CodeForces - 707C Pythagorean Triples (数学)
2018-01-21 19:51
507 查看
C. Pythagorean Triples
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Katya studies in a fifth grade. Recently her class studied right triangles and the Pythagorean theorem. It appeared, that there are triples of positive integers such that you can construct a right triangle with segments of lengths corresponding to triple. Such
triples are called Pythagorean triples.
For example, triples (3, 4, 5), (5, 12, 13) and (6, 8, 10) are
Pythagorean triples.
Here Katya wondered if she can specify the length of some side of right triangle and find any Pythagorean triple corresponding to such length? Note that the side which length is specified can be a cathetus as well as hypotenuse.
Katya had no problems with completing this task. Will you do the same?
Input
The only line of the input contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 109) —
the length of some side of a right triangle.
Output
Print two integers m and k (1 ≤ m, k ≤ 1018),
such that n, m and k form
a Pythagorean triple, in the only line.
In case if there is no any Pythagorean triple containing integer n, print - 1 in
the only line. If there are many answers, print any of them.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
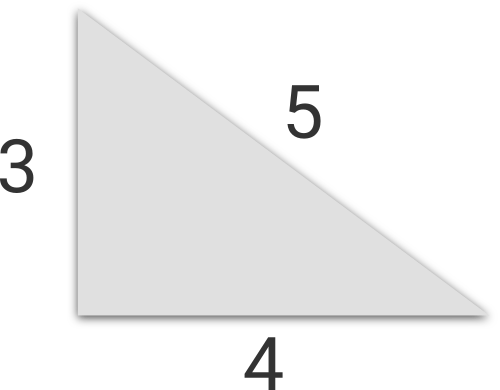
Illustration for the first sample.
给定N 求 直接三角形 另外两条边.
根据直角三角形的两条性质
当n*n为奇数时 有 a+b=n*n ; a-b=1;
当n*n为偶数时,有 a+b=(n*n)/2; a-b=2;
联立 解 a,b;
并且 当 n=1 || n=2 时 无解; A B C
分析: 可以发现 从3 开始是 3,5,7,11,13,15 素数 是 可以组成的, 3-4-5 已知A B=(A*A-1)/2; C=B+1;
对于偶数, 一定 可以变成素数的倍数, 那么 队友 6-8-10- 6是3的倍数, 那么 就可以转成成 3*2-4*2-5*2; k=6/3;
对于是2的倍数的, 要特殊处理, 因为2 无法构成直角三角形, 4 可以, 是2的倍数就一定是4 的倍数 4-3-5 成倍数关系就可以
例如 1024 是2 的倍数1024/2=512 1024/4=256 3*256=768 5*256=1280 1024-768-1280;
代码实现:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <math.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include <vector>
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define findx(x,b,n) lower_bound(b+1,b+1+n,x)-b
#define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin)
#define FOUT freopen("output.txt","w",stdout)
#define SHUT ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cout.setf(ios::fixed);cout.precision(20); cout.tie(nullptr); cin.tie(nullptr);
#define lson rt << 1, l, mid
#define rson rt << 1|1, mid + 1, r
#define FI(n) IO::read(n)
#define Be IO::begin()
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double PI=acos(-1);
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double esp=1e-6;
const int maxn=1e6+5;
const int MAXN=1e5+5;
const int MOD=1e9+7;
const int mod=1e9+7;
int dir[5][2]={0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0};
namespace IO {
const int MT = 5e7;
char buf[MT]; int c,sz;
void begin(){
c = 0;
sz = fread(buf, 1, MT, stdin);//一次性输入
}
template<class T>
inline bool read(T &t){
while( c < sz && buf[c] != '-' && ( buf[c]<'0' || buf[c] >'9')) c++;
if( c>=sz) return false;
bool flag = 0; if( buf[c]== '-') flag = 1,c++;
for( t=0; c<=sz && '0' <=buf[c] && buf[c] <= '9'; c++ ) t= t*10 + buf[c]-'0';
if(flag) t=-t;
return true;
}
}
ll inv[maxn*2];
inline void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){ x=1; y=0; d=a; }else{ ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x); y-=x*(a/b);};}
inline ll gcd(ll a,ll b){ return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
inline ll exgcd(ll a,ll b,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){x=1;y=0;return a;}ll ans=exgcd(b,a%b,x,y);ll temp=x;x=y;y=temp-a/b*y;return ans;}
inline ll lcm(ll a,ll b){ return b/gcd(a,b)*a;}
inline ll qpow(ll x,ll n){ll res=1;for(;n;n>>=1){if(n&1)res=(res*x)%MOD;x=(x*x)%MOD;}return res;}
inline ll inv_exgcd(ll a,ll n){ll d,x,y;ex_gcd(a,n,d,x,y);return d==1?(x+n)%n:-1;}
inline ll inv1(ll b){return b==1?1:(MOD-MOD/b)*inv1(MOD%b)%MOD;}
inline ll inv2(ll b){return qpow(b,MOD-2);}
int main()
{
ll n;
cin>>n;
ll p=n*n;
if(n==1||n==2)
{
cout<<-1<<endl;
return 0;
}
if(p%2==0)
{
cout<<(p/2+2)/2-2<<" "<<(p/2+2)/2<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<(p-1)/2<<" "<<(p-1)/2+1<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
123
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Katya studies in a fifth grade. Recently her class studied right triangles and the Pythagorean theorem. It appeared, that there are triples of positive integers such that you can construct a right triangle with segments of lengths corresponding to triple. Such
triples are called Pythagorean triples.
For example, triples (3, 4, 5), (5, 12, 13) and (6, 8, 10) are
Pythagorean triples.
