Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) D (树状数组+二分)
2018-01-29 10:59
232 查看
D. Friends and Subsequences
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
512 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Mike and !Mike are old childhood rivals, they are opposite in everything they do, except programming. Today they have a problem they cannot solve on their own, but together (with you) — who knows?
Every one of them has an integer sequences a and b of length n. Being given a query of the form of pair of integers (l, r), Mike can instantly
tell the value of
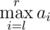
while
!Mike can instantly tell the value of
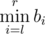
.
Now suppose a robot (you!) asks them all possible different queries of pairs of integers (l, r) (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n) (so he will make exactlyn(n + 1) / 2 queries) and counts
how many times their answers coincide, thus for how many pairs
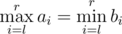
is
satisfied.
How many occasions will the robot count?
Input
The first line contains only integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000).
The second line contains n integer numbers a1, a2, ..., an ( - 109 ≤ ai ≤ 109) —
the sequence a.
The third line contains n integer numbers b1, b2, ..., bn ( - 109 ≤ bi ≤ 109) —
the sequence b.
Output
Print the only integer number — the number of occasions the robot will count, thus for how many pairs
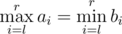
is
satisfied.
Examples
input
output
input
output
Note
The occasions in the first sample case are:
1.l = 4,r = 4 since max{2} = min{2}.
2.l = 4,r = 5 since max{2, 1} = min{2, 3}.
There are no occasions in the second sample case since Mike will answer 3 to any query pair, but !Mike will always answer 1.
题意是两个数组a,b,每个数组给定n个数,求有多少个区间满足a数组的最大值等于b数组的最小值。
首先可以想到从区间[1,n]的最大值在不断增大,最小值在不断减少,也就是说明如果只维护最大或者最小值的话,这个维护的数组肯定是有序的。然后就是想办法维护这样一个数组,树状数组可以在非线性时间内完成数组的创建与查询,得到这样一个数组之后,我们可以枚举一个端点,然后去二分另一个端点,求出最大值==最小值的mid的最大值与最小值,然后相减再累加就是这样的区间的数量。如果是枚举左端点,维护树状数组的话,单点更新,很容易出现出现最大值之后将后面所有的值都覆盖的情况,这样我们就无法再去查找区间内的最值。此时,可以维护数组的后缀,枚举右端点,这
bc7f
样最值不会影响i之前的最值,因为只有遍历到maxi或者mini的时候才会更新后面的值,此时后面的值我们已经计算在内,所以并不会产生影响。
所以此题可以跑后缀,枚举左端点,二分右端点,树状数组维护区间最值并查询。
代码实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<cstdio>
#define ll long long
#define mset(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a))
using namespace std;
const double PI=acos(-1);
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps=1e-12;
const int maxn=1e6+5;
const int mod=1e9+7;
int dir[4][2]={0,1,1,0,0,-1,-1,0};
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
ll lcm(ll a,ll b){return a/gcd(a,b)*b;}
ll inv(ll b){if(b==1)return 1; return (mod-mod/b)*inv(mod%b)%mod;}
ll fpow(ll n,ll k){ll r=1;for(;k;k>>=1){if(k&1)r=r*n%mod;n=n*n%mod;}return r;}
ll Fpow(ll n,ll k){ll r=1;for(;k;k>>=1){if(k&1)r=r*n;n=n*n;}return r;}
ll upd(ll x,ll v){x=x+v>=mod?x+v-mod:x+v;return x;}
int minn[maxn],maxx[maxn],arr_a[maxn],arr_b[maxn],n;
void init()
{
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
maxx[i]=-(minn[i]=inf);
}
int lowbit(int k)
{
return k&(-k);
