ASP.NET MVC中Controller与View之间的传值
2018-02-06 21:19
375 查看
一、 Controller向View传递数据
1. 使用ViewData传递数据
Control:ViewData["Message_ViewData"] = " Hello ViewData!";
View中读取Controller中定义的ViewData数据
@ViewData["Message_ViewData"]
js中读取ViewData中数据
<script type="text/javascript"> var viewData = '@ViewData["Message_ViewData"]'; </script>
2. 使用ViewBag传递数据
Control:ViewBag.Message_ViewBag = " Hello ViewBag!";
View中读取Controller中定义的ViewData数据
@ViewBag.Message_ViewBag
js中读取ViewBag中数据
<script type="text/javascript"> var viewBag = '@ViewBag.Message_ViewBag'; </script>
3. 使用TempData传递数据
Control:TempData["Message_TempData"] = "Hello TempData!";
View中读取Controller中定义的TempData数据
@TempData["Message_TempData"]
js中读取TempData中数据
<script type="text/javascript"> var TempData= '@TempData["Message_TempData"]'; </script>
4. 使用Model传递数据
首先要有ModelPublic class Pig{
public string Name{get;set;}
public string Age {get;set;}
}创建强类型视图,即:
@using Test.Pig;
Control
Pig pig = new Pig(){
Name="小猪",
Age=10
}
return View(pig);View中接受Control的数据
@{
Pig pig = Model as Pig;
var name = pig.Name;
猪的年龄为:@name
}总结:
ViewData与TempData方式是弱类型的方式传递数据,而使用Model传递数据是强类型的方式。
ViewData与TempData是完全不同的数据类型,ViewData数据类型是ViewDataDictionary类的实例化对象,而TempData的数据类型是TempDataDictionary类的实例化对象。
TempData实际上保存在Session中,控制器每次执行请求时都会从Session中获取TempData数据并删除该Session。TempData数据只能在控制器中传递一次,其中的每个元素也只能被访问一次,访问之后会被自动删除。
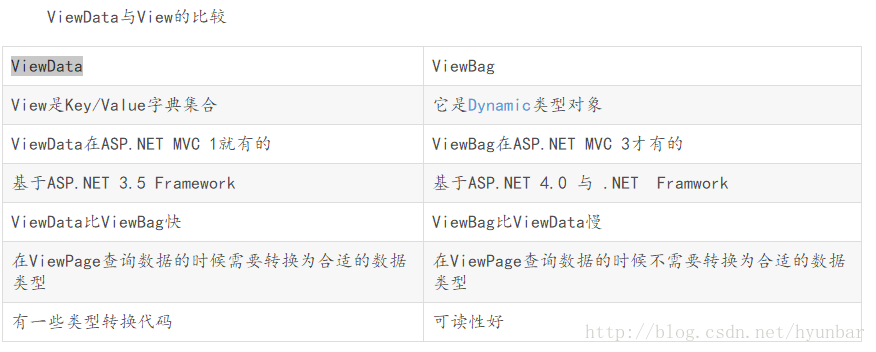
二、 View向Controller传递数据
1. 通过Request.Form读取表单数据
View@using (Html.BeginForm("HelloModelTest", "Home", FormMethod.Post))
{
@Html.TextBox("Name");
@Html.TextBox("Text");
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
}HelloModelTest为对应的Action名,Home为对应的Controller名称
然后在Controller层,通过Request.Form读取表单数据
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult HelloModelTest()
{
string name= Request.Form["Name"];
string text= Request.Form["Text"];
return View();
}2. 通过FormCollection读取表单数据
View@using (Html.BeginForm("HelloModelTest", "Home", FormMethod.Post))
{
@Html.TextBox("Name");
@Html.TextBox("Text");
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
}HelloModelTest为对应的Action名,Home为对应的Controller名称
然后在Controller层,通过Request.Form读取表单数据
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult HelloModelTest(FormCollection fc)
{
string name= fc["Name"];
string text = fc["Text"];
return View();
}3.模型绑定
View@using (Html.BeginForm("HelloModelTest", "Home", FormMethod.Post))
{
@Html.TextBox("Name");
@Html.TextBox("Text");
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
}默认的模型绑定
[HttpPost]
//public ActionResult HelloModelTest( string name,string text)
public ActionResult HelloModelTest( HelloModel model)
{
// ...
