codeforces Hello 2018 B. Christmas Spruce
2018-01-09 15:30
701 查看
B. Christmas Spruce
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Consider a rooted tree. A rooted tree has one special vertex called the root. All edges are directed from the root. Vertex u is
called a childof vertex v and vertex v is
called a parent of vertex u if there
exists a directed edge from v to u.
A vertex is called a leaf if it doesn't have children and has a parent.
Let's call a rooted tree a spruce if its every non-leaf vertex has at least 3 leaf
children. You are given a rooted tree, check whether it's a spruce.
The definition of a rooted tree can be found here.
Input
The first line contains one integer n — the number of vertices in the tree (3 ≤ n ≤ 1 000).
Each of the next n - 1 lines contains one integer pi (1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1) —
the index of the parent of the i + 1-th vertex (1 ≤ pi ≤ i).
Vertex 1 is the root. It's guaranteed that the root has at least 2 children.
Output
Print "Yes" if the tree is a spruce and "No"
otherwise.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
The first example:
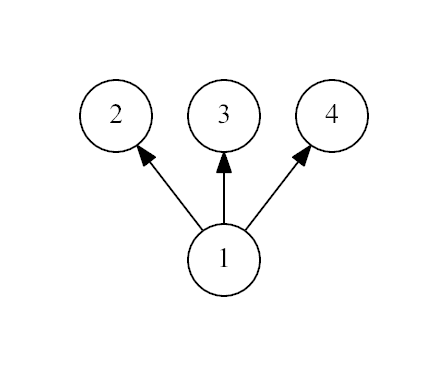
The second example:
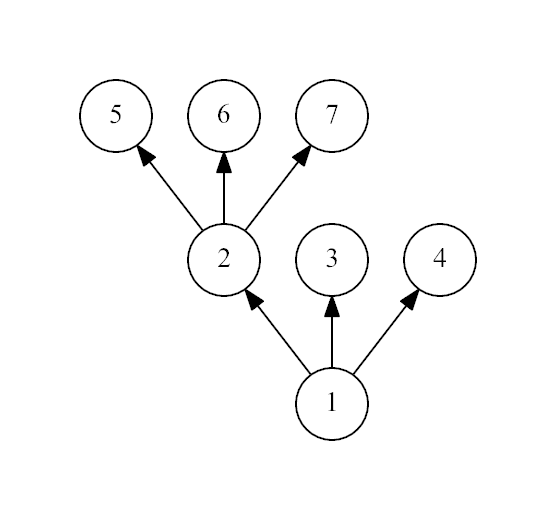
It is not a spruce, because the non-leaf vertex 1 has only 2 leaf
children.
The third example:
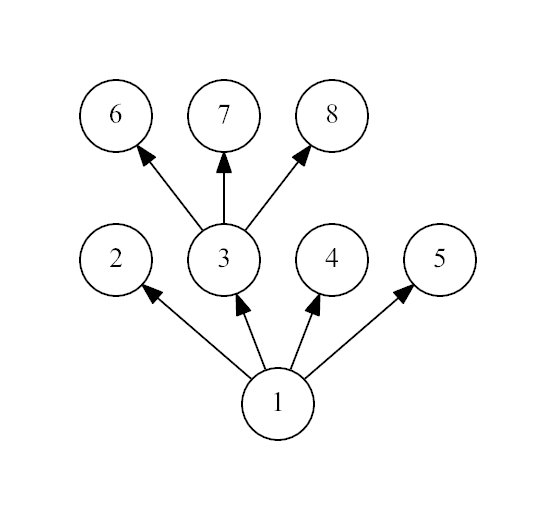
。。。裸奔dfs判断一下。
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
vector<int> vec[1050];
bool dfs(int u) {
if (vec[u].empty())
return true;
int times = 0;
bool res = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < vec[u].size(); ++i) {
int v = vec[u][i];
if (vec[v].empty())
times++;
res &= dfs(v);
}
return (times >= 3) & res;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
int a;
cin >> a;
vec[a].push_back(i);
}
if (dfs(1))
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else
cout << "No" << endl;
}
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Consider a rooted tree. A rooted tree has one special vertex called the root. All edges are directed from the root. Vertex u is
called a childof vertex v and vertex v is
called a parent of vertex u if there
exists a directed edge from v to u.
A vertex is called a leaf if it doesn't have children and has a parent.
Let's call a rooted tree a spruce if its every non-leaf vertex has at least 3 leaf
children. You are given a rooted tree, check whether it's a spruce.
The definition of a rooted tree can be found here.
Input
The first line contains one integer n — the number of vertices in the tree (3 ≤ n ≤ 1 000).
Each of the next n - 1 lines contains one integer pi (1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1) —
the index of the parent of the i + 1-th vertex (1 ≤ pi ≤ i).
Vertex 1 is the root. It's guaranteed that the root has at least 2 children.
Output
Print "Yes" if the tree is a spruce and "No"
otherwise.
Examples
input
4 1 1 1
output
Yes
input
7 1 1 1 2 2 2
output
No
input
8 1 1 1 1 3 3 3
output
Yes
Note
The first example:

The second example:

It is not a spruce, because the non-leaf vertex 1 has only 2 leaf
children.
The third example:

。。。裸奔dfs判断一下。
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
vector<int> vec[1050];
bool dfs(int u) {
if (vec[u].empty())
return true;
int times = 0;
bool res = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < vec[u].size(); ++i) {
int v = vec[u][i];
if (vec[v].empty())
times++;
res &= dfs(v);
}
return (times >= 3) & res;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
int a;
cin >> a;
vec[a].push_back(i);
}
if (dfs(1))
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else
cout << "No" << endl;
}
相关文章推荐
- Codeforces Hello 2018——Party Lemonade(DP)
- Codeforces Hello 2018 D. Too Easy Problems (二分)
- codeforces Hello 2018(A-E)
- codeforces Hello 2018(A-E)
- codeforces Hello 2018(A-E)
- Codeforces Hello 2018
- codeforces Hello 2018(A-E)
- codeforces Hello 2018 C. Party Lemonade(贪心)
- codeforces Hello 2018 C. Party Lemonade(DP+思维)
- Codeforces Hello 2018
- Codeforces Hello 2018 C. Party Lemonade 贪心、优先队列
- Codeforces Hello 2018 [ABC]
- codeforces Hello 2018(A-E)
- Codeforces Hello 2018 - A - Modular Exponentiation
- Codeforces Hello 2018
- codeforces Hello 2018(A-E)
- Codeforces Hello 2018 - B - Christmas Spruce
- Codeforces Hello 2018 D. Too Easy Problems 二分+贪心
- codeforces Hello 2018(A-E)
- Christmas Spruce—codeforces(hello_2018)