}
int query_max(int x)
{
int ans=-inf;
while(x)
{
ans=max(ans,maxx[x]);
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return ans;
}
int query_min(int x)
{
int ans=inf;
while(x)
{
ans=min(ans,minn[x]);
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return ans;
}
void add_max(int x,int y)
{
while(x<=n)
{
maxx[x]=max(maxx[x],y);
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
void add_min(int x,int y)
{
while(x<=n)
{
minn[x]=min(minn[x],y);
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j,k;
scanf("%d",&n);
init();
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&arr_a[i]);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&arr_b[i]);
ll ans=0;
//最大值只会越来越大,最小值只会越来越小
for(i=n;i>0;i--)
{
add_max(i,arr_a[i]); //得到后缀最大值
add_min(i,arr_b[i]); //得到后缀最小值
int l=i,r=n+1,mid;
while(l<r) //后缀二分,即二分右端点
{
mid=(l+r)/2;
if(query_max(mid)>=query_min(mid)) //二分到最小的max==min的下标
r=mid;
else
l=mid+1;
}
int temp=l;
l=i;r=n+1;
while(l<r)
{
mid=(l+r)/2;
if(query_max(mid)>query_min(mid)) //二分到最大的max==min的下标
r=mid;
else
l=mid+1;
}
ans+=l-temp;
}
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
512 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Mike and !Mike are old childhood rivals, they are opposite in everything they do, except programming. Today they have a problem they cannot solve on their own, but together (with you) — who knows?
Every one of them has an integer sequences a and b of length n. Being given a query of the form of pair of integers (l, r), Mike can instantly
tell the value of
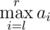
while
!Mike can instantly tell the value of
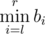
.
Now suppose a robot (you!) asks them all possible different queries of pairs of integers (l, r) (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n) (so he will make exactlyn(n + 1) / 2 queries) and counts
how many times their answers coincide, thus for how many pairs
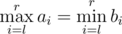
is
satisfied.
How many occasions will the robot count?
Input
The first line contains only integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000).
The second line contains n integer numbers a1, a2, ..., an ( - 109 ≤ ai ≤ 109) —
the sequence a.
The third line contains n integer numbers b1, b2, ..., bn ( - 109 ≤ bi ≤ 109) —
the sequence b.
Output
Print the only integer number — the number of occasions the robot will count, thus for how many pairs
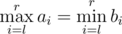
is
satisfied.
Examples
input
6 1 2 3 2 1 4 6 7 1 2 3 2
output
2
input
3 3 3 3 1 1 1
output
0
Note
The occasions in the first sample case are:
1.l = 4,r = 4 since max{2} = min{2}.
2.l = 4,r = 5 since max{2, 1} = min{2, 3}.
There are no occasions in the second sample case since Mike will answer 3 to any query pair, but !Mike will always answer 1.
题意是两个数组a,b,每个数组给定n个数,求有多少个区间满足a数组的最大值等于b数组的最小值。
首先可以想到从区间[1,n]的最大值在不断增大,最小值在不断减少,也就是说明如果只维护最大或者最小值的话,这个维护的数组肯定是有序的。然后就是想办法维护这样一个数组,树状数组可以在非线性时间内完成数组的创建与查询,得到这样一个数组之后,我们可以枚举一个端点,然后去二分另一个端点,求出最大值==最小值的mid的最大值与最小值,然后相减再累加就是这样的区间的数量。如果是枚举左端点,维护树状数组的话,单点更新,很容易出现出现最大值之后将后面所有的值都覆盖的情况,这样我们就无法再去查找区间内的最值。此时,可以维护数组的后缀,枚举右端点,这
bc7f
