【懒懒的计算机视觉笔记之Harris角点检测二】
2018-01-12 09:37
651 查看
Harris角点检测算法仅仅能检测出图像中的兴趣点,但是没有给出通过比较图像间的兴趣点来寻找匹配点。为此我们需要加入描述算子来描述这些兴趣点。兴趣点描述子就是给兴趣点定义一个向量,描述该点附近的图像的表观信息。
Harris角点的描述子通常是周围像素的灰度值,以及用于比较的归一化的互相关矩阵组成。通常两个相同大小的像素块
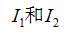
的相关矩阵的定义如下:
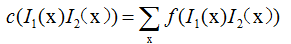
其中
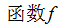
随着实际情况选择,上式取所有像素位置X的和,通常对于互相关矩阵,函数
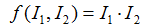
,其中·表示向量乘法,函数值越大表示相似度越高。实际应用中使用的是归一化的互相关矩阵,定义如下:

其中n为像素块的总像素数,μ1和μ2分别是每个像素块的平均像素值,σ1和σ2是每个像素块的标准差,Harris角点检测可以从上一篇博客中找到,链接:传送门
我们将下面的代码加入上一篇博客的代码中,这段代码的作用是获取图像每个兴趣点的像素块:
def get_descriptors(image, filtered_coords, wid=5):
'''
对每个兴趣点,返回周围2*wid+1个像素的值
:param image:
:param filtered_coordes:
:param wid:
:return:
'''
desc = []
for coords in filtered_coords:
patch = image[coords[0] - wid: coords[0] + wid + 1, coords[1] - wid: coords[1] + wid + 1].flatten()
desc.append(patch)
return desc
下面代码是计算互相关矩阵和筛选大于阈值的点,为了更好的选择匹配点,先从第一幅图向第二幅图匹配,然后再反过来匹配,去除非对称的匹配:
def match(desc1, desc2, threshold=0.5):
'''
计算互相关矩阵和筛选大于阈值的点
:param desc1:
:param desc2:
:param threshold:
:return:
'''
n = len(desc1[0])
# 互相关矩阵的计算和筛选
d = -np.ones((len(desc1), len(desc2)))
for i in range(len(desc1)):
for j in range(len(desc2)):
d1 = (desc1[i] - mean(desc1[i])) / std(desc1[i])
d2 = (desc2[j] - mean(desc2[j])) / std(desc2[j])
ncc_value = sum(d1 * d2) / (n - 1)
if ncc_value > threshold:
d[i, j] = ncc_value
# 排序
ndx = np.argsort(-d)
matchscores = ndx[:, 0]
return matchscores
def match_twosided(desc1, desc2, threshold=0.5):
'''
两边对称的匹配,删除不匹配的点
:param desc1:
:param desc2:
:param threshold:
:return:
'''
matches_12 = match(desc1, desc2, threshold)
matches_21 = match(desc2, desc1, threshold)
ndx_12 = where(matches_12 > 0)[0]
# 去除不对称的匹配
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[matches_12
] != n:
matches_12
= -1
return matches_12
最后我们在图片上用连接线显示匹配点:
def appendimages(im1, im2):
'''
将图像拼接成一幅大图像
:param im1:
:param im2:
:return:
'''
row1 = im1.shape[0]
row2 = im2.shape[0]
if row1 < row2:
im1 = concatenate((im1, zeros((row2 - row1, im1.shape[1]))), axis=0)
elif row1 > row2:
im2 = concatenate((im2, zeros((row1 - row2, im2.shape[1]))), axis=0)
return concatena
a235
te((im1, im2), axis=1)
def plot_matches(im1, im2, losc1, losc2, matchscores, show_below=True):
'''
显示图像匹配点之间的连接线
:param im1:
:param im2:
:param losc1:
:param losc2:
:param matchscores:
:param show_below:
:return:
'''
im3 = appendimages(im1, im2)
if show_below:
im3 = vstack((im3, im3))
imshow(im3)
cols1 = im1.shape[1]
for i, m in enumerate(matchscores):
if m > 0:
plot([losc1[i][1], losc2[m][1] + cols1], [losc1[i][0], losc2[m][0]], 'c')
