Good Bye 2017
2017-12-31 15:47
246 查看
B. New Year and Buggy Bot
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Bob programmed a robot to navigate through a 2d maze.
The maze has some obstacles. Empty cells are denoted by the character '.', where obstacles are denoted by '#'.
There is a single robot in the maze. It's start position is denoted with the character 'S'. This position has no obstacle in it. There is also a single exit
in the maze. It's position is denoted with the character 'E'. This position has no obstacle in it.
The robot can only move up, left, right, or down.
When Bob programmed the robot, he wrote down a string of digits consisting of the digits 0 to 3, inclusive. He intended for each digit to correspond to a distinct direction, and the robot would follow the directions in order to reach the exit. Unfortunately,
he forgot to actually assign the directions to digits.
The robot will choose some random mapping of digits to distinct directions. The robot will map distinct digits to distinct directions. The robot will then follow the instructions according to the given string in order and chosen mapping. If an instruction would
lead the robot to go off the edge of the maze or hit an obstacle, the robot will crash and break down. If the robot reaches the exit at any point, then the robot will stop following any further instructions.
Bob is having trouble debugging his robot, so he would like to determine the number of mappings of digits to directions that would lead the robot to the exit.
Input
The first line of input will contain two integers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 50),
denoting the dimensions of the maze.
The next n lines will contain exactly m characters
each, denoting the maze.
Each character of the maze will be '.', '#', 'S',
or 'E'.
There will be exactly one 'S' and exactly one 'E' in the
maze.
The last line will contain a single string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 100) —
the instructions given to the robot. Each character of s is a digit from 0 to 3.
Output
Print a single integer, the number of mappings of digits to directions that will lead the robot to the exit.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
For the first sample, the only valid mapping is
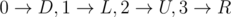
,
where D is down, L is
left, U is up, R is
right.
思路:
给你一串数字,每个数字代表一个方向,让你确定数字代表的方向,看到达E点总共有几个方案
代码:
QAQ24种方案都写出来的纯菜鸡
还有就是搜索了
代码:
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Bob programmed a robot to navigate through a 2d maze.
The maze has some obstacles. Empty cells are denoted by the character '.', where obstacles are denoted by '#'.
There is a single robot in the maze. It's start position is denoted with the character 'S'. This position has no obstacle in it. There is also a single exit
in the maze. It's position is denoted with the character 'E'. This position has no obstacle in it.
The robot can only move up, left, right, or down.
When Bob programmed the robot, he wrote down a string of digits consisting of the digits 0 to 3, inclusive. He intended for each digit to correspond to a distinct direction, and the robot would follow the directions in order to reach the exit. Unfortunately,
he forgot to actually assign the directions to digits.
The robot will choose some random mapping of digits to distinct directions. The robot will map distinct digits to distinct directions. The robot will then follow the instructions according to the given string in order and chosen mapping. If an instruction would
lead the robot to go off the edge of the maze or hit an obstacle, the robot will crash and break down. If the robot reaches the exit at any point, then the robot will stop following any further instructions.
Bob is having trouble debugging his robot, so he would like to determine the number of mappings of digits to directions that would lead the robot to the exit.
Input
The first line of input will contain two integers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 50),
denoting the dimensions of the maze.
The next n lines will contain exactly m characters
each, denoting the maze.
Each character of the maze will be '.', '#', 'S',
or 'E'.
There will be exactly one 'S' and exactly one 'E' in the
maze.
The last line will contain a single string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 100) —
the instructions given to the robot. Each character of s is a digit from 0 to 3.
Output
Print a single integer, the number of mappings of digits to directions that will lead the robot to the exit.
Examples
input
5 6 .....# S....# .#.... .#.... ...E.. 333300012
output
1
input
6 6
......
......
..SE..
......
......
......
01232123212302123021
output
14
input
5 3 ... .S. ### .E. ... 3
output
0
Note
For the first sample, the only valid mapping is
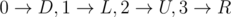
,
where D is down, L is
left, U is up, R is
right.
