设计模式之策略设计模式
2017-12-21 22:15
344 查看
1. 策略设计模式介绍
策略设计模式定义了一系列算法,并将每一个算法封装起来,而且使他们可以相互替换。策略设计模式让算法独立与使用它的客户而独立变化。
2. 策略设计模式使用场景
针对同一类型的问题的多种处理方式,仅仅是具体行为有差别时。需要安全地封装多种同一类型的操作时。
出现同一抽象类有多个子类,而又需要使用if-else 或者switch-case来选择具体子类时。
3. 策略设计模式的UML类图
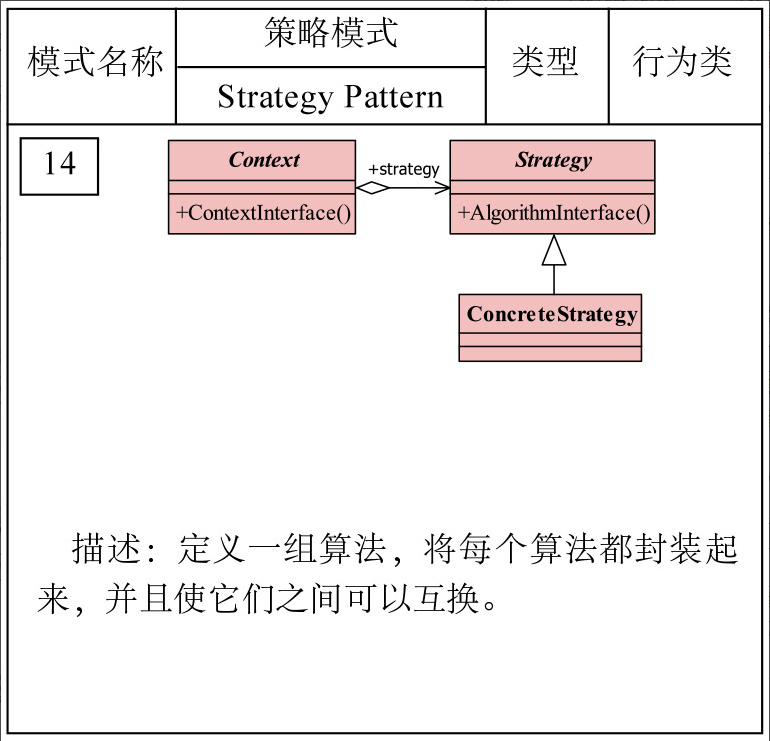
4. 策略设计模式的简单实现
情景描述:现在有一个计算的案例,如果满足了大于0的条件,那么就采用method1()的算法,如果满足了小于0的情况,就采用method2的算法。一般情况下我们会采用如下形式:public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
int result1 = calculator.method1(1);
int result2 = calculator.method2(-1);
System.out.println("result1:" + result1);
System.out.println("result2:" + result2);
}
/**
* 计算
* 采用if-else 的方式
*
* @return
*/
public int calculate(int param) {
int result;
if (param > 0) {
result = method1(param);
} else {
result = method2(param);
}
return result;
}
/**
* 方案1
*
* @return
*/
private int method1(int param) {
return 1;
}
/**
* 方案2
*
* @return
*/
private int method2(int param) {
return -1;
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
如上述代码所示,加入现在又出现了一种情况,等于0时,采用method3算法,那么我们就必须修改if-else,同时加入method3()的具体实现。
假如我们采用策略设计模式,代码如下所示:
首先定义一个接口:CalculateStrategy
public interface CalculateStrategy {
int method();
}12
3
接着所有的method1、method2方法将实现此接口,同时给出具体的实现算法。
public class Method1Stategy implements CalculateStrategy {
@Override
public int method() {
return 1;
}
}
public class Method2Stategy implements CalculateStrategy {
@Override
public int method() {
return -1;
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
在Calculator类中,有两个方法setStrategy(CalculateStrategy strategy) 、calculate() ,用户首先设置策略,设置完成后,调用calculate()方法,calculate()方法调用具体策略的具体算法。
public class Calculator {
CalculateStrategy calculateStrategy;
/**
* 设置策略
*
* @param strategy
*/
public void setStrategy(CalculateStrategy strategy) {
this.calculateStrategy = strategy;
}
public int calculate() {
return calculateStrategy.method();
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
测试类:Client
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
//设置策略1
calculator.setStrategy(new Method1Stategy());
int result1 = calculator.calculate();
System.out.println("result1:" + result1);
calculator.setStrategy(new Method2Stategy());
int result2 = calculator.calculate();
System.out.println("result2:" + result2);
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
现在如果我们想加入新的算法,只需要实现CalculateStrategy这个接口,同时通过calculator.setStrategy()即可切换算法,不必修改if-else等等。
通过上述代码我们可以看到两者的区别,前者采用了if-else的方式,简单、单一,但是代码臃肿,难以升级维护;后者建立了抽象,将不同的策略构成各自的具体的策略实现,通过设置不同的策略实现算法的替换,增强了系统的可读性、维护性、可拓展性。
5. 策略设计模式在Android源码中
其实我们平时使用的属性动画,内部的实现原理采用时插值器(TimeInterpolator)实现的,也叫时间插值器。 当我们通过如下代码设置插值器时:
animation.setInterpolator();1