axis('off')
最后附上全部代码和效果图:
# coding=UTF-8
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from pylab import *
from scipy.ndimage import filters
def compute_harris_response(im, sigma=3):
'''
对每个像素值计算Harris角点检测器响应函数
:param im:
:param sigma:
:return:
'''
# 计算导数
im_x = np.zeros(im.shape)
im_y = np.zeros(im.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(im, (sigma, sigma), (0, 1), im_x)
filters.gaussian_filter(im, (sigma, sigma), (1, 0), im_y)
# 计算Harris矩阵分量
Ixx = filters.gaussian_filter(im_x * im_x, sigma)
Ixy = filters.gaussian_filter(im_x * im_y, sigma)
Iyy = filters.gaussian_filter(im_y * im_y, sigma)
# 计算特征值和迹
Idet = Ixx * Iyy - Ixy ** 2
Itrace = Ixx + Iyy
return Idet / Itrace
def get_harris_points(harrisim, min_dist=10, threshold=0.1):
'''
从Harrris响应图像中筛选角点
:param harrisim:
:param min_dist:
:param threshold:
:return:
'''
corner_threshold = harrisim.max() * threshold
harrisim_t = (harrisim > corner_threshold) * 1
# 获得候选点的坐标和对应的值
coords = np.array(harrisim_t.nonzero()).T
candidate_values = [harrisim[c[0], c[1]] for c in coords]
# 对候选点排序
index = np.argsort(candidate_values)
# 将可行点存储在数组中
allowed_locations = np.zeros(harrisim.shape)
allowed_locations[min_dist:-min_dist, min_dist:-min_dist] = 1
# 按照最小间距原则选择最佳Harris角点
filtered_coords = []
for i in index:
if allowed_locations[coords[i,0], coords[i,1]] == 1:
filtered_coords.append(coords[i])
allowed_locations[(coords[i, 0]-min_dist):(coords[i, 0]+min_dist), (coords[i, 1]-min_dist):(coords[i, 1]+min_dist)] = 0
return filtered_coords
def plot_corner_points(image, filtered_coords ):
'''
绘制图像中的角点
:param image:
:param filtered_coords:
:return:
'''
imshow(image)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords], [p[0] for p in filtered_coords], '*')
axis('off')
def get_descriptors(image, filtered_coords, wid=5):
'''
对每个兴趣点,返回周围2*wid+1个像素的值
:param image:
:param filtered_coordes:
:param wid:
:return:
'''
desc = []
for coords in filtered_coords:
patch = image[coords[0] - wid: coords[0] + wid + 1, coords[1] - wid: coords[1] + wid + 1].flatten()
desc.append(patch)
return desc
def match(desc1, desc2, threshold=0.5):
'''
计算互相关矩阵和筛选大于阈值的点
:param desc1:
:param desc2:
:param threshold:
:return:
'''
n = len(desc1[0])
# 互相关矩阵的计算和筛选
d = -np.ones((len(desc1), len(desc2)))
for i in range(len(desc1)):
for j in range(len(desc2)):
d1 = (desc1[i] - mean(desc1[i])) / std(desc1[i])
d2 = (desc2[j] - mean(desc2[j])) / std(desc2[j])
ncc_value = sum(d1 * d2) / (n - 1)
if ncc_value > threshold:
d[i, j] = ncc_value
# 排序
ndx = np.argsort(-d)
matchscores = ndx[:, 0]
return matchscores
def match_twosided(desc1, desc2, threshold=0.5):
