语音信号处理之(二)基音周期估计(Pitch Detection)
2018-02-03 00:00
337 查看
语音信号处理之(二)基音周期估计(Pitch Detection)
zouxy09@qq.com
http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09
这学期有《语音信号处理》这门课,快考试了,所以也要了解了解相关的知识点。呵呵,平时没怎么听课,现在只能抱佛脚了。顺便也总结总结,好让自己的知识架构清晰点,也和大家分享下。下面总结的是第二个知识点:基音周期估计。我们用C++实现了基于自相关函数法的基音周期检测,并且结合了OpenCV来显示语音波形。因为花的时间不多,所以可能会有不少说的不妥的地方,还望大家指正。谢谢。
一、概述
1.1、基音与基音周期估计
人在发音时,根据声带是否震动可以将语音信号分为清音跟浊音两种。浊音又称有声语言,携带者语言中大部分的能量,浊音在时域上呈现出明显的周期性;而清音类似于白噪声,没有明显的周期性。发浊音时,气流通过声门使声带产生张弛震荡式振动,产生准周期的激励脉冲串。这种声带振动的频率称为基音频率,相应的周期就成为基音周期。
通常,基音频率与个人声带的长短、薄厚、韧性、劲度和发音习惯等有关系,在很大程度上反应了个人的特征。此外,基音频率还跟随着人的性别、年龄不同而有所不同。一般来说,男性说话者的基音频率较低,而女性说话者和小孩的基音频率相对较高。
基音周期的估计称谓基音检测,基音检测的最终目的是为了找出和声带振动频率完全一致或尽可能相吻合的轨迹曲线。
基因周期作为语音信号处理中描述激励源的重要参数之一,在语音合成、语音压缩编码、语音识别和说话人确认等领域都有着广泛而重要的问题,尤其对汉语更是如此。汉语是一种有调语言,而基因周期的变化称为声调,声调对于汉语语音的理解极为重要。因为在汉语的相互交谈中,不但要凭借不同的元音、辅音来辨别这些字词的意义,还需要从不同的声调来区别它,也就是说声调具有辨义作用;另外,汉语中存在着多音字现象,同一个字的不同的语气或不同的词义下具有不同的声调。因此准确可靠地进行基音检测对汉语语音信号的处理显得尤为重要。
1.2、基音周期估计的现有方法
到目前为止,基音检测的方法大致上可以分为三类:
1)时域估计法,直接由语音波形来估计基音周期,常见的有:自相关法、并行处理法、平均幅度差法、数据减少法等;
2)变换法,它是一种将语音信号变换到频域或者时域来估计基音周期的方法,首先利用同态分析方法将声道的影响消除,得到属于激励部分的信息,然后求取基音周期,最常用的就是倒谱法,这种方法的缺点就是算法比较复杂,但是基音估计的效果却很好;
3)混合法,先提取信号声道模型参数,然后利用它对信号进行滤波,得到音源序列,最后再利用自相关法或者平均幅度差法求得基因音周期。
三、基于自相关的基音周期检测
3.1、自相关函数
能量有限的语音信号x(n)的短时自相关函数定义为:
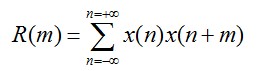
此公式表示一个信号和延迟m点后该信号本身的相似性。如果信号x(n)具有周期性,那么它的自相关函数也具有周期性,而且周期与信号x(n)的周期性相同。自相关函数提供了一种获取周期信号周期的方法。在周期信号周期的整数倍上,它的自相关函数可以达到最大值,因此可以不考虑起始时间,而从自相关函数的第一个最大值的位置估计出信号的基音周期,这使自相关函数成为信号基音周期估计的一种工具。
3.2、短时自相关函数法
语音信号是非稳态信号它的特征是随时间变化的,但在一个很短的时间段内可以认为具有相对稳定的特征即短时平稳性。因此语音具有短时自相关性。这个时间段约5ms-50ms。为其统计特性和频谱特性都是对短时段而言的。这使得要对语音信号作数字处理必须先按短时段对语音信号分帧。这样每一帧信号都具有短时平稳性从而进行短时相关分析。
能量有限的语音信号s(n)的短时自相关函数定义为:
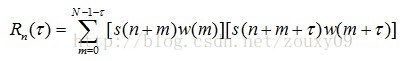
一般要求一帧至少包含2个以上的周期。一般,基频最低50Hz,故周期最长为20ms。而且相邻帧之间要有足够的重叠。具体应用时,窗口长度根据采样率确定帧长。
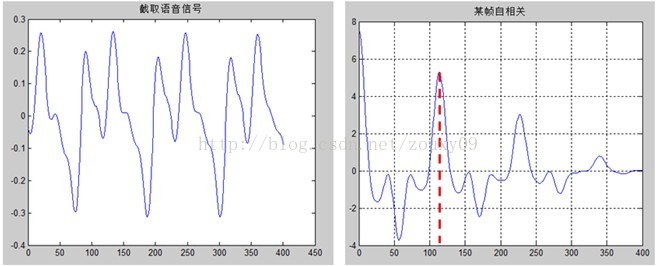
该帧的自相关函数中,除去第一个最大值后(0处),最大值Kmax= 114,那么该帧对应的基频16kHz/114=140Hz。
四、基于自相关的基音周期检测算法实现
这个实现课程要求是用C++来实现的。然后为了画波形,我用到了我比较熟悉的OpenCV。OpenCV画出来的波形还是不错的,而且如果是动态的波形平移,挺好看的,就像心电图那么动人。
实验采用一段男声读“播放”两个字的声音wav文件,其为16KHz采样率,16bit量化。整段语音长656.7ms,节点共10508个。
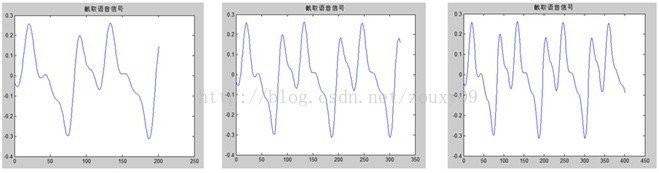
我们先要确定帧长。下面分别是帧长200,320和400个节点时所包含的周期数。200时只有一个周期,而400有三个周期,所以我们采用400的帧长。
