort(s, i + 1, r);
}
}
void sift(Node r[], int low, int high)
{
int i = low;
int j = 2 * i;
Node temp = r[i];
while(j <= high)
{
if(j < high && r[j].count > r[j + 1].count)
{
j++;
}
if(temp.count > r[j].count)
{
r[i] = r[j];
i = j;
j = 2 * i;
}
else break;
}
r[i] = temp;
}
//将有二个有序数列a[first...mid]和a[mid...last]合并。
void mergearray(Node a[], int first, int mid, int last, Node temp[])
{
int i = first, j = mid + 1;
int m = mid, n = last;
int k = 0;
while (i <= m && j <= n)
{
if (a[i].count > a[j].count)
temp[k++] = a[i++];
else
temp[k++] = a[j++];
}
while (i <= m)
temp[k++] = a[i++];
while (j <= n)
temp[k++] = a[j++];
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
a[first + i] = temp[i];
}
void mergesort(Node a[], int first, int last, Node temp[])
{
if (first < last)
{
int mid = (first + last) / 2;
mergesort(a, first, mid, temp); //使左边有序
mergesort(a, mid + 1, last, temp); //使右边有序
mergearray(a, first, mid, last, temp); //再将二个有序数列合并
}
}
void beginsort()
{
FILE *fp;//已检验password共有37318不同的数据
clock_t start;
Node tem[38000];
Node tmp[38000];
if((fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\password.txt","r"))==NULL)
{
printf("Please make sure the input file exist\n");//如果不存在输出提示
exit(0);
}
int k = 0;
while(fscanf(fp,"%s\t%d\n",tem[k].pass,&tem[k].count)!=EOF)
{
tmp[k] = tem[k];
k++;
}
fclose(fp);//关闭文件password.txt
//开始直接插入排序
int j;
start = clock();//初始化时间
for(int i = 1; i < k; i++)
{
if(tmp[i].count > tmp[i-1].count)
{
Node temp = tmp[i];
for(j = i-1; j>=0 && tmp[j].count<temp.count; j--)
{
tmp[j+1] = tmp[j];
}
tmp[j+1] = temp;
}
}
printf("The cost time of straight insertion sort(zhi jie cha ru sort):\n%ldms\n",clock()-start);//直接插入插入排序结束
if((fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\straight_insertion_sort.txt","w"))==NULL) //判断文件是否存在,fp指向straight_insertion_sort.txt
{
fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\straight_insertion_sort.txt","w"); //如果文件不存在,新建一个文件
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
fprintf(fp,"%d\t%s\n",tmp[i].count,tmp[i].pass);
}
fclose(fp);
//开始希尔排序
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
tmp[i] = tem[i];//初始化tmp数组
}
start = clock();//初始化时间
for (int gap = k>>1; gap > 0; gap >>= 1)//开始希尔排序
{
for (int i = gap; i < k; i++)
{
Node temp = tmp[i];
for (j = i-gap; j >= 0 && tmp[j].count < temp.count; j -= gap)
{
tmp[j + gap] = tmp[j];
}
tmp[j + gap] = temp;
}
}
printf("The cost time of shell_sort(xi er sort):\n%ldms\n",clock()-start);//希尔排序结束
if((fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\shell_sort.txt","w"))==NULL) //判断文件是否存在,fp指向shell_sort
{
fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\shell_sort.txt","w"); //如果文件不存在,新建一个文件
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
fprintf(fp,"%d\t%s\n",tmp[i].count,tmp[i].pass);
}
fclose(fp);
//开始冒泡排序
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
tmp[i] = tem[i];//初始化tmp数组
}
start = clock();//初始化时间
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)//开始冒泡排序
{
for(j = i; j < k; j ++)
{
if(tmp[i].count < tmp[j].count)
{
Node temp = tmp[i];
tmp[i] = tmp[j];
tmp[j] = temp;
}
}
}
printf("The cost time of bubble sort(mao pao sort):\n%ldms\n",clock()-start);//冒泡插入排序结束
if((fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\bubble_sort.txt","w"))==NULL) //判断文件是否存在,fp指向shell_sort
{
fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\bubble_sort.txt","w"); //如果文件不存在,新建一个文件
