java中的输入输出流(字节流 字符流 节点流 过滤流)
2017-12-03 23:25
543 查看
输入输出流有关的类在java.io包下,jdk1.4起加了java.nio包,jdk1.7对其做了改进,称为nio2。
按流中处理的数据是以字节(8位)为单位还是以字符(16位)为单位分为字节流和字符流
InputStream是抽象类,不能直接用
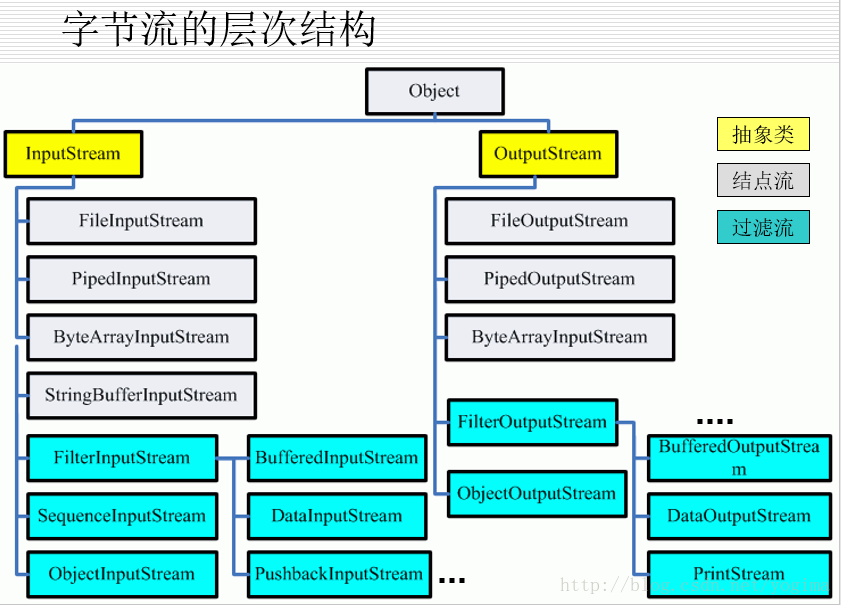
InputStream类的read()方法:逐字节以二进制的原始方式读取数据
[b]OutputStream[/b]
常用方法:
OutputStream是抽象类,不能直接用new OutputStream()构造实例。 FileOutputStream是OutputStream的子类,可以生成实例。 FileOutputStream最常用的构造方法如下:
利用字节流复制文件:
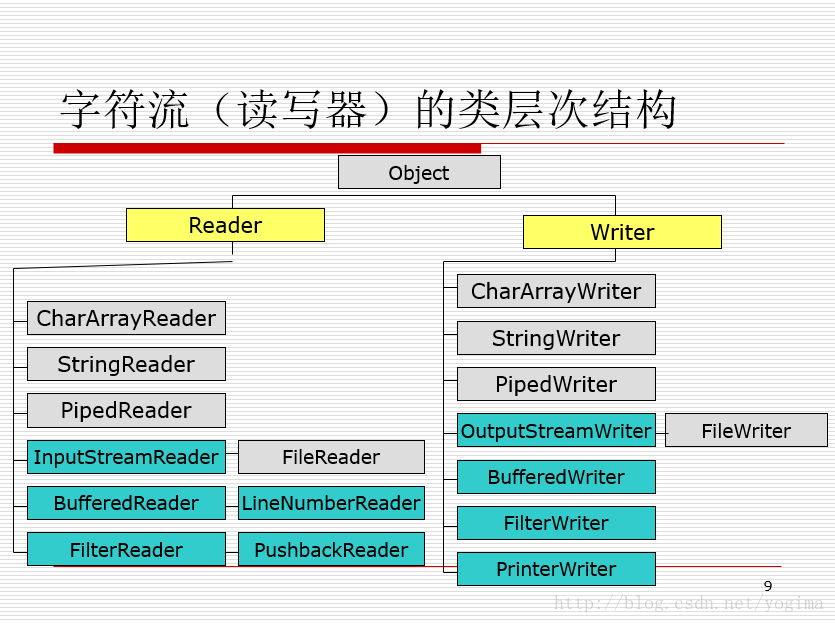
Reader类读取的是字符,而不是字节。
Reader类的重要方法read():
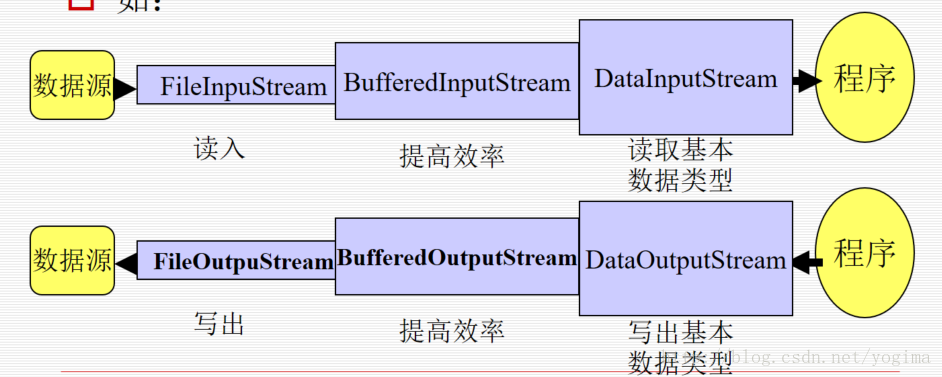
过滤流 (Filter Stream):使用其它的流作为输入源或输出目的地,对流中的数据提供进一步处理的流。其他的流可以是节点流,也可以是另一种过滤流。过滤流不能单独使用。
一个输入流链或输出流链中一定有且只有一个节点流;可以没有,也可以有多个过滤流。
过滤流和节点流的套接:
[b]标准输入输出流和错误流
1.System.out: -PrintStream类型
把输出送到缺省的显示(通常是显示器)
2.System.in - InputStream类型
从标准输入获取输入(通常是键盘)
3.System.err - PrintStream类型
out的用法大家已熟知了,err的用法与out一样
System是final类,in,out,err是System的静态成员变量,因此可以用System.in等形式直接使用。
由于System,.in是InputStream类型,因此需要包装 :
注:
1.输入/输出流的方法会抛出异常,因此必须进行异常处理。
2.标准输入/输出/错误流对象System.in, System.out、 System.err 始终存在 ,不需要实例化,也 不需要关闭。
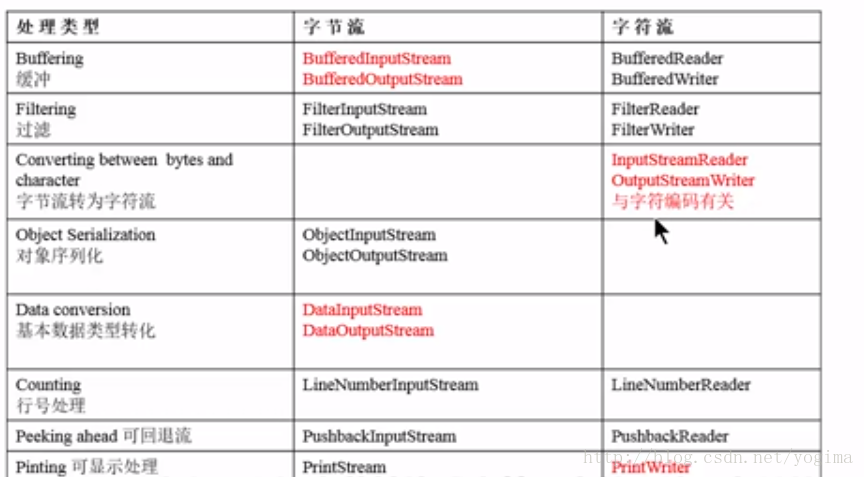
最后附上两张图