通过计算短时能量区分voice和unvoice。语音信号{x(n)}的某帧信号的短时平均能量En的定义为:
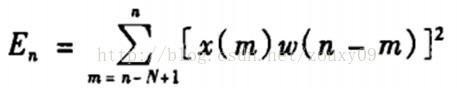
语音中浊音段的短时平均能量远远大于清音段的短时平均能量。因此,短时平均能量的计算给出了区分清音段与浊音段的依据,即En(浊)>En(清)。
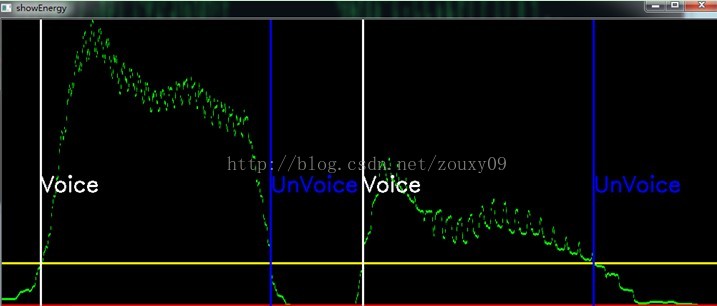
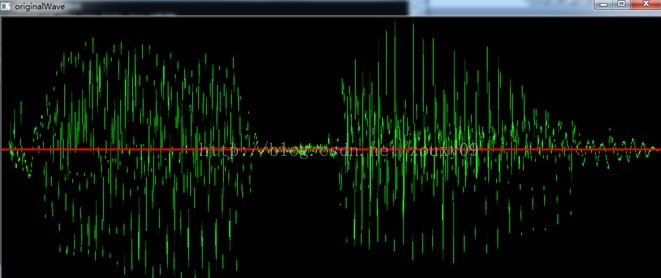
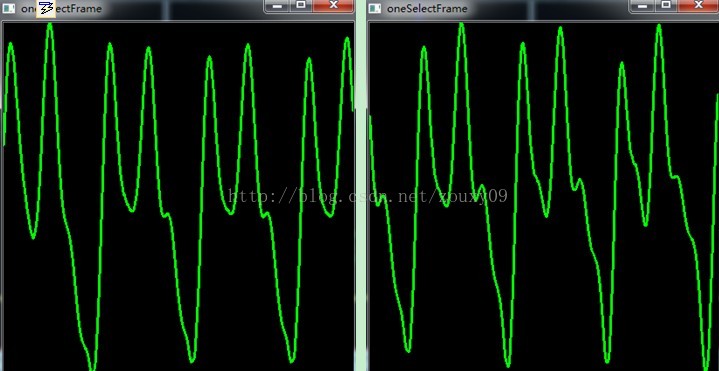
计算每一帧的过程中,会显示在原来波形中的位置,并且实时显示该帧得到的基音周期。另外还会在另一个窗口实时显示该帧的原始波形。
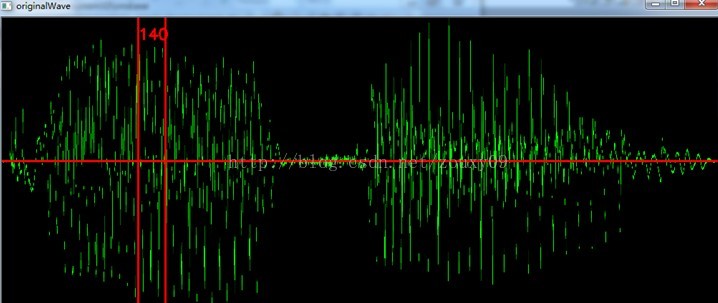
该帧的原始波形图(以下为不同时间的两帧,会动态变化):
下面左边的图是计算该语音的所有帧对应的基音周期的点,由图可以看出存在不少的野点。因为,需要对此进行进一步的处理,即去除野点。这里通过中值滤波来除去野点,滤波结果见右图。
C++程序如下:(每按一次空格进入下一个步骤)
zouxy09@qq.com
http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09
这学期有《语音信号处理》这门课,快考试了,所以也要了解了解相关的知识点。呵呵,平时没怎么听课,现在只能抱佛脚了。顺便也总结总结,好让自己的知识架构清晰点,也和大家分享下。下面总结的是第二个知识点:基音周期估计。我们用C++实现了基于自相关函数法的基音周期检测,并且结合了OpenCV来显示语音波形。因为花的时间不多,所以可能会有不少说的不妥的地方,还望大家指正。谢谢。
一、概述
1.1、基音与基音周期估计
人在发音时,根据声带是否震动可以将语音信号分为清音跟浊音两种。浊音又称有声语言,携带者语言中大部分的能量,浊音在时域上呈现出明显的周期性;而清音类似于白噪声,没有明显的周期性。发浊音时,气流通过声门使声带产生张弛震荡式振动,产生准周期的激励脉冲串。这种声带振动的频率称为基音频率,相应的周期就成为基音周期。
通常,基音频率与个人声带的长短、薄厚、韧性、劲度和发音习惯等有关系,在很大程度上反应了个人的特征。此外,基音频率还跟随着人的性别、年龄不同而有所不同。一般来说,男性说话者的基音频率较低,而女性说话者和小孩的基音频率相对较高。
基音周期的估计称谓基音检测,基音检测的最终目的是为了找出和声带振动频率完全一致或尽可能相吻合的轨迹曲线。
基因周期作为语音信号处理中描述激励源的重要参数之一,在语音合成、语音压缩编码、语音识别和说话人确认等领域都有着广泛而重要的问题,尤其对汉语更是如此。汉语是一种有调语言,而基因周期的变化称为声调,声调对于汉语语音的理解极为重要。因为在汉语的相互交谈中,不但要凭借不同的元音、辅音来辨别这些字词的意义,还需要从不同的声调来区别它,也就是说声调具有辨义作用;另外,汉语中存在着多音字现象,同一个字的不同的语气或不同的词义下具有不同的声调。因此准确可靠地进行基音检测对汉语语音信号的处理显得尤为重要。
1.2、基音周期估计的现有方法
到目前为止,基音检测的方法大致上可以分为三类:
1)时域估计法,直接由语音波形来估计基音周期,常见的有:自相关法、并行处理法、平均幅度差法、数据减少法等;
2)变换法,它是一种将语音信号变换到频域或者时域来估计基音周期的方法,首先利用同态分析方法将声道的影响消除,得到属于激励部分的信息,然后求取基音周期,最常用的就是倒谱法,这种方法的缺点就是算法比较复杂,但是基音估计的效果却很好;
3)混合法,先提取信号声道模型参数,然后利用它对信号进行滤波,得到音源序列,最后再利用自相关法或者平均幅度差法求得基因音周期。
三、基于自相关的基音周期检测
3.1、自相关函数
能量有限的语音信号x(n)的短时自相关函数定义为:
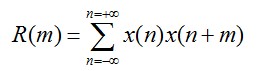
此公式表示一个信号和延迟m点后该信号本身的相似性。如果信号x(n)具有周期性,那么它的自相关函数也具有周期性,而且周期与信号x(n)的周期性相同。自相关函数提供了一种获取周期信号周期的方法。在周期信号周期的整数倍上,它的自相关函数可以达到最大值,因此可以不考虑起始时间,而从自相关函数的第一个最大值的位置估计出信号的基音周期,这使自相关函数成为信号基音周期估计的一种工具。
3.2、短时自相关函数法
语音信号是非稳态信号它的特征是随时间变化的,但在一个很短的时间段内可以认为具有相对稳定的特征即短时平稳性。因此语音具有短时自相关性。这个时间段约5ms-50ms。为其统计特性和频谱特性都是对短时段而言的。这使得要对语音信号作数字处理必须先按短时段对语音信号分帧。这样每一帧信号都具有短时平稳性从而进行短时相关分析。
能量有限的语音信号s(n)的短时自相关函数定义为:
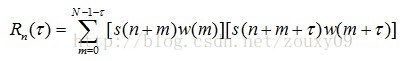