我们来看看,它内部做了什么?
public abstract class Animation implements Cloneable {
public void setInterpolator(Interpolator i) {
mInterpolator = i;
}
public Interpolator getInterpolator() {
return mInterpolator;
}
/**
* Gets the transformation to apply at a specified point in time. Implementations of this
* method should always replace the specified Transformation or document they are doing
* otherwise.
*
*/
public boolean getTransformation(long currentTime, Transformation outTransformation) {
//省略
final float interpolatedTime = mInterpolator.getInterpolation(normalizedTime);
//省略
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
在内部保留了插值器的引用。
此外这里面有一个重要的方法getTransformation()。
在这个方法里面,会调用插值器的 getInterpolation(normalizedTime), 它的作用就是根据时间的流逝的计算出当前属性改变的百分比。
这个相当于策略设计模式中的接口的方法。
它的代码如下,实际上确实也是一个接口,相当于我们上面例子的CalculateStrategy这个接口。
TimeInterpolator代码如下
public interface TimeInterpolator {
float getInterpolation(float input);
}12
3
4
5
Interpolator代码如下:
public interface Interpolator extends TimeInterpolator {
}12
3
BaseInterpolator代码如下:
abstract public class BaseInterpolator implements Interpolator {
}12
3
所以我们小结一下:
BaeInterpolator 继承自Interpolator,Interpolator继承自TimeInterpolator。
TimeInterpolator接口里面有
float getInterpolation(float input);
所以,三个具体的插值器直接继承自BaseInterpolator,并实现各自的getInterpolation方法即可。
然后我们可以看看其他三个插值器的具体实现:
* LinearInterpolator如下:
public class LinearInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
public LinearInterpolator() {
}
public LinearInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
}
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
return input;
}
/** @hide */
@Override
public long createNativeInterpolator() {
return NativeInterpolatorFactoryHelper.createLinearInterpolator();
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
AccelerateInterpolator如下:
@HasNativeInterpolator
public class AccelerateInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
private final float mFactor;
private final double mDoubleFactor;
//省略不相关代码
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
if (mFactor == 1.0f) {
return input * input;
} else {
return (float)Math.pow(input, mDoubleFactor);
}
}
/** @hide */
@Override
public long createNativeInterpolator() {
return NativeInterpolatorFactoryHelper.createAccelerateInterpolator(mFactor);
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
DecelerateInterpolator 代码如下:
public class DecelerateInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
float result;
if (mFactor == 1.0f) {
result = (float)(1.0f - (1.0f - input) * (1.0f - input));
} else {
result = (float)(1.0f - Math.pow((1.0f - input), 2 * mFactor));