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
fprintf(fp,"%d\t%s\n",tmp[i].count,tmp[i].pass);
}
//开始快速排序
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
tmp[i] = tem[i];//初始化tmp数组
}
start = clock();//初始化时间
quick_sort(tmp,0,k-1);
printf("The cost time of quick sort(kuai su sort):\n%ldms\n",clock()-start);//快速排序结束
if((fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\quick_sort.txt","w"))==NULL) //判断文件是否存在,fp指向shell_sort
{
fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\quick_sort.txt","w"); //如果文件不存在,新建一个文件
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
fprintf(fp,"%d\t%s\n",tmp[i].count,tmp[i].pass);
}
fclose(fp);
//开始直接选择排序
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
tmp[i] = tem[i];//初始化tmp数组
}
start = clock();//初始化时间
for(int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++)//开始直接选择排序
{
int x = i;
for(int j = i + 1; j < k; j++)
{
if (tmp[j].count > tmp[x].count)
{
x = j;
}
}
if(x != i)
{
Node temp = tmp[i];
tmp[i] = tmp[x];
tmp[x] = temp;
}
}
printf("The cost time of straight select sort(zhi jie xuan ze sort):\n%ldms\n", clock()-start);//直接选择排序结束
if((fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\straight_select_sort.txt","w"))==NULL) //判断文件是否存在,fp指向shell_sort
{
fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\straight_select_sort.txt","w"); //如果文件不存在,新建一个文件
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
fprintf(fp,"%d\t%s\n",tmp[i].count,tmp[i].pass);
}
fclose(fp);
//开始堆排序
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
tmp[i] = tem[i];//初始化tmp数组
}
start = clock();//初始化时间
for(int i = k / 2; i >= 1; i--)//开始堆排序
{
sift(tmp, i, k);
}
for(int i = k; i >= 2; i--)
{
Node temp = tmp[1];
tmp[1] = tmp[i];
tmp[i] = temp;
sift(tmp, 1, i - 1);
}
printf("The cost time of sift sort(dui sort):\n%ldms\n", clock()-start);//堆排序结束
if((fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\sift_sort.txt","w"))==NULL) //判断文件是否存在,fp指向shell_sort
{
fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\sift_sort.txt","w"); //如果文件不存在,新建一个文件
}
for(int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
fprintf(fp,"%d\t%s\n",tmp[i].count,tmp[i].pass);
}
fclose(fp);
//开始归并排序
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
tmp[i] = tem[i];//初始化tmp数组
}
start = clock();//初始化时间
Node *p = new Node[k];
mergesort(tmp,0,k-1,p);
printf("The cost time of merge sort (gui bing sort):\n%ldms\n",clock()-start);//归并排序结束
if((fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\merge_sort.txt","w"))==NULL) //判断文件是否存在,fp指向shell_sort
{
fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\merge_sort.txt","w"); //如果文件不存在,新建一个文件
}
int count20 = 0;
printf("The top twenty most used passwords and frequency:\n");
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
if(count20 < 20)
{
count20++;
printf("%s\t%d\n",tmp[i].pass,tmp[i].count);
}
fprintf(fp,"%d\t%s\n",tmp[i].count,tmp[i].pass);
}
fclose(fp);
delete[] p;
}
void insertBST(User &root, int key,char tt[])
{
User f,p = root;
f = p;
while(p)
{
f = p;
if(p->user_num < key)
p = p->rchild;
else p = p->lchild;
}
p = (struct ser*)malloc(sizeof(ser));
p->user_num = key;
p->lchild = p->rchild = NULL;
//strcpy(p->pw,tt);
if(f == NULL)
root = p;
else if(f->user_num < key)
f->rchild = p;
else f->lchild = p;
}
bool SearchBST(User root,int key)
{
while(root)
{
if(key == root->user_num)
return true;