一般要求一帧至少包含2个以上的周期。一般,基频最低50Hz,故周期最长为20ms。而且相邻帧之间要有足够的重叠。具体应用时,窗口长度根据采样率确定帧长。

该帧的自相关函数中,除去第一个最大值后(0处),最大值Kmax= 114,那么该帧对应的基频16kHz/114=140Hz。
四、基于自相关的基音周期检测算法实现
这个实现课程要求是用C++来实现的。然后为了画波形,我用到了我比较熟悉的OpenCV。OpenCV画出来的波形还是不错的,而且如果是动态的波形平移,挺好看的,就像心电图那么动人。
实验采用一段男声读“播放”两个字的声音wav文件,其为16KHz采样率,16bit量化。整段语音长656.7ms,节点共10508个。

我们先要确定帧长。下面分别是帧长200,320和400个节点时所包含的周期数。200时只有一个周期,而400有三个周期,所以我们采用400的帧长。

通过计算短时能量区分voice和unvoice。语音信号{x(n)}的某帧信号的短时平均能量En的定义为:
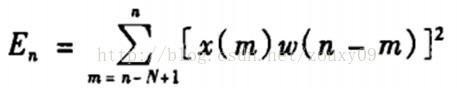
语音中浊音段的短时平均能量远远大于清音段的短时平均能量。因此,短时平均能量的计算给出了区分清音段与浊音段的依据,即En(浊)>En(清)。

计算每一帧的过程中,会显示在原来波形中的位置,并且实时显示该帧得到的基音周期。另外还会在另一个窗口实时显示该帧的原始波形。

该帧的原始波形图(以下为不同时间的两帧,会动态变化):

下面左边的图是计算该语音的所有帧对应的基音周期的点,由图可以看出存在不少的野点。因为,需要对此进行进一步的处理,即去除野点。这里通过中值滤波来除去野点,滤波结果见右图。

C++程序如下:(每按一次空格进入下一个步骤)
// Description : Pitch detection // Author : Zou Xiaoyi // HomePage : http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 // Date : 2013/06/08 // Rev. : 0.1 #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include "opencv2/opencv.hpp" #include "ReadWriteWav.h" #include <string> using namespace std; using namespace cv; #define MAXLENGTH 1000 void wav2image(Mat &img, vector<short> wavData, int wav_start, int width, int max_amplitude) { short max(0), min(0); for (int i = 0; i < wavData.size(); i++) { if (wavData[i] > max) max = wavData[i]; if (wavData[i] < min) min = wavData[i]; } cout<<max<<'\t'<<min<<endl; max_amplitude = max_amplitude > 480 ? 480 : max_amplitude; // normalize for (int i = 0; i < wavData.size(); i++) { wavData[i] = (wavData[i] - min) * max_amplitude / (max - min); } int j = 0; Point prePoint, curPoint; if (width >= 400) { img.create(max_amplitude, width, CV_8UC3); img.setTo(Scalar(0, 0, 0)); for (int i = wav_start; i < wav_start + width; i++) { prePoint = Point(j, img.rows - (int)wavData[i]); if (j) line(img, prePoint, curPoint, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2); curPoint = prePoint; j++; } if (width > MAXLENGTH) { cout<<"The wav is too long to show, and it will be resized to 1200"<<endl; resize(img, img, Size(MAXLENGTH, img.rows)); } } else { img.create(max_amplitude, 400, CV_8UC3); img.setTo(Scalar(0, 0, 0)); for (int i = wav_start; i < wav_start + width; i++) { prePoint = Point(j*400/width, img.rows - (int)wavData[i]); circle(img, prePoint, 3, Scalar(0, 0, 255), CV_FILLED); j++; } cout<<"The wav is too small to show, and it will be resized to 400"<<endl; } } short calOneFrameACF(vector<short> wavFrame, int sampleRate) { vector<float> acf; acf.empty(); // calculate ACF for (int k = 0; k < wavFrame.size(); k++) { float sum = 0.0; for (int i = 0; i < wavFrame.size() - k; i++) { sum = sum + wavFrame[i] * wavFrame[ i + k ]; } acf.push_back(sum); } // find the max one float max(-999); int index = 0; for (int k = 0; k < wavFrame.size(); k++) { if (k > 25 && acf[k] > max) { max = acf[k]; index = k; } } return (short)sampleRate / index; } int main() { const char *wavFile = "bofang.wav"; vector<short> data; int nodesPerFrame = 400; /************* Write data to file part Start ***************/ fstream writeFile; writeFile.open("statistics.txt", ios::out); /************* Write data to file part End ***************/ /************* Read and show the input wave part Start ***************/ int sampleRate; int dataLength = wav2allsample(wavFile, data, sampleRate); if (!dataLength) { cout <<"Reading wav file error!"<<endl; return -1; } Mat originalWave; wav2image(originalWave, data, 0, dataLength, 400); line(originalWave, Point(0, originalWave.rows * 0.5), Point(originalWave.cols, originalWave.rows * 0.5), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2); imshow("originalWave", originalWave); // write data writeFile<<"Filename: "<<wavFile<<endl<<"SampleRate: "<<sampleRate<<"Hz"<<endl<<"dataLength: "<<dataLength<<endl; cout<<"Press space key to continue"<<endl; while (waitKey(30) != ' '); /************* Read and show the input wave part End ***************/ /******** Calculate energy to separate voice and unvoice part Start *********/ int nodeCount = 0; // The sum must be double type vector<double> energyTmp; double maxEnergy(0); while(nodeCount < (dataLength - nodesPerFrame)) { double sum(0); for (int i = nodeCount; i < (nodeCount + nodesPerFrame); i++) { sum += (double)data[i] * data[i]; } if (sum > maxEnergy) { maxEnergy = sum; } energyTmp.push_back(sum); nodeCount++; } // Transform