思路:
给你一串数字,每个数字代表一个方向,让你确定数字代表的方向,看到达E点总共有几个方案
代码:
QAQ24种方案都写出来的纯菜鸡
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#define ll long long
#define maxn 100005
#define mod 1000000007
char s[55][55];
char ss[105];
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n,m;
int sx,sy,ex,ey;
while(cin>>n>>m){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
cin>>s[i][j];
if(s[i][j]=='S'){
sx=i;
sy=j;
}
if(s[i][j]=='E'){
ex=i;
ey=j;
}
}
cin>>ss;
bool flag=true;
int len=strlen(ss);
int ans=0;
int s1=sx,s2=sy;
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='1') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='2') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='3') sx++;//r
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) { ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='1') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='2') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='3') sx--;//l
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='1') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='2') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='3') sx++;//r
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='1') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='2') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='3') sy++;//d
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='1') sx++;//rr
else if(ss[i]=='2') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='3') sx--;//l
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='1') sx++;//rr
else if(ss[i]=='2') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='3') sy++;//d
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='1') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='2') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='3') sx++;//r
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='1') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='2') sx++;//l
else if(ss[i]=='3') sx--;//r
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='1') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='2') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='3') sy--;//u
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='1') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='2') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='3') sx--;//l
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='1') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='2') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='3') sx++;//r
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='1') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='2') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='3') sy--;//u
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='1') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='2') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='3') sy++;//d
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='1') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='2') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='3') sx++;//r
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='1') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='2') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='3') sx++;//r
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='1') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='2') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='3') sy--;//u
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='1') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='2') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='3') sy++;//d
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='1') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='2') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='3') sy--;//u
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='1') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='2') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='3') sy++;//d
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='1') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='2') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='3') sx--;//l
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='1') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='2') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='3') sy--;//u
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='1') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='2') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='3') sx--;//l
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='1') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='2') sy--;//u
else if(ss[i]=='3') sy++;//d
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
if(flag){
sx=s1;
sy=s2;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(ss[i]=='0') sx++;//r
else if(ss[i]=='1') sx--;//l
else if(ss[i]=='2') sy++;//d
else if(ss[i]=='3') sy--;//u
if(s[sx][sy]=='#') break;
if(sx<0||sx>=n||sy<0||sy>=m) break;
if(sx==ex&&sy==ey) {ans++; break;}
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}还有就是搜索了
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
string s;
char ma[55][55];
int ans,n,m,x1,x2,yy,y2,num,look[4],pan[4];//pan记录这个方向有没有定下,look记录确定的方向,如果题目里的1代表实际方向0,那就look【1】=0int a[4]={1,-1,0,0},b[4]={0,0,1,-1};
void dfs(int x,int y,int p)
{//cout<<x<<" "<<y<<" "<<p<<" "<<ans<<endl;
if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m) {return;}
if(ma[x][y]=='#') {return;}
if(ma[x][y]=='E')
{
int ss=0;
for(int i=0;i<=3;i++)
if(look[i]==-1) ss++;
if(ss==1) ans++;//三个方向都已确定,那么只有一种方案
else if(ss==2) ans+=2;
else if(ss==3) ans+=6;
else if(ss==0)ans++;
return;
}
if(p>=num) return;
int now=s[p]-'0';
if(look[now]==-1)
{
for(int i=0;i<=3;i++)
{
if(pan[i]==0)
{
pan[i]=1;
look[now]=i;
dfs(x+a[i],y+b[i],p+1);
look[now]=-1;
pan[i]=0;
//cout<<x<<"!!!!"<<y<<" "<<i<<endl;
}
}
}
else
{
dfs(x+a[look[now]],y+b[look[now]],p+1);
}
}
int main()
{
memset(look,-1,sizeof(look));
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{scanf("%s",ma[i]);
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
if(ma[i][j]=='S') {x1=i;yy=j;}
}
cin>>s;
num=s.size();
dfs(x1,yy,0);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
相关文章推荐
- Good Bye 2017 D.New Year and Arbitrary Arrangement - 数学
- Good Bye 2017 E. New Year and Entity Enumeration
- Codeforces Good Bye 2017
- Codeforces Good Bye 2017 C. New Year and Curling 几何、枚举
- Good Bye 2017 A - New Year and Counting Cards
- EOJ Monthly 2018.2 (Good bye 2017) F 回家咯
- Codeforces-Good Bye 2017 B. New Year and Buggy Bot(模拟)
- Good Bye 2017 E. New Year and Entity Enumeration
- Codeforces Good Bye 2017
- Good Bye 2017 B - New Year and Buggy Bot
- Codeforces Good Bye 2017 908F - New Year and Rainbow Roads 贪心+模拟
- EOJ Monthly 2018.2 (Good bye 2017) B. 无聊的游戏
- Codeforces Good Bye 2017 D. New Year and Arbitrary Arrangement
- Good Bye 2017 D - New Year and Arbitrary Arrangement
- Good Bye 2017-A. New Year and Counting Cards
- codeforces Good Bye 2017
- Good Bye 2017 F-New Year and Rainbow Roads
- Good Bye 2017
- Good Bye 2017-B. New Year and Buggy Bot
- Codeforces Good Bye 2017 Div.2 908A,B