样最值不会影响i之前的最值,因为只有遍历到maxi或者mini的时候才会更新后面的值,此时后面的值我们已经计算在内,所以并不会产生影响。
所以此题可以跑后缀,枚举左端点,二分右端点,树状数组维护区间最值并查询。
代码实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<cstdio>
#define ll long long
#define mset(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a))
using namespace std;
const double PI=acos(-1);
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps=1e-12;
const int maxn=1e6+5;
const int mod=1e9+7;
int dir[4][2]={0,1,1,0,0,-1,-1,0};
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
ll lcm(ll a,ll b){return a/gcd(a,b)*b;}
ll inv(ll b){if(b==1)return 1; return (mod-mod/b)*inv(mod%b)%mod;}
ll fpow(ll n,ll k){ll r=1;for(;k;k>>=1){if(k&1)r=r*n%mod;n=n*n%mod;}return r;}
ll Fpow(ll n,ll k){ll r=1;for(;k;k>>=1){if(k&1)r=r*n;n=n*n;}return r;}
ll upd(ll x,ll v){x=x+v>=mod?x+v-mod:x+v;return x;}
int minn[maxn],maxx[maxn],arr_a[maxn],arr_b[maxn],n;
void init()
{
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
maxx[i]=-(minn[i]=inf);
}
int lowbit(int k)
{
return k&(-k);
}
int query_max(int x)
{
int ans=-inf;
while(x)
{
ans=max(ans,maxx[x]);
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return ans;
}
int query_min(int x)
{
int ans=inf;
while(x)
{
ans=min(ans,minn[x]);
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return ans;
}
void add_max(int x,int y)
{
while(x<=n)
{
maxx[x]=max(maxx[x],y);
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
void add_min(int x,int y)
{
while(x<=n)
{
minn[x]=min(minn[x],y);
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j,k;
scanf("%d",&n);
init();
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&arr_a[i]);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&arr_b[i]);
ll ans=0;
//最大值只会越来越大,最小值只会越来越小
for(i=n;i>0;i--)
{
add_max(i,arr_a[i]); //得到后缀最大值
add_min(i,arr_b[i]); //得到后缀最小值
int l=i,r=n+1,mid;
while(l<r) //后缀二分,即二分右端点
{
mid=(l+r)/2;
if(query_max(mid)>=query_min(mid)) //二分到最小的max==min的下标
r=mid;
else
l=mid+1;
}
int temp=l;
l=i;r=n+1;
while(l<r)
{
mid=(l+r)/2;
if(query_max(mid)>query_min(mid)) //二分到最大的max==min的下标
r=mid;
else
l=mid+1;
}
ans+=l-temp;
}
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- Codeforces Round #220 (Div. 2) D 树状数组 && 二分
- Codeforces Round #452 (Div. 2)-F-Letters Removing(树状数组+set+二分)
- Codeforces Round #285 (Div.1 B & Div.2 D) Misha and Permutations Summation --二分+树状数组
- Codeforces Round #261 (Div. 2) D. Pashmak and Parmida's problem (树状数组)
- codeforces 191 E (树状数组+二分)
- 【poj 2104】K-th Number【整体二分+树状数组】
- POJ 2892 Tunnel Warfare || HDU 1540(树状数组+二分 || 线段树的单点更新+区间查询)
- 【树状数组】Codeforces Round #423 (Div. 1, rated, based on VK Cup Finals) C. DNA Evolution
- Codeforces Round #423 (Div. 2) E. DNA Evolution(树状数组)
- bzoj3110 K大数查询 整体二分&树状数组
- POJ-2182 Lost Cows (二分 + 树状数组 或者平衡树)
- 【POJ2104】【整体二分+树状数组】区间第k大
- BZOJ2527 [Poi2011]Meteors 【整体二分 + 树状数组】
- Codeforces Round #424 (Div. 2, rated, based on VK Cup Finals) Cards Sorting(树状数组)
- bzoj 2527 Meteors - 整体二分 - 树状数组
- ZOJ3635——Cinema in Akiba(树状数组+二分)
- ZOJ 3635 Cinema in Akiba (树状数组+二分)
- Codeforces Round #365 (Div. 2) D.Mishka and Interesting sum (树状数组维护异或值) ★ ★
- Codeforces Beta Round #12 (Div 2 Only) D. Ball 树状数组查询后缀、最值
- HDU3030最长上升子序列个数+树状数组求和+二分优化
