Linked List Random Node
2017-12-29 00:00
281 查看
问题:
Given a singly linked list, return a random node's value from the linked list. Each node must have the same probability of being chosen.
Follow up:
What if the linked list is extremely large and its length is unknown to you? Could you solve this efficiently without using extra space?
Example:
解决:
① 先统计出链表的长度,然后根据长度随机生成一个位置,然后从开头遍历到这个位置即可。
class Solution { //142ms
ListNode head;
int len;
/** @param head The linked list's head.
Note that the head is guaranteed to be not null, so it contains at least one node. */
public Solution(ListNode head) {
this.head = head;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
len ++;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
/** Returns a random node's value. */
public int getRandom() {
Random random = new Random();
int next = random.nextInt(len);
ListNode cur = head;
while(next != 0){
next --;
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.val;
}
}
蓄水池抽样(Reservoir Sampling )是一个很有趣的问题,它能够在o(n)时间内对n个数据进行等概率随机抽取,例如:从1000个数据中等概率随机抽取出100个。另外,如果数据集合的量特别大或者还在增长(相当于未知数据集合总量),该算法依然可以等概率抽样。
蓄水池抽样:从N个元素中随机的等概率的抽取k个元素,其中N无法确定。
先给出代码:
上述伪代码的意思是:先选中第1到k个元素,作为被选中的元素。然后依次对第k+1至第N个元素做如下操作:
每个元素都有k/x的概率被选中,然后等概率的(1/k)替换掉被选中的元素。其中x是元素的序号。
解法:我们总是选择第一个对象,以1/2的概率选择第二个,以1/3的概率选择第三个,以此类推,以1/m的概率选择第m个对象。当该过程结束时,每一个对象具有相同的选中概率,即1/n,证明如下。
证明:第m个对象最终被选中的概率P = 选择m的概率 * 其后面所有对象不被选择的概率,即
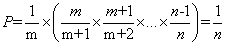
① 链表可能很长,我们没法提前知道长度。所以使用蓄水池抽样来解决,具体步骤如下:
1、初始答案为第一个数,此时链表的下标指向第一个数,即此时第一个数被选中的概率为1;
2、下标后移一位指向第二个数,用Random函数随机抽取0-1的数,抽取的范围是2,抽中1的概率为1/2,如果抽中1,把答案改为此时下标所指的数,否则不改变答案的值。
3、以此类推,用Random函数抽取的范围不断加1,即Random rd = new Random(i),抽取范围为i,从0 -( i-1)中取到 i-1 的概率为1 / i。如果抽中i-1,把答案改为此时下标所指的数,否则不改变答案的值。
4、直到链表为空,得到答案;
第 i 个数被选中的概率为它被选中的概率:1 / i ,乘以后面的数不被选中的概率:[ i / ( i + 1 ) ] * [ ( i + 1 ) / ( i + 2 ) ] *... * [ ( n - 1 ) / ( n )]
即P(第 i 个数被选中) = ( 1 / i )* [ i / ( i + 1 ) ] * [ ( i + 1 ) / ( i + 2 ) ] *... * [ ( n - 1 ) / ( n)] = 1 / n 。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {//135ms
ListNode head;
Random random;
/** @param head The linked list's head.
Note that the head is guaranteed to be not null, so it contains at least one node. */
public Solution(ListNode head) {
this.head = head;
random = new Random();
}
/** Returns a random node's value. */
public int getRandom() {
ListNode res = null;
ListNode cur = head;
for (int i = 1;cur != null;i ++){
if (random.nextInt(i) == 0){
res = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return res.val;
}
}
/**
* Your Solution object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Solution obj = new Solution(head);
* int param_1 = obj.getRandom();
*/
Given a singly linked list, return a random node's value from the linked list. Each node must have the same probability of being chosen.
Follow up:
What if the linked list is extremely large and its length is unknown to you? Could you solve this efficiently without using extra space?
Example:
// Init a singly linked list [1,2,3]. ListNode head = new ListNode(1); head.next = new ListNode(2); head.next.next = new ListNode(3); Solution solution = new Solution(head); // getRandom() should return either 1, 2, or 3 randomly. Each element should have equal probability of returning. solution.getRandom();
解决:
① 先统计出链表的长度,然后根据长度随机生成一个位置,然后从开头遍历到这个位置即可。
class Solution { //142ms
ListNode head;
int len;
/** @param head The linked list's head.
