Java 作业 1202/1203
2017-12-07 23:32
357 查看
多线程 一、判断题(T为正确,F为错误),每题1分 1.如果线程死亡,它便不能运行。(T) 2.在Java中,高优先级的可运行线程会抢占低优先级线程。(T) 3.线程可以用yield方法使低优先级的线程运行。(F) 4...程序开发者必须创建一个线程去管理内存的分配。(F) 5.一个线程在调用它的start方法,之前,该线程将一直处于出生期。(T) 6.当调用一个正在进行线程的stop( )方法时,该线程便会进入休眠状态。(F) 7.一个线程可以调用yield方法使其他线程有机会运行。(T) 8.多线程没有安全问题(F) 9.多线程安全问题的解决方案可以使用Lock提供的具体的锁对象操作(T) 10.Stop()方法是终止当前线程的一种状态(T) 二、选择题(不定项选择题),每题2分 1.Java语言中提供了一个▁D线程,自动回收动态分配的内存。 A.异步 B.消费者 C.守护 D.垃圾收集 2.Java语言避免了大多数的▁C错误。 A.数组下标越界 B.算术溢出 C.内存泄露 D.非法的方法参数 3.有三种原因可以导致线程不能运行,它们是▁ACD。 A.等待 B.阻塞 C.休眠 D.挂起及由于I/O操作而阻塞 4.当▁A方法终止时,能使线程进入死亡状态。 A.run B.setPrority//更改线程优先级 C.yield//暂停当前线程的执行 执行其他线程 D.sleep//线程休眠 5.用▁B方法可以改变线程的优先级。 A.run B.setPrority C.yield D.sleep 6.线程通过▁C▁方法可以使具有相同优先级线程获得处理器。 A.run B.setPrority C.yield D.sleep 7.线程通过▁D▁方法可以休眠一段时间,然后恢复运行。 A.run B.setPrority C.yield D.sleep 8.方法resume( )负责重新开始▁▁D线程的执行。 A.被stop( )方法停止 B.被sleep( )方法停止 C.被wait( )方法停止 D.被suspend( )方法停止 9.▁B C D▁方法可以用来暂时停止当前线程的运行。 A.stop( ) B.sleep( ) C.wait( ) D.suspend( ) 10.请问下列哪些类是定义在java.io包中的抽象类(A B D ) A.InputStream B.OutputStream C.PrintStream D.Reader E.FileInputStream F.FileWriter 三、简述题,每题5分 1.简述程序、进程和线程之间的关系?什么是多线程程序? 一个程序可以有多个进程 一个进程可以有多个线程 多线程: 一个进程里开启了多个线程,每个线程都在抢占CPU的执行权 3.什么是线程调度?Java的线程调度采用什么策略? 按照一定的策略将CPU的执行权分配给线程 时间片轮转加优先级 4.如何在Java程序中实现多线程? 多线程的实现方式1: 1) 创建一个自定义类,继承Thread类 2) 重写自定义类中的run()方法 3) 在主程序中,创建自定义的类的对象,通过star()方法启动它 多线程的实现方式2: 1) 自定义类,该类实现Runnable接口 2) 实现接口中的run()方法 3 在主程序中,创建该类对象的实例 4) 再创建Thread类的对象,将步骤3中创建的对象当做参数传递进去 5) 通过star()方法启动它 多线程实现的方式3: 1)自定义类中实现Callable接口,实现call()方法 2)创建线程池对象public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) 参数是直接指定在当前线程池中有多少个线程 3)<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) 该返回值表示:异步计算的结果! Threadpool.submit(new MyCallable()) 4)Threadpool.shutdown() 结束线程池 5.试简述Thread类的子类或实现Runnable接口两种方法的异同? 相同: 都重写了run方法 都可以实现多线程 不同; Thread类子类实现多线程是通过创建子类对象然后调用star方法 实现Runnable接口是创建子接口对象,然后将对象当做参数传入到Thread对象的构造方法中,再调用star方法 6.说明缓冲流的优点和原理 优点: 节省内存 速度快 原理; 创建一个缓冲区 将数据放到缓冲区里 8:在Java中wait()和sleep()方法的不同? Wait是让当前线程等待 sleep是过...秒之后执行 9:Java中Runnable和Callable有什么不同? . Runnable接口不用写泛型,Callable要写泛型 Runnable实现run方法 Callable实现call方法 四、程序设计题 1.