}显式模型绑定
当Action有参数的时候,会隐式地执行模型绑定。你还可以在控制器里面使用UpdateModel和 TryUpdateModel来显式调用模型绑定。调用UpdateModel的时候,如果模型对象是无效的或者绑定期间发生错误则会抛出异常。TryUpdateModel则不会抛出异常,它返回一个布尔值:如果绑定成功并且模型验证通过则返回true,否则返回false。[HttpPost]
public ActionResult HelloModelTest( )
{
HelloModel model = new HelloModel();
if (this.TryUpdateModel(model))
{
//绑定成功
}
else<
c0e6
/span>
{
//绑定失败
}
}模型状态是模型绑定产生的副产物。每次绑定器绑定值到模型时,都会在模型状态中进行记录。你可以在模型绑定之后查看模型状态来判断绑定是否成功:
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult HelloModelTest( )
{
HelloModel model = new HelloModel();
this.TryUpdateModel(model);
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
//绑定成功
}
else
{
//绑定失败
}
}三.两个Action之间的传值
在ASP.NET MVC框架的ControllerBase中存在一个叫做TempData的Property,它的类型为TempDataDictionary,顾名思义是一个字典类。TempData在ASP.NET MVC中的作用是:可用于在Action执行过程之间传值。简单的说,你可以在执行某个Action的时候,将数据存放在TempData中,那么在下一次Action执行过程中可以使用TempData中的数据。public ActionResult Index()
{
this.TempData["MyNane"] = "XiaoMing";
return View();
}
public ActionResult Index2()
{
string MyName=this.TempData["MyNane"] as string;
return View();
}上面的代码中,Index()给TempData添加了一个键值对,假设我们先请求Index这个Action,接着请求Index2这个Action,那么在Index2中,我们便可以得到之前添加到TempData的键值对。有趣的是,这时如果再次请求Index2,那么从TempData中读到的MyName的值会是null。于是,我们需要了解TempData的生命周期。
相关文章推荐
- ASP.NET MVC_Controller和View之间数据传递(前后台数据传递)方式
- 【Asp.Net MVC】Controller和View之间传递数据
- Asp.Net MVC中Controller与View之间传递的Model
- ASP.NET MVC中Controller与View之间的数据传递
- ASP.NET MVC中Controller与View之间的数据传递总结
- ASP.NET MVC中Controller与View之间的数据传递总结
- ASP.NET MVC中Controller与View之间的数据传递总结
- 【转载】ASP.NET MVC中Controller与View之间的数据传递总结
- Asp.net MVC中 Controller 与 View之间的数据传递
- ASP.NET MVC中Controller与View之间的数据传递总结
- 【ASP.NET MVC】View与Controller之间传递数据
- (转)ASP.NET MVC中Controller与View之间的数据传递总结
- ASP.NET MVC中Controller与View之间的数据传递总结
- 【转载】ASP.NET MVC中Controller与View之间的数据传递总结
- Asp.net MVC 学习笔记 (3) --Controller 与View 之间的数据传递
- Asp.net mvc Controller与 View之间的传递
- ASP.NET MVC中Controller与View之间的数据传递总结 (来自网络)
- 创建ASP.NET Core MVC应用程序(1)-添加Controller和View
- 【jqGrid for ASP.NET MVC Documentation】.学习笔记.2.jqGrid Model-View-Controller 分离
- asp.net mvc 如何将controller 里一个action 返回值为list<>的值输出到view