else if(key > root->user_num)
root = root->rchild;
else root = root->lchild;
}
return false;
}
void deleteBST(User root)
{
if(root)
{
deleteBST(root->lchild); //释放左子树
deleteBST(root->rchild); //释放右子树
free(root); //释放根结点
}
}
void binary_sort_tree(int k)//k是有多少个user_ID
{
clock_t start,mid,end;
User root;
root = NULL;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
insertBST(root,user_ID[i].id,user_ID[i].pw);
//开始生成随机的2200的id
int randint[2030];
srand(unsigned(time(0)));
for(int i = 0; i < 2000; i++)
{
int tmp = rand();
randint[i] = (tmp*40+rand())%1230000;
}
for(int i = 2000; i < 2020; i++)
{
int tmp = rand();
randint[i] = (tmp*40+rand())%1230000 + 1230000;
}
//将产生的随机函数存入randint;
start = clock();
for(int i = 0; i < 2000; i++)
{
SearchBST(root,randint[i]);
/*if(SearchBST(root,randint[i]))
printf("1");
else printf("0\n");*/
//可以用来测试是否查找到了
}
mid = clock();
for(int i = 2000; i < 2020; i++)
{
SearchBST(root,randint[i]);
}
end = clock();
printf("The cost of binary_sort_tree to find 2000 userids(1~1230000)is:\n%ldms\n",mid-start);
printf("The cost of binary_sort_tree to find 20 userids(bigger than 1230000)is:\n%ldms\n",end-mid);
printf("The cost of binary_sort_tree to find 2020 userids is:\n%ldms\n",end-start);
deleteBST(root);
}
int halfsearch(int k,int tmp)
{
int mid,low,high;
low = 0;
high = k-1;
mid = (low+high)>>1;
while(low <= high)
{
mid = (low+high)>>1;
if(user_ID[mid].id == tmp)
return 1;
else if(user_ID[mid].id > tmp)
high = mid-1;
else low = mid+1;
}
return 0;
}
bool cmp(struct ppp a,struct ppp b)
{
if(a.id > b.id)
return true;
return false;
}
void half_interval_search(int k)
{
FILE *fp;
clock_t start,mid,end;
int flag;
if((fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\user_sorted.txt","w"))==NULL)
{
fp=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\user_sorted.txt","w");
}
sort(user_ID,user_ID+k,cmp);
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
fprintf(fp,"%d\t%s\n",user_ID[i].id,user_ID[i].pw);//写入文件user_sorted。txt
}
fclose(fp);
//开始生成随机的2200的id
int randint[2030];
srand(unsigned(time(0)));
for(int i = 0; i < 2000; i++)
{
int tmp = rand();
randint[i] = (tmp*40+rand())%1230000;
}
for(int i = 2000; i < 2020; i++)
{
int tmp = rand();
randint[i] = (tmp*40+rand())%1230000 + 1230000;
}
//将产生的随机函数存入randint
start = clock();
for(int i = 0; i < 2000; i++)
{
flag = halfsearch(k,randint[i]);
/*if(halfsearch(k,randint[i]))
printf("1");
else printf("0\n");
//可以用来测试是否查找到了*/
}
mid = clock();
for(int i = 2000; i < 2020; i++)
{
flag = halfsearch(k,randint[i]);
/*if(halfsearch(k,randint[i]))
printf("1");
else printf("0\n");*/
}
end = clock();
printf("The cost of half_interval_search to find 2000 userids(1~1230000)is:\n%ldms\n",mid-start);
printf("The cost of half_interval_search to find 20 userids(bigger than 1230000)is:\n%ldms\n",end-mid);
printf("The cost of half_interval_search to find 2020 userids is:\n%ldms\n",end-start);
}
void read()
{
struct no *head, *p;
head = Crea();
find(head);
Des(head);
}
struct no *Crea()
{
FILE *fp1;
struct no *head, *p;
int num;
char pass[15];
head = NULL;
if((fp1 = fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\user.txt", "r")) == NULL)
{
printf("NO OPEN!!!\n");
exit(0);
}
while(fscanf(fp1, "%d\t%s\n", &num, pass) != EOF)
{
p = (struct no*)malloc(sizeof(struct no));
strcpy(p->pw,pass);
p->num = num;
head = Insert(head, p);
}
fclose(fp1);
return head;