'''
两边对称的匹配,删除不匹配的点
:param desc1:
:param desc2:
:param threshold:
:return:
'''
matches_12 = match(desc1, desc2, threshold)
matches_21 = match(desc2, desc1, threshold)
ndx_12 = where(matches_12 > 0)[0]
# 去除不对称的匹配
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[matches_12
] != n:
matches_12
= -1
return matches_12
def appendimages(im1, im2):
'''
将图像拼接成一幅大图像
:param im1:
:param im2:
:return:
'''
row1 = im1.shape[0]
row2 = im2.shape[0]
if row1 < row2:
im1 = concatenate((im1, zeros((row2 - row1, im1.shape[1]))), axis=0)
elif row1 > row2:
im2 = concatenate((im2, zeros((row1 - row2, im2.shape[1]))), axis=0)
return concatenate((im1, im2), axis=1)
def plot_matches(im1, im2, losc1, losc2, matchscores, show_below=True):
'''
显示图像匹配点之间的连接线
:param im1:
:param im2:
:param losc1:
:param losc2:
:param matchscores:
:param show_below:
:return:
'''
im3 = appendimages(im1, im2)
if show_below:
im3 = vstack((im3, im3))
imshow(im3)
cols1 = im1.shape[1]
for i, m in enumerate(matchscores):
if m > 0:
plot([losc1[i][1], losc2[m][1] + cols1], [losc1[i][0], losc2[m][0]], 'c')
axis('off')
def function_1():
'''
显示兴趣点
:return:
'''
im = array(Image.open('1.jpg').convert('L'))
harrsim = compute_harris_response(im)
filter_coords1 = get_harris_points(harrsim, 10, 0.1)
filter_coords2 = get_harris_points(harrsim, 10, 0.4)
filter_coords3 = get_harris_points(harrsim, 10, 0.7)
figure()
gray()
subplot(131)
plot_corner_points(im, filter_coords1)
title('threshold = 0.1')
subplot(132)
plot_corner_points(im, filter_coords2)
title('threshold = 0.4')
subplot(133)
plot_corner_points(im, filter_coords3)
title('threshold = 0.7')
show()
def function_2():
'''
检测图像间的匹配点
:return:
'''
wid = 5
im1 = np.array(Image.open('crans_1_small.jpg').convert('L'))
im2 = np.array(Image.open('crans_2_small.jpg').convert('L'))
harrisiim = compute_harris_response(im1, 5)
filtered_coords1 = get_harris_points(harrisiim, wid + 1)
d1 = get_descriptors(im1, filtered_coords1, wid)
harrisiim = compute_harris_response(im2, 5)
filtered_coords2 = get_harris_points(harrisiim, wid + 1)
d2 = get_descriptors(im2, filtered_coords2, wid)
matches = match_twosided(d1, d2, 1)
figure()
gray()
plot_matches(im1, im2, filtered_coords1, filtered_coords2, matches)
show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
function_2()
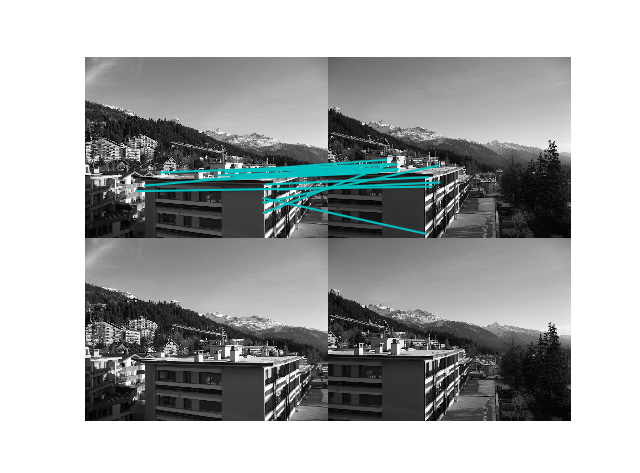

从结果看出,该算法存在一些不正确的匹配,这是由于互相关矩阵描述性不强造成的,同时它还不具有尺度不变性和旋转不变性,实际过程中通常使用更加稳健的算法来进行匹配点检测如SIFT算子等。
Harris角点的描述子通常是周围像素的灰度值,以及用于比较的归一化的互相关矩阵组成。通常两个相同大小的像素块
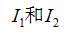
的相关矩阵的定义如下:
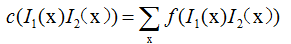
其中
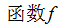