}
return result;
}
private float mFactor = 1.0f;
/** @hide */
@Override
public long createNativeInterpolator() {
return NativeInterpolatorFactoryHelper.createDecelerateInterpolator(mFactor);
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
我们发现上述的三个插值器都实现了BaseInterpolator这个接口。三个类里面getInterpolation()的具体实现又各不相同。通过设置不同的插值器,实现不同的效果。
所以我们的属性动画采用的就是策略设计模式。
6. 策略设计模式在Android开发中
google的网络请求框架volley,里面设置请求超时策略,用到的就是策略设计模式。RequestQueue requestQueue = Volley.newRequestQueue(MainActivity.this);
StringRequest stringRequest = new StringRequest(Request.Method.GET, "http://www.baidu.com", new Response.Listener<String>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(String response) {
}
}, new Response.ErrorListener() {
@Override
public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {
}
});
//给请求设置超时重连策略
stringRequest.setRetryPolicy(new DefaultRetryPolicy());
requestQueue.add(stringRequest);12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
DefaultRetryPolicy是默认请求超时策略,我们可以根据不同的需求,定制不同的策略。只需要设置相关参数即可。
//定制请求超时重连策略
stringRequest.setRetryPolicy(new DefaultRetryPolicy(STRING_TIMEOUT_MS, STRING_MAX_RETRIES, STRING_BACKOFF_MULT)))
DefaultRetryPolicy 继承自接口:RetryPolicy
public interface RetryPolicy {
public int getCurrentTimeout();
public int getCurrentRetryCount();
public void retry(VolleyError error) throws VolleyError;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
在setRetryPolicy()方法中,保留了我们之前设置的超时重连策略。并且在getTimeoutMs()方法中,返回了超时重连策略的超时时间。
public abstract class Request<T> implements Comparable<Request<T>> {
/** The retry policy for this request. */
private RetryPolicy mRetryPolicy;
public Request<?> setRetryPolicy(RetryPolicy retryPolicy) {
mRetryPolicy = retryPolicy;
return this;
}
public final int getTimeoutMs() {
return mRetryPolicy.getCurrentTimeout();
}
public RetryPolicy getRetryPolicy() {
return mRetryPolicy;
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
所以,当通过setRetryPolicy()方法设置不同的超时重连策略,就会返回不同的参数,达到不同的效果。
此外,Adapter也是一个策略模式,我们平时在开发中,一般情况下会继承自BaseAdapter,然后实现不同的View返回,当我们的数据源不同时,getView返回不同的View时,可以通过切换不同的adapter,达到切换View视图的效果。具体代码就不做分析了。
7. 总结
策略设计模式主要用来分离算法,在相同的行为抽象下有不同的具体实现策。这个模式很好地演示了开闭原则,也就是定义抽象,注入不同的实现,从而达到很好的扩展性。优点:
结构清晰明了,使用简单直观
耦合度相对而言较低,扩展方便。
操作封装业更为彻底,数据更为安全
缺点:
随着策略的增加,子类会变得繁多。
相关文章推荐
- 设计模式_策略模式
- 理解js设计模式之策略模式
- 设计模式:策略模式
- 设计模式之——策略模式
- 设计模式--行为型--策略模式
- 设计模式——简单工厂+策略模式
- 设计模式学习--策略模式
- 理解设计模式之策略模式
- 设计模式-策略模式(Strategy)
- 23种java设计模式之策略模式
- 用C++实现设计模式中的策略模式
- 设计模式(21)-行为型-策略模式(Strategy)
- c# 设计模式:策略模式
- Java设计模式透析之 —— 策略(Strategy)
- 设计模式—策略模式
- C语言设计模式之策略模式
- java设计模式学习笔记之策略模式
- 设计模式(8)之策略模式
- Java与设计模式-策略模式
- 设计模式之策略模式