}
struct no *Insert(struct no *head, struct no *p)
{
struct no *ptr, *ptr1, *ptr2;
ptr2 = head;
ptr = p;
if(head == NULL)
{
head = ptr;
head->next = NULL;
}
else{
head = ptr;
ptr->next = ptr2;
}
return head;
}
void Des(struct no *head)
{
struct no *p, *ptr;
ptr = head;
p = head->next;
while(p != NULL)
{
free(ptr);
ptr = p;
p = p->next;
}
free(ptr);
}
void find(struct no *head)
{
struct no *ptr;
//开始生成随机的2200的id
int randint[2030];
srand(unsigned(time(0)));
for(int i = 0; i < 2000; i++)
{
int tmp = rand();
randint[i] = (tmp*40+rand())%1230000;
}
for(int i = 2000; i < 2020; i++)
{
int tmp = rand();
randint[i] = (tmp*40+rand())%1230000 + 1230000;
}
//将产生的随机函数存入randint
clock_t start, mid, end;
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("List is NULL! ! !\n");
return;
}
start = clock();
for(int i = 0; i < 2000; i++)
{
for(ptr = head; ptr != NULL;ptr = ptr->next)
{
if(ptr->num == randint[i])
{
break;
}
}
}
mid = clock();
printf("The cost of link_list to find 2000 userids(1~1230000)is: \n%dms\n",mid-start);
for(int i = 2000; i < 2020; i++)
{
for(ptr = head; ptr != NULL;ptr = ptr->next)
{
if(ptr->num == randint[i])
{
break;
}
}
}
end = clock();
printf("The cost of link_list to find 20 userids(bigger than 1230000)is: \n%dms\n", end-mid);
printf("The cost of lind_list to find 2020 userids is:\n%dms\n",end-start);
}
int main()
{
int hehe,k;
char user_Pass[15];
FILE *fp1,*fp2;
printf("Welcome to the home of A_Code_Mokey\nPlease enter the number 520\n");// 请忽视
while(scanf("%d",&hehe))
{
map<string,int> pass;
pass.clear();
if((fp1=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\user.txt","r"))==NULL) //判断文件是否存在,fp1指向user.txt
{
printf("Please make sure the input file exist\n");//如果不存在输出提示
exit(0);
}
if((fp2=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\password.txt","w"))==NULL) //判断文件是否存在,fp2指向passord.txt
{
fp2=fopen("D:\\A_Code_Mokey\\password.txt","w"); //如果文件不存在,新建一个文件
}
k = 0;
while (fscanf(fp1,"%d\t%s\n",&user_ID[k].id,user_Pass)!=EOF)//从文件读入usr_ID password
{
strcpy(user_ID[k].pw,user_Pass);
string user_Password(user_Pass);//强制类型转化,char 转化为 string,因为使用map<char*,int>会出现错误
pass[user_Password]++;
k++;//将user_id全部存入数组user-ID中
}
fclose(fp1); //关闭文件user.txt
fclose(fp1); //关闭文件password.txt
map<string,int>::iterator iter;
for(iter = pass.begin(); iter != pass.end(); iter++)//把统计密码的结果写入password.txt
{
string user_Password = iter->first;
const int len = user_Password.length();
char* user_Pass=new char [len+1];
strcpy(user_Pass,user_Password.c_str()); //制类型转化,string 转化为 char
fprintf(fp2, "%s\t%d\n", user_Pass,iter->second);//写入password.txt.
delete[] user_Pass;
}
/*到现在为止已经完成 (1)统计密码出现次数*/
beginsort();//让这个来完成(2)神圣的排序,嗯,就是这样
read();//链表存放查找(3)
binary_sort_tree(k);//二叉排序查找(4),k是有多少个user_ID
half_interval_search(k);//二分查找(5),k是有多少个user_ID
printf("GAME OVER\n");
}
return 0;
}Shell's Sort别 名缩小增量排序类 型插入排序时间复杂度O(n^1.3)空间复杂度O(1)Shell's Sort
相关文章推荐
- 多种方式的oracle排序
- 单例设计模式多种实现方式
- C#中排序的多种实现方式
- 大一的第一篇的C语言课程设计完成了,链表的选择排序
- 冒泡、快速、归并排序课程设计
- 支持多种登录方式的数据库设计
- java list对元素进行指定多个字段属性按多种排序方式进行排序
- 数据结构各种内部排序课程设计
- 数据结构课程设计----基数排序
- 架构设计之设计模式 (四) Java中多种方式实现单例模式
- 一个小小的课程设计 -- 对排序的总结
- 课程设计2--排序(Sort)
- 设计模式之生产者消费者模式的多种实现方式(java)
- 架构设计之设计模式 (四) Java中多种方式实现单例模式
- Storm的消息队列接入以及多种方式落地实例需求分析和设计
- 最新课程信息 - 课堂风格视频教程,中规中矩的教学思路设计和插诨打科的讲解方式
- 课程设计:混合数据排序
- 掌握多种排序方式
- 多种方式登陆模块设计
- 数据结构课程设计-通讯录管理系统c++版(顺序表存储,折半查找,递增排序)