编写一个应用程序,在线程同步的情况下来实现“生产者―消费者”问题。 2.修改上题,由于各个线程是异步运行的,因此无法预计其相对速度,为了使生产者能够不断地生产,可以使用循环缓冲区,保证有足够多的内存区保存更多的产品。(生产者——仓库——消费者) 3 : 1)将若干个Student对象;若干个Teacher对象,写出到d:/0404/a.txt中, 2)将该文件中所有的Student对象反序列化回来,装入List,所有的Teacher对象反序列化回来装入另一个List 4:实现字符串和字节数组之间的相互转换,比如:将字符串”西部开源技术中心xbkyjszx”转换为字节数组,并将字节数组再转换回字符串! 5:用Java编程一个会导致死锁的程序,你将怎么解决?请你设计 6:递归实现输入任意目录,列出文件以及文件夹
编程题:
package org.westos.Homework;
public class Homework01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
GetThread gt = new GetThread(s);
SetThread st = new SetThread(s);
Thread t1 = new Thread(gt);
Thread t2 = new Thread(st);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
package org.westos.Homework;
public class GetThread implements Runnable{
private Student s;
public GetThread (Student s) {
this.s = s;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true) {
e815
synchronized (s) {
if(!s.flag) {
try {
s.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
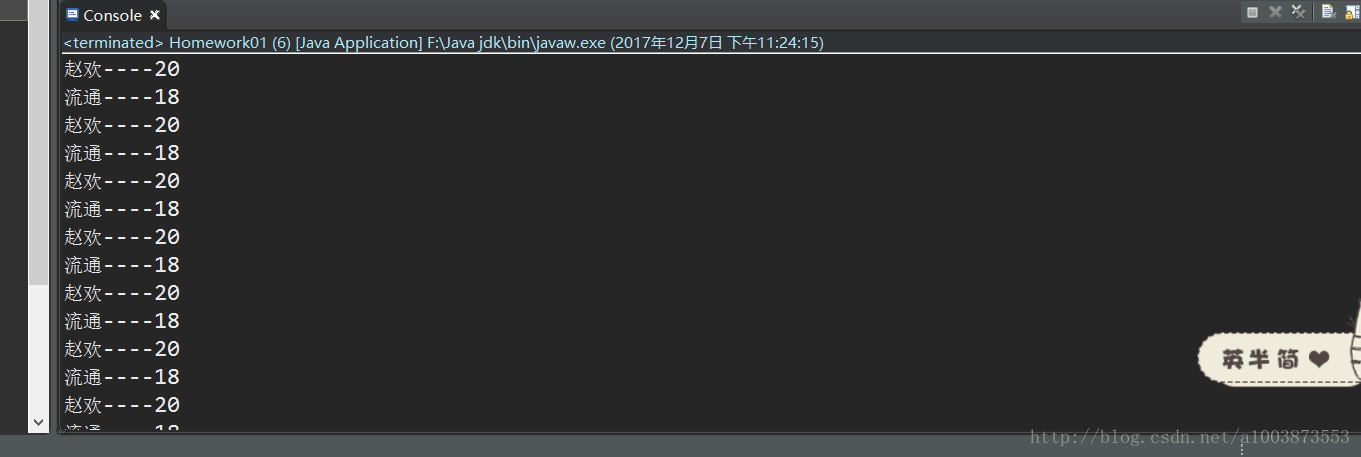
System.out.println(s.name+"----"+s.age);
s.flag = false;
s.notify();
}
}
}
}
package org.westos.Homework;
public class SetThread implements Runnable{
private Student s;
public SetThread (Student s) {
this.s = s;
}
private int x = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true) {
synchronized (s) {
if(s.flag) {
try {
s.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(x%2==0) {
s.name = "流通";
s.age = 18;
}else {
s.name = "赵欢";
s.age = 20;
}
x++;
s.flag = true;
s.notify();
}
}
}
}
package org.westos.Homework;
public class Student {
String name;
int age;
boolean flag;
}
package org.westos.Homework02;
public class Homework01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student("流通",18,100);
GetThread gt = new GetThread(s);
SetThread st = new SetThread(s);
Thread t1 = new Thread(gt);
Thread t2 = new Thread(st);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
package org.westos.Homework02;
public class GetThread implements Runnable {
private Student s;
public GetThread(Student s) {
this.s = s;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (s) {