Here Katya wondered if she can specify the length of some side of right triangle and find any Pythagorean triple corresponding to such length? Note that the side which length is specified can be a cathetus as well as hypotenuse.
Katya had no problems with completing this task. Will you do the same?
Input
The only line of the input contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 109) —
the length of some side of a right triangle.
Output
Print two integers m and k (1 ≤ m, k ≤ 1018),
such that n, m and k form
a Pythagorean triple, in the only line.
In case if there is no any Pythagorean triple containing integer n, print - 1 in
the only line. If there are many answers, print any of them.
Examples
input
3
output
4 5
input
6
output
8 10
input
1
output
-1
input
17
output
144 145
input
67
output
2244 2245
Note

Illustration for the first sample.
给定N 求 直接三角形 另外两条边.
根据直角三角形的两条性质
当n*n为奇数时 有 a+b=n*n ; a-b=1;
当n*n为偶数时,有 a+b=(n*n)/2; a-b=2;
联立 解 a,b;
并且 当 n=1 || n=2 时 无解; A B C
分析: 可以发现 从3 开始是 3,5,7,11,13,15 素数 是 可以组成的, 3-4-5 已知A B=(A*A-1)/2; C=B+1;
对于偶数, 一定 可以变成素数的倍数, 那么 队友 6-8-10- 6是3的倍数, 那么 就可以转成成 3*2-4*2-5*2; k=6/3;
对于是2的倍数的, 要特殊处理, 因为2 无法构成直角三角形, 4 可以, 是2的倍数就一定是4 的倍数 4-3-5 成倍数关系就可以
例如 1024 是2 的倍数1024/2=512 1024/4=256 3*256=768 5*256=1280 1024-768-1280;
代码实现:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <math.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include <vector>
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define findx(x,b,n) lower_bound(b+1,b+1+n,x)-b
#define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin)
#define FOUT freopen("output.txt","w",stdout)
#define SHUT ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cout.setf(ios::fixed);cout.precision(20); cout.tie(nullptr); cin.tie(nullptr);
#define lson rt << 1, l, mid
#define rson rt << 1|1, mid + 1, r
#define FI(n) IO::read(n)
#define Be IO::begin()
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double PI=acos(-1);
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double esp=1e-6;
const int maxn=1e6+5;
const int MAXN=1e5+5;
const int MOD=1e9+7;
const int mod=1e9+7;
int dir[5][2]={0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0};
namespace IO {
const int MT = 5e7;
char buf[MT]; int c,sz;
void begin(){
c = 0;
sz = fread(buf, 1, MT, stdin);//一次性输入
}
template<class T>
inline bool read(T &t){
while( c < sz && buf[c] != '-' && ( buf[c]<'0' || buf[c] >'9')) c++;
if( c>=sz) return false;
bool flag = 0; if( buf[c]== '-') flag = 1,c++;
for( t=0; c<=sz && '0' <=buf[c] && buf[c] <= '9'; c++ ) t= t*10 + buf[c]-'0';
if(flag) t=-t;
return true;
}
}
ll inv[maxn*2];
inline void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){ x=1; y=0; d=a; }else{ ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x); y-=x*(a/b);};}
inline ll gcd(ll a,ll b){ return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
inline ll exgcd(ll a,ll b,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){x=1;y=0;return a;}ll ans=exgcd(b,a%b,x,y);ll temp=x;x=y;y=temp-a/b*y;return ans;}
inline ll lcm(ll a,ll b){ return b/gcd(a,b)*a;}
inline ll qpow(ll x,ll n){ll res=1;for(;n;n>>=1){if(n&1)res=(res*x)%MOD;x=(x*x)%MOD;}return res;}
inline ll inv_exgcd(ll a,ll n){ll d,x,y;ex_gcd(a,n,d,x,y);return d==1?(x+n)%n:-1;}
inline ll inv1(ll b){return b==1?1:(MOD-MOD/b)*inv1(MOD%b)%MOD;}
inline ll inv2(ll b){return qpow(b,MOD-2);}
int main()
{
ll n;
cin>>n;
ll p=n*n;
if(n==1||n==2)
{
cout<<-1<<endl;
return 0;
}
if(p%2==0)
{
cout<<(p/2+2)/2-2<<" "<<(p/2+2)/2<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<(p-1)/2<<" "<<(p-1)/2+1<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
123
相关文章推荐
- CodeForces - 140A New Year Table (数学几何&精度)大圆内能放几个小圆
- CodeForces 468 C.Hack it!(数学)
- codeforces 55D beautiful number [数学+数位DP]【动态规划+数论】
- codeforces 30D King's Problem? 数学
- codeforces 559C|51nod1486 Gerald and Giant Chess(组合数学+逆元)
- Codeforces--660A--Co-prime Array(数学水题)
- CodeForces - 660D Number of Parallelograms (数学几何)给出n个点问能组成的平行四边形个数
- CodeForces 366A Dima and Guards(结构体,数学)
- CodeForces 433C Ryouko's Memory Note (数学)
- codeforces 434A A. Ryouko's Memory Note(数学)
- Codeforces 715A. Plus and Square Root[数学构造]
- CodeForces 454C Little Pony and Expected Maximum (数学推导)
- codeforces 4A Watermelon(数学水题)
- codeforces 101C C. Vectors(数学)
- Codeforces 577 B Modulo Sum 简单数学+dp
- Codeforces 807C Success Rate【二分+数学思维】
- codeforces 257 C. View Angle (数学)
- Codeforces 625A Guest From the Past 【基础数学】
- Codeforces 758C Unfair Poll 【数学】【思维】
- codeforces 347 c Alice and Bob(博弈 && 数学)
