Hello 2018 B. Christmas Spruce
2018-01-22 11:46
337 查看
B. Christmas Spruce
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Consider a rooted tree. A rooted tree has one special vertex called the root. All edges are directed from the root. Vertex u is called
a child of vertex v and vertex v is
called a parent of vertex u if there exists a directed edge from v to u.
A vertex is called a leaf if it doesn't have children and has a parent.
Let's call a rooted tree a spruce if its every non-leaf vertex has at least 3 leaf
children. You are given a rooted tree, check whether it's a spruce.
The definition of a rooted tree can be found here.
Input
The first line contains one integer n — the number of vertices in the tree (3 ≤ n ≤ 1 000).
Each of the next n - 1 lines contains one integer pi (1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1) —
the index of the parent of the i + 1-th vertex (1 ≤ pi ≤ i).
Vertex 1 is the root. It's guaranteed that the root has at least 2 children.
Output
Print "Yes" if the tree is a spruce and "No" otherwise.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
The first example:
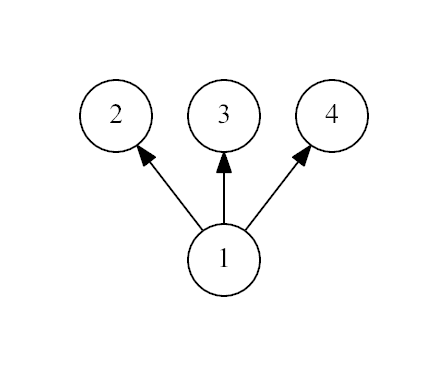
The second example:
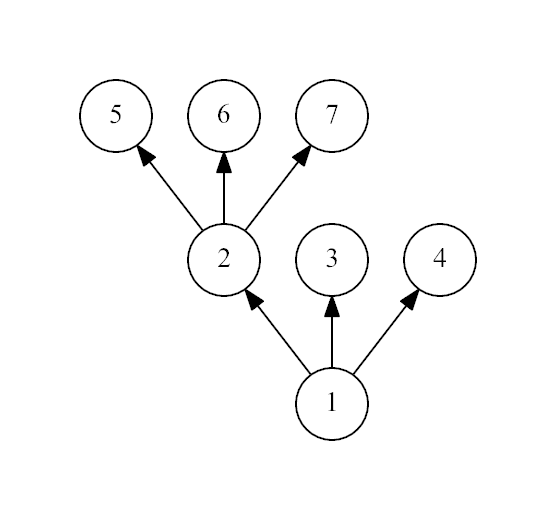
It is not a spruce, because the non-leaf vertex 1 has only 2 leaf
children.
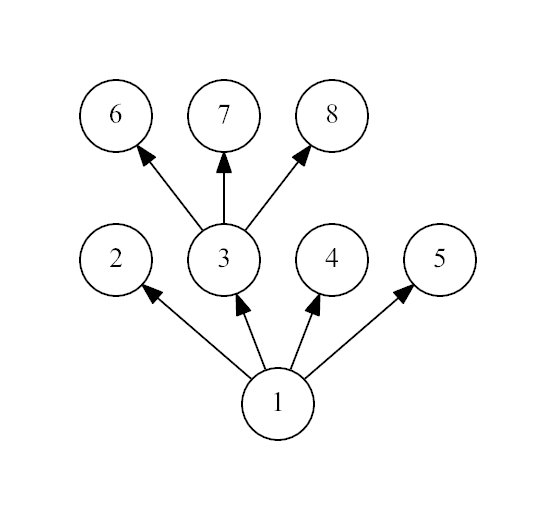
The third example:
要求所有的点满足其中一个要求即可。①没有子节点 ②有至少三个没有子节点的子节点。
用vector来存图,之后利用size来判断即可
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
vector<int>mp[1100];
int dfs(int num)
{
if(mp[num].size()==0)
{
return 1;
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<mp[num].size();i++)
{
if(mp[mp[num][i]].size()==0)
{
ans++;
}
}
if(ans>=3)
return 1;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
int u;
cin>>u;
mp[u].push_back(i);
}
int flag=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(dfs(i)==0)
{
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
{
cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
}
}
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Consider a rooted tree. A rooted tree has one special vertex called the root. All edges are directed from the root. Vertex u is called
a child of vertex v and vertex v is
called a parent of vertex u if there exists a directed edge from v to u.
A vertex is called a leaf if it doesn't have children and has a parent.
Let's call a rooted tree a spruce if its every non-leaf vertex has at least 3 leaf
children. You are given a rooted tree, check whether it's a spruce.
The definition of a rooted tree can be found here.
Input
The first line contains one integer n — the number of vertices in the tree (3 ≤ n ≤ 1 000).
Each of the next n - 1 lines contains one integer pi (1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1) —
the index of the parent of the i + 1-th vertex (1 ≤ pi ≤ i).
Vertex 1 is the root. It's guaranteed that the root has at least 2 children.
Output
Print "Yes" if the tree is a spruce and "No" otherwise.
Examples
input
4 1 1 1
output
Yes
input
7 1 1 1 2 2 2
output
No
input
8 1 1 1 1 3 3 3
output
Yes
Note
The first example:

The second example:

It is not a spruce, because the non-leaf vertex 1 has only 2 leaf
children.
The third example:

要求所有的点满足其中一个要求即可。①没有子节点 ②有至少三个没有子节点的子节点。
用vector来存图,之后利用size来判断即可
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
vector<int>mp[1100];
int dfs(int num)
{
if(mp[num].size()==0)
{
return 1;
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<mp[num].size();i++)
{
if(mp[mp[num][i]].size()==0)
{
ans++;
}
}
if(ans>=3)
return 1;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
int u;
cin>>u;
mp[u].push_back(i);
}
int flag=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(dfs(i)==0)
{
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
{
cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
}
}
相关文章推荐
- 【Hello 2018 B】Christmas Spruce
- Hello 2018-B. Christmas Spruce
- codeforces Hello 2018(A-E)
- printf("Hello 2018!");
- 【Hello 2018 C】Party Lemonade
- codeforces Hello 2018(A-E)
- 【Hello 2018 D】Too Easy Problems
- [Codeforces] Hello 2018
- codeforces Hello 2018(A-E)
- Christmas Spruce—codeforces(hello_2018)
- Hello 2018, Bye 2017
- Codeforces Hello 2018 [ABC]
- codeforces Hello 2018 B. Christmas Spruce
- codeforces Hello 2018(A-E)
- Hello 2018(B、C)
- codeforces Hello 2018(A-E)
- Hello 2018 A
- Hello 2018 C. Party Lemonade (dp好题)
- Codeforces Hello 2018 B.Christmas Spruce
- Codeforces Hello 2018