if (s.number <= 0) {
try {
s.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
s.number--;
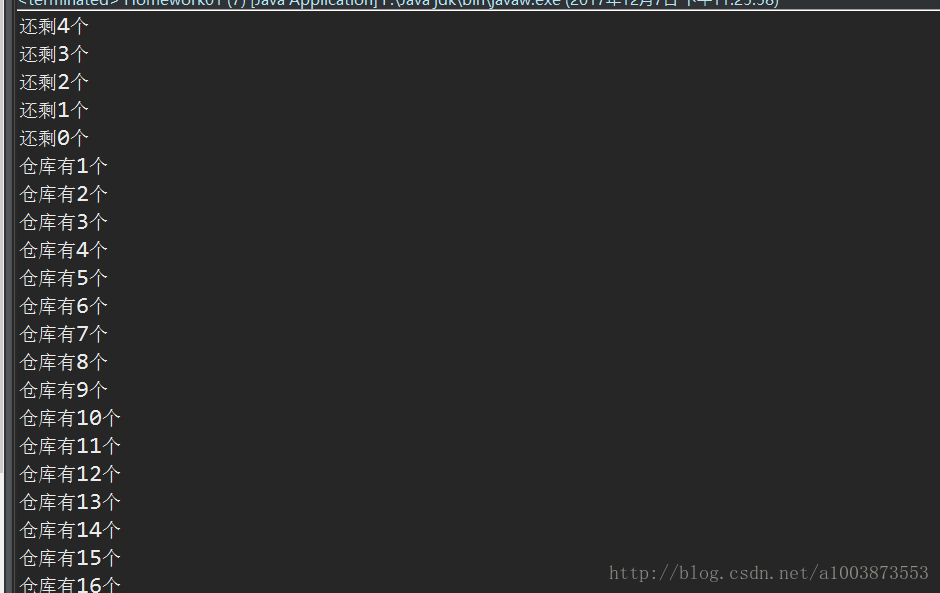
System.out.println("还剩" + s.number + "个");
s.notify();
}
}
}
}
package org.westos.Homework02;
public class SetThread implements Runnable {
private Student s;
public SetThread(Student s) {
this.s = s;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (s) {
if (s.number >= 300) {
try {
s.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
s.number++;
System.out.println("仓库有" + s.number + "个");
s.notify();
}
}
}
}
package org.westos.Homework02;
public class Student {
String name;
int age;
int number;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, int number) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.number = number;
}
public String toString() {
return name+"--"+age;
}
}
package org.westos.Homework03;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* 3 : 1)将若干个Student对象;若干个Teacher对象,写出到d:/0404/a.txt中,
* 2)将该文件中所有的Student对象反序列化回来,装入List,所有的Teacher对象反序列化回来装入另一个List
*/
public class Homework01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
method1();
method2();
}
private static void method2() throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\0404\\a.txt"));
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
ArrayList<Student> al1 = new ArrayList<Student>();
ArrayList<Teacher> al2 = new ArrayList<Teacher>();
al = (ArrayList) ois.readObject();
for (Object a : al) {
if (a instanceof Student) {
al1.add((Student) a);
} else {
al2.add((Teacher) a);
}
}
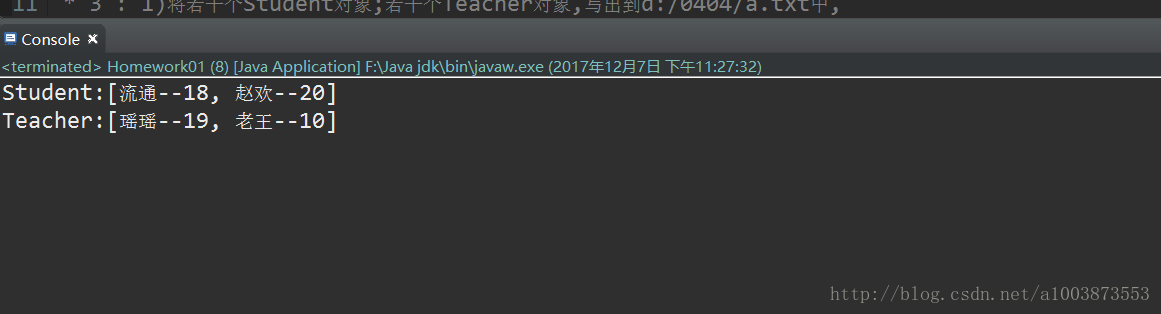
System.out.println("Student:" + al1);
System.out.println("Teacher:" + al2);
}
private static void method1() throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\0404\\a.txt"));
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.add(new Student("流通", 18));
al.add(new Student("赵欢", 20));
al.add(new Teacher("瑶瑶", 19));
al.add(new Teacher("老王", 10));
oos.writeObject(al);
oos.close();
}
}
package org.westos.Homework04;
/**
* :实现字符串和字节数组之间的相互转换,比如:将字符串”西部开源技术中心xbkyjszx”转换为字节数组, 并将字节数组再转换回字符串!