to short type for show vector<short> energy; // Fill element of boundary short tmp = (short)(energyTmp[0] * 400 / maxEnergy); for (int i = 0; i < nodesPerFrame * 0.5; i++) { energy.push_back(tmp); } for (int i = 0; i < energyTmp.size(); i++) { energy.push_back((short)(energyTmp[i] * 400 / maxEnergy)); } // Fill element of boundary tmp = (short)(energyTmp[energyTmp.size() - 1] * 400 / maxEnergy); for (int i = 0; i < nodesPerFrame * 0.5; i++) { energy.push_back(tmp); } // show Mat showEnergy; wav2image(showEnergy, energy, 0, energy.size(), 400); line(showEnergy, Point(0, showEnergy.rows - 1), Point(showEnergy.cols, showEnergy.rows - 1), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2); imshow("showEnergy", showEnergy); while (waitKey(30) != ' '); // separate voice and unvoice float thresVoice = 400 * 0.15; line(showEnergy, Point(0, showEnergy.rows - thresVoice), Point(showEnergy.cols, showEnergy.rows - thresVoice), Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2); imshow("showEnergy", showEnergy); while (waitKey(30) != ' '); // Find the Transition point and draw them bool high = false; vector<int> separateNode; for (int i = 0; i < energy.size(); i++) { if ( !high && energy[i] > thresVoice) { separateNode.push_back(i); high = true; writeFile<<"UnVoice to Voice: "<<i<<endl; line(showEnergy, Point(i * MAXLENGTH / dataLength, 0), Point(i * MAXLENGTH / dataLength, showEnergy.rows), Scalar(255, 255, 255), 2); putText(showEnergy, "Voice", Point(i * MAXLENGTH / dataLength, showEnergy.rows * 0.5 + 40), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, Scalar(255, 255, 255), 2); imshow("showEnergy", showEnergy); while (waitKey(30) != ' '); } if ( high && energy[i] < thresVoice) { separateNode.push_back(i); high = false; writeFile<<"Voice to UnVoice: "<<i<<endl; line(showEnergy, Point(i * MAXLENGTH / dataLength, 0), Point(i * MAXLENGTH / dataLength, showEnergy.rows), Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2); putText(showEnergy, "UnVoice", Point(i * MAXLENGTH / dataLength, showEnergy.rows * 0.5 + 40), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2); imshow("showEnergy", showEnergy); while (waitKey(30) != ' '); } } /******** Calculate