随着实际情况选择,上式取所有像素位置X的和,通常对于互相关矩阵,函数
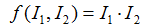
,其中·表示向量乘法,函数值越大表示相似度越高。实际应用中使用的是归一化的互相关矩阵,定义如下:

其中n为像素块的总像素数,μ1和μ2分别是每个像素块的平均像素值,σ1和σ2是每个像素块的标准差,Harris角点检测可以从上一篇博客中找到,链接:传送门
我们将下面的代码加入上一篇博客的代码中,这段代码的作用是获取图像每个兴趣点的像素块:
def get_descriptors(image, filtered_coords, wid=5):
'''
对每个兴趣点,返回周围2*wid+1个像素的值
:param image:
:param filtered_coordes:
:param wid:
:return:
'''
desc = []
for coords in filtered_coords:
patch = image[coords[0] - wid: coords[0] + wid + 1, coords[1] - wid: coords[1] + wid + 1].flatten()
desc.append(patch)
return desc
下面代码是计算互相关矩阵和筛选大于阈值的点,为了更好的选择匹配点,先从第一幅图向第二幅图匹配,然后再反过来匹配,去除非对称的匹配:
def match(desc1, desc2, threshold=0.5):
'''
计算互相关矩阵和筛选大于阈值的点
:param desc1:
:param desc2:
:param threshold:
:return:
'''
n = len(desc1[0])
# 互相关矩阵的计算和筛选
d = -np.ones((len(desc1), len(desc2)))
for i in range(len(desc1)):
for j in range(len(desc2)):
d1 = (desc1[i] - mean(desc1[i])) / std(desc1[i])
d2 = (desc2[j] - mean(desc2[j])) / std(desc2[j])
ncc_value = sum(d1 * d2) / (n - 1)
if ncc_value > threshold:
d[i, j] = ncc_value
# 排序
ndx = np.argsort(-d)
matchscores = ndx[:, 0]
return matchscores
def match_twosided(desc1, desc2, threshold=0.5):
'''
两边对称的匹配,删除不匹配的点
:param desc1:
:param desc2:
:param threshold:
:return:
'''
matches_12 = match(desc1, desc2, threshold)
matches_21 = match(desc2, desc1, threshold)
ndx_12 = where(matches_12 > 0)[0]
# 去除不对称的匹配
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[matches_12
] != n:
matches_12
= -1
return matches_12
最后我们在图片上用连接线显示匹配点:
def appendimages(im1, im2):
'''
将图像拼接成一幅大图像
:param im1:
:param im2:
:return:
'''
row1 = im1.shape[0]
row2 = im2.shape[0]
if row1 < row2:
im1 = concatenate((im1, zeros((row2 - row1, im1.shape[1]))), axis=0)
elif row1 > row2:
im2 = concatenate((im2, zeros((row1 - row2, im2.shape[1]))), axis=0)
return concatena
a235
te((im1, im2), axis=1)
def plot_matches(im1, im2, losc1, losc2, matchscores, show_below=True):
'''
显示图像匹配点之间的连接线
:param im1:
:param im2:
:param losc1:
:param losc2:
:param matchscores:
:param show_below:
:return:
'''
im3 = appendimages(im1, im2)
if show_below:
im3 = vstack((im3, im3))
imshow(im3)
cols1 = im1.shape[1]
for i, m in enumerate(matchscores):
if m > 0:
plot([losc1[i][1], losc2[m][1] + cols1], [losc1[i][0], losc2[m][0]], 'c')
axis('off')
最后附上全部代码和效果图:
# coding=UTF-8
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from pylab import *
from scipy.ndimage import filters
def compute_harris_response(im, sigma=3):
'''
对每个像素值计算Harris角点检测器响应函数
:param im:
:param sigma:
:return:
'''
# 计算导数
im_x = np.zeros(im.shape)