*/
public class Homework04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "西部开源技术中心xbkyjszx";
// 字符串转成字节数组
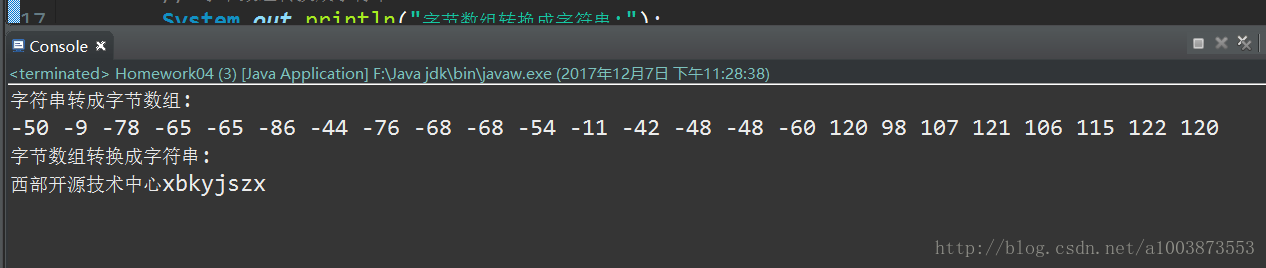
System.out.println("字符串转成字节数组:");
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
for (byte b : bytes) {
System.out.print(b + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 字节数组转换成字符串
System.out.println("字节数组转换成字符串:");
String s = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
package org.westos.Homework05;
/**
* :用Java编程一个会导致死锁的程序,你将怎么解决?请你设计
* 解决办法:
* 不让两个线程请求同一个锁对象
* 锁对象改为this
* */
class Demo1 implements Runnable {
private int a;
private int b;
public Demo1() {
super();
}
public Demo1(int a, int b) {
super();
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (Integer.valueOf(a)) {
synchronized (Integer.valueOf(b)) {
System.out.println(a + b);
}
}
}
}
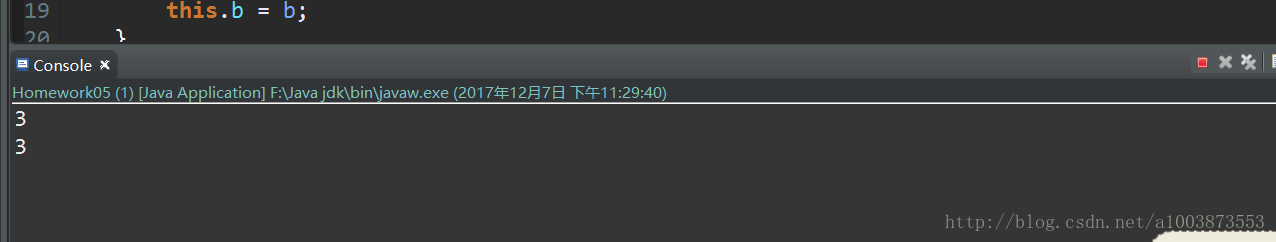
public class Homework05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
new Thread(new Demo1(1, 2)).start();
new Thread(new Demo1(2, 1)).start();
}
}
}
package org.westos.Homework06;
import java.io.File;
/**
* 6:递归实现输入任意目录,列出文件以及文件夹
*/
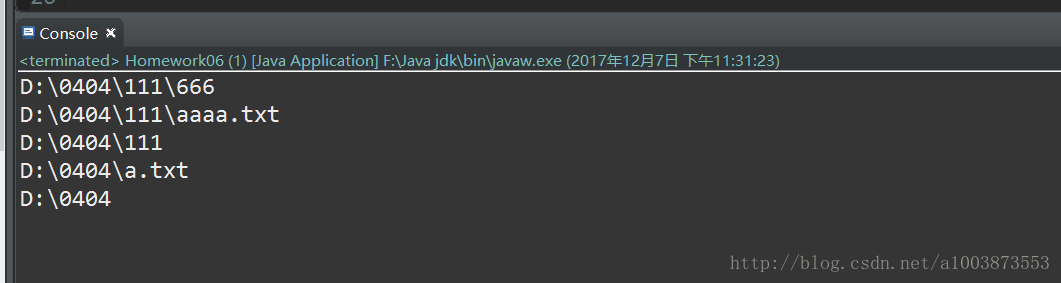
public class Homework06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("D://0404");
show(file);
}
private static void show(File file) {
File[] fl = file.listFiles();
for (File f : fl) {
if (f.isDirectory()) {
show(f);
} else if (f.isFile()) {
System.out.println(f);
}
}
System.out.println(file);
}
}
相关文章推荐
- Java 总结 1202/1203
- java作业:复数的加减法
- IT十八掌作业_java基础第十三天_IO
- 【JAVA_SE】作业练习1016
- Java作业:求解1到100之间的偶数
- 2017-2018-1 Java演绎法 第一周 作业
- java作业(3.24)
- 第七周Java作业
- Java 大作业 个人通讯录的实现
- 第九周java作业
- JAVA第三次作业
- java第三周作业
- IT十八掌作业_java基础第七天_匿名内部类、异常、包和jar
- 2016 java web 期末大作业心得体会 -- 小型的新闻发布系统(承认自己做的很烂)
- 吉软_java57_第八次作业
- Java_9+8实训Day0906作业题
- Java作业-Map排序
- java第三周作业,P45 -3
- [Hadoop] hadoop的mapreduce作业中经常出现Java heap space
- 第十一周java作业