energy to separate voice and unvoice part End ***********/ /******************* Calculate all frame part Start ***************/ int frames = 0; vector<short> allPitchFre; writeFile<<"The pitch frequency is:"<<endl; while(frames < 2 * dataLength / nodesPerFrame) { vector<short> wavFrame; wavFrame.empty(); // get one frame, 400 nodes per frame, and shift 200 nodes, or overlap 200 nodes int start = frames * nodesPerFrame * 0.5; for (int i = start; i < start + nodesPerFrame; i++) wavFrame.push_back(data[i]); // calculate the ACF of this frame float pitchFreqency = calOneFrameACF(wavFrame, sampleRate); allPitchFre.push_back(pitchFreqency); cout<<"The pitch frequency is: "<<pitchFreqency <<" Hz"<<endl; writeFile<<pitchFreqency<<endl; // show current frame in the whole wave Mat originalWave; wav2image(originalWave, data, 0, dataLength, 400); line(originalWave, Point(0, originalWave.rows * 0.5), Point(originalWave.cols, originalWave.rows * 0.5), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2); line(originalWave, Point(start * MAXLENGTH / dataLength, 0), Point(start * MAXLENGTH / dataLength, originalWave.rows), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2); line(originalWave, Point((start + nodesPerFrame)* MAXLENGTH / dataLength, 0), Point((start + nodesPerFrame)* MAXLENGTH / dataLength, originalWave.rows), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2); // put the pitchFreqency of this frame in the whole wave stringstream buf; buf << pitchFreqency; string num = buf.str(); putText(originalWave, num, Point(start * MAXLENGTH / dataLength, 30), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2); imshow("originalWave", originalWave); // show current frame in zoom out model Mat oneSelectFrame; wav2image(oneSelectFrame, wavFrame, 0, wavFrame.size(), 400); imshow("oneSelectFrame", oneSelectFrame); if (!frames) while (waitKey(30) != ' '); frames++; waitKey(50); } cout<<"Num of frames is: "<<frames<<endl; /******************* Calculate all frame part End ***************/ // show all pitch frequency before smooth Mat showAllPitchFre; wav2image(showAllPitchFre, allPitchFre, 0, allPitchFre.size(), 