im_y = np.zeros(im.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(im, (sigma, sigma), (0, 1), im_x)
filters.gaussian_filter(im, (sigma, sigma), (1, 0), im_y)
# 计算Harris矩阵分量
Ixx = filters.gaussian_filter(im_x * im_x, sigma)
Ixy = filters.gaussian_filter(im_x * im_y, sigma)
Iyy = filters.gaussian_filter(im_y * im_y, sigma)
# 计算特征值和迹
Idet = Ixx * Iyy - Ixy ** 2
Itrace = Ixx + Iyy
return Idet / Itrace
def get_harris_points(harrisim, min_dist=10, threshold=0.1):
'''
从Harrris响应图像中筛选角点
:param harrisim:
:param min_dist:
:param threshold:
:return:
'''
corner_threshold = harrisim.max() * threshold
harrisim_t = (harrisim > corner_threshold) * 1
# 获得候选点的坐标和对应的值
coords = np.array(harrisim_t.nonzero()).T
candidate_values = [harrisim[c[0], c[1]] for c in coords]
# 对候选点排序
index = np.argsort(candidate_values)
# 将可行点存储在数组中
allowed_locations = np.zeros(harrisim.shape)
allowed_locations[min_dist:-min_dist, min_dist:-min_dist] = 1
# 按照最小间距原则选择最佳Harris角点
filtered_coords = []
for i in index:
if allowed_locations[coords[i,0], coords[i,1]] == 1:
filtered_coords.append(coords[i])
allowed_locations[(coords[i, 0]-min_dist):(coords[i, 0]+min_dist), (coords[i, 1]-min_dist):(coords[i, 1]+min_dist)] = 0
return filtered_coords
def plot_corner_points(image, filtered_coords ):
'''
绘制图像中的角点
:param image:
:param filtered_coords:
:return:
'''
imshow(image)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords], [p[0] for p in filtered_coords], '*')
axis('off')
def get_descriptors(image, filtered_coords, wid=5):
'''
对每个兴趣点,返回周围2*wid+1个像素的值
:param image:
:param filtered_coordes:
:param wid:
:return:
'''
desc = []
for coords in filtered_coords:
patch = image[coords[0] - wid: coords[0] + wid + 1, coords[1] - wid: coords[1] + wid + 1].flatten()
desc.append(patch)
return desc
def match(desc1, desc2, threshold=0.5):
'''
计算互相关矩阵和筛选大于阈值的点
:param desc1:
:param desc2:
:param threshold:
:return:
'''
n = len(desc1[0])
# 互相关矩阵的计算和筛选
d = -np.ones((len(desc1), len(desc2)))
for i in range(len(desc1)):
for j in range(len(desc2)):
d1 = (desc1[i] - mean(desc1[i])) / std(desc1[i])
d2 = (desc2[j] - mean(desc2[j])) / std(desc2[j])
ncc_value = sum(d1 * d2) / (n - 1)
if ncc_value > threshold:
d[i, j] = ncc_value
# 排序
ndx = np.argsort(-d)
matchscores = ndx[:, 0]
return matchscores
def match_twosided(desc1, desc2, threshold=0.5):
'''
两边对称的匹配,删除不匹配的点
:param desc1:
:param desc2:
:param threshold:
:return:
'''
matches_12 = match(desc1, desc2, threshold)
matches_21 = match(desc2, desc1, threshold)
ndx_12 = where(matches_12 > 0)[0]
# 去除不对称的匹配
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[matches_12
] != n:
matches_12
= -1
return matches_12
def appendimages(im1, im2):