Note that the head is guaranteed to be not null, so it contains at least one node. */
public Solution(ListNode head) {
this.head = head;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
len ++;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
/** Returns a random node's value. */
public int getRandom() {
Random random = new Random();
int next = random.nextInt(len);
ListNode cur = head;
while(next != 0){
next --;
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.val;
}
}
蓄水池抽样(Reservoir Sampling )是一个很有趣的问题,它能够在o(n)时间内对n个数据进行等概率随机抽取,例如:从1000个数据中等概率随机抽取出100个。另外,如果数据集合的量特别大或者还在增长(相当于未知数据集合总量),该算法依然可以等概率抽样。
蓄水池抽样:从N个元素中随机的等概率的抽取k个元素,其中N无法确定。
先给出代码:
Init : a reservoir with the size: k for i= k+1 to N M=random(1, i); if( M < k) SWAP the Mth value and ith value end for
上述伪代码的意思是:先选中第1到k个元素,作为被选中的元素。然后依次对第k+1至第N个元素做如下操作:
每个元素都有k/x的概率被选中,然后等概率的(1/k)替换掉被选中的元素。其中x是元素的序号。
解法:我们总是选择第一个对象,以1/2的概率选择第二个,以1/3的概率选择第三个,以此类推,以1/m的概率选择第m个对象。当该过程结束时,每一个对象具有相同的选中概率,即1/n,证明如下。
证明:第m个对象最终被选中的概率P = 选择m的概率 * 其后面所有对象不被选择的概率,即
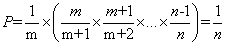
① 链表可能很长,我们没法提前知道长度。所以使用蓄水池抽样来解决,具体步骤如下:
1、初始答案为第一个数,此时链表的下标指向第一个数,即此时第一个数被选中的概率为1;
2、下标后移一位指向第二个数,用Random函数随机抽取0-1的数,抽取的范围是2,抽中1的概率为1/2,如果抽中1,把答案改为此时下标所指的数,否则不改变答案的值。
3、以此类推,用Random函数抽取的范围不断加1,即Random rd = new Random(i),抽取范围为i,从0 -( i-1)中取到 i-1 的概率为1 / i。如果抽中i-1,把答案改为此时下标所指的数,否则不改变答案的值。
4、直到链表为空,得到答案;
第 i 个数被选中的概率为它被选中的概率:1 / i ,乘以后面的数不被选中的概率:[ i / ( i + 1 ) ] * [ ( i + 1 ) / ( i + 2 ) ] *... * [ ( n - 1 ) / ( n )]
即P(第 i 个数被选中) = ( 1 / i )* [ i / ( i + 1 ) ] * [ ( i + 1 ) / ( i + 2 ) ] *... * [ ( n - 1 ) / ( n)] = 1 / n 。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {//135ms
ListNode head;
Random random;
/** @param head The linked list's head.
Note that the head is guaranteed to be not null, so it contains at least one node. */
public Solution(ListNode head) {
this.head = head;
random = new Random();
}
/** Returns a random node's value. */
public int getRandom() {
ListNode res = null;
ListNode cur = head;
for (int i = 1;cur != null;i ++){
if (random.nextInt(i) == 0){
res = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return res.val;
}
}
/**
* Your Solution object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Solution obj = new Solution(head);
* int param_1 = obj.getRandom();
*/
相关文章推荐
- 382. Linked List Random Node
- linked-list-random-node
- Linked List Random Node
- 382. Linked List Random Node
- Linked List Random Node问题及解法
- 148. Linked List Random Node
- Linked List Random Node
- leetcode:Linked List Random Node…
- LeetCode-Linked List Random Node
- Linked List Random Node -- LeetCode
- Linked List Random Node
- Linked List Random Node
- 382. Linked List Random Node
- 【Leetcode】Linked List Random Node
- LeetCode - Linked List Random Node
- LeetCode-难题集之Linked List Random Node
- 382. Linked List Random Node
- LeetCode 382: Linked List Random Node
- [382]Linked List Random Node
- Linked List Random Node