400); putText(showAllPitchFre, "Before smooth", Point(10, showAllPitchFre.rows - 20), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, Scalar(60, 200, 255), 1); imshow("showAllPitchFre", showAllPitchFre); /******************* Smooth by medium filter part Start **************/ int kernelSize = 5; vector<short> afterMedFilter; short sum(0); afterMedFilter.assign(allPitchFre.size(), allPitchFre[0]); for (int k = cvFloor(kernelSize/2); k < allPitchFre.size(); k++) { vector<short> kernelData; for (int i = -cvFloor(kernelSize/2); i < cvCeil (kernelSize/2); i++) kernelData.push_back(allPitchFre[k+i]); nth_element(kernelData.begin(), kernelData.begin() + cvCeil (kernelSize/2), kernelData.end()); afterMedFilter[k] = kernelData[cvCeil (kernelSize/2)]; sum += afterMedFilter[k]; cout<<afterMedFilter[k]<<endl; } // show all pitch frequency and mean pitch frequency after smooth Mat showAfterMedFilter; wav2image(showAfterMedFilter, afterMedFilter, 0, afterMedFilter.size(), 400); putText(showAfterMedFilter, "After smooth", Point(10, showAfterMedFilter.rows - 20), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, Scalar(60, 200, 255), 1); short mean = sum / (afterMedFilter.size() - cvFloor(kernelSize/2)); writeFile<<"The mean pitch frequency is: "<<mean<<endl; stringstream buf; buf << mean; string num = "Mean: " + buf.str() + "Hz"; putText(showAfterMedFilter, num, Point(10, 40), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, Scalar(255, 200, 255), 2); imshow("showAfterMedFilter", showAfterMedFilter); /******************* Smooth by medium filter part End ***************/ while (waitKey(30) != 27); return 0; }
相关文章推荐
- 语音信号处理之(二)基音周期估计(Pitch Detection)
- 数字语音信号处理学习笔记——语音信号的数字模型(3)
- 语音信号处理之(四)梅尔频率倒谱系数(MFCC)
- 语音专题第一讲,麦克风阵列的语音信号处理技术
- 预加重——语音信号处理之一
- 数字语音信号处理学习笔记——语音信号的同态处理(3)
- 语音信号处理之(三)矢量量化(Vector Quantization)
- 【转】语音信号处理由浅入深
- 数字语音信号处理学习笔记——语音信号的同态处理(4)
- 语音专题第一讲,麦克风阵列的语音信号处理技术
- 【VS开发】【智能语音处理】语音信号处理之(一)动态时间规整(DTW)
- 数字语音信号处理学习笔记——绪论(1)
- 语音信号处理-matlab 【引用】
- Automotive radar 信号处理 第1课 距离估计
- 语音信号处理-矢量量化VQ
- 语音信号的预加重和加窗处理
- 数字语音信号处理学习笔记——语音信号的数字模型(1)
- 数字语音信号处理学习笔记——语音信号的短时时域分析(2)
- 语音信号处理-动态时间规整DTW
- 模式识别,计算机视觉,计算机图形学,智能控制,信号处理,语音识别,知识处理,机器学习,数据挖掘领域区别