'''
将图像拼接成一幅大图像
:param im1:
:param im2:
:return:
'''
row1 = im1.shape[0]
row2 = im2.shape[0]
if row1 < row2:
im1 = concatenate((im1, zeros((row2 - row1, im1.shape[1]))), axis=0)
elif row1 > row2:
im2 = concatenate((im2, zeros((row1 - row2, im2.shape[1]))), axis=0)
return concatenate((im1, im2), axis=1)
def plot_matches(im1, im2, losc1, losc2, matchscores, show_below=True):
'''
显示图像匹配点之间的连接线
:param im1:
:param im2:
:param losc1:
:param losc2:
:param matchscores:
:param show_below:
:return:
'''
im3 = appendimages(im1, im2)
if show_below:
im3 = vstack((im3, im3))
imshow(im3)
cols1 = im1.shape[1]
for i, m in enumerate(matchscores):
if m > 0:
plot([losc1[i][1], losc2[m][1] + cols1], [losc1[i][0], losc2[m][0]], 'c')
axis('off')
def function_1():
'''
显示兴趣点
:return:
'''
im = array(Image.open('1.jpg').convert('L'))
harrsim = compute_harris_response(im)
filter_coords1 = get_harris_points(harrsim, 10, 0.1)
filter_coords2 = get_harris_points(harrsim, 10, 0.4)
filter_coords3 = get_harris_points(harrsim, 10, 0.7)
figure()
gray()
subplot(131)
plot_corner_points(im, filter_coords1)
title('threshold = 0.1')
subplot(132)
plot_corner_points(im, filter_coords2)
title('threshold = 0.4')
subplot(133)
plot_corner_points(im, filter_coords3)
title('threshold = 0.7')
show()
def function_2():
'''
检测图像间的匹配点
:return:
'''
wid = 5
im1 = np.array(Image.open('crans_1_small.jpg').convert('L'))
im2 = np.array(Image.open('crans_2_small.jpg').convert('L'))
harrisiim = compute_harris_response(im1, 5)
filtered_coords1 = get_harris_points(harrisiim, wid + 1)
d1 = get_descriptors(im1, filtered_coords1, wid)
harrisiim = compute_harris_response(im2, 5)
filtered_coords2 = get_harris_points(harrisiim, wid + 1)
d2 = get_descriptors(im2, filtered_coords2, wid)
matches = match_twosided(d1, d2, 1)
figure()
gray()
plot_matches(im1, im2, filtered_coords1, filtered_coords2, matches)
show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
function_2()

从结果看出,该算法存在一些不正确的匹配,这是由于互相关矩阵描述性不强造成的,同时它还不具有尺度不变性和旋转不变性,实际过程中通常使用更加稳健的算法来进行匹配点检测如SIFT算子等。
相关文章推荐
- 【懒懒的计算机视觉笔记之Harris角点检测一】
- 【懒懒的计算机视觉笔记之SIFT角点检测】
- 【计算机视觉】运动目标检测算法文献阅读笔记
- 《OpenCV 3计算机视觉:Python语言实现》学习笔记——目标跟踪中基本运动检测的思考
- 计算机视觉之(一)利用Harris检测子进行角点特征检测(含matlab源码)
- 【懒懒的计算机视觉笔记之单应性变换】
- 计算机视觉目标检测的框架与过程 .
- 斯坦福CS231n—深度学习与计算机视觉----学习笔记 课时14&&15
- 论文笔记:基于视觉显著性检测的图像分类方法
- 计算机视觉笔记(一) 初探计算机视觉
- 计算机视觉标准数据集整理—人脸识别/检测数据集
- python计算机视觉2:图像边缘检测
- 张正友标定法 【计算机视觉学习笔记--双目视觉几何框架系列】
- 视频监控 形态学 OpenCV致力于计算机视觉技术研究(高密度环境下行人检测和统计)
- 【计算机视觉】【视频开发】遗留物检测中的物体遗留和移除检测
- 【计算机视觉】森林火灾检测-2
- PCL—低层次视觉—关键点检测(Harris)
- CS231n-深度学习与计算机视觉-笔记-Lecture3 损失函数和优化
- “计算机视觉”阅读笔记
- 推荐-计算机视觉、图像处理方面的论文阅读笔记