1、常用节点流:
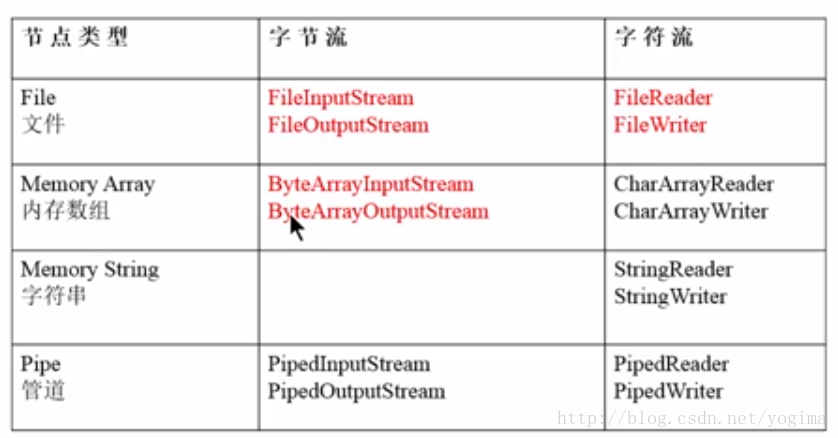
2.常用过滤流:
按流中处理的数据是以字节(8位)为单位还是以字符(16位)为单位分为字节流和字符流
字节流: InputStream和OutputStream
[b]InputStream[/b]InputStream是抽象类,不能直接用
new InputStream()构造实例。 FileInputStream是InputStream的子类,可以生成实例。 FileInputStream有三个构造方法,最常用的构造方法如下:
Public FileInputStream(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException Public FileInputStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException //fileName用来指定输入文件名及其路径,file是一个File对象

InputStream类的read()方法:逐字节以二进制的原始方式读取数据
public int read();//读入一个字节,-1表示无 public int read(byte b[]);//返回读入的字节数 public int read(byte[] b,int off.int len);//返回从某个位置开始制定长度的字节数
[b]OutputStream[/b]
常用方法:
//写一个字节 void write( int ) throws IOException //关闭输出流 void close( ) throws IOException //强行将缓冲区的数据写到目的地。 void flush( ) throws IOException //写一个字节数组 void write(byte[ ] b) throws IOException void write(byte[ ] b, int offset, int length ) throws IOException
OutputStream是抽象类,不能直接用new OutputStream()构造实例。 FileOutputStream是OutputStream的子类,可以生成实例。 FileOutputStream最常用的构造方法如下:
Public FileOutputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException Public FileOutputStream(String name,boolean append) throws FileNotFoundException //Name用来指定输入文件名及其路径,append为true时数据将添加到文件已有内容的末尾
利用字节流复制文件:
import java.io.*;
class CopyAFile
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
InputStream in;
OutputStream out;
try
{
in=new FileInputStream("test.txt");
out=new FileOutputStream("copyResult.txt");
// out=new FileOutputStream("copyResult.txt",true);
int aByte;
aByte=in.read();
while (aByte!=-1)
{
out.write(aByte);
aByte=in.read();
}
in.close();
out.close();
System.out.println("文件复制完毕。test.txt已经复制到copyResult.txt中。");
}
catch(FileNotFoundException e)
{
System.out.println("当前目录下文件test.txt不存在!");
}
catch(IOException e)
{
System.out.println("发生输入输出错误!");
}
}
}字符流: Reader和Writer
字符流不一定对应两个字节,要考虑到编码问题。
Reader类读取的是字符,而不是字节。
Reader类的重要方法read():
public int read();//需要将int转为char public int read(char b[]); public int read(char[] b,int off,int len)
节点流和过滤流
节点流(Node Stream) :直接与原始数据存在的特定介质(如磁盘文件或其他外部设备、内存某区域或其他程序)打交道的流,在流的序列中离程序最远。过滤流 (Filter Stream):使用其它的流作为输入源或输出目的地,对流中的数据提供进一步处理的流。其他的流可以是节点流,也可以是另一种过滤流。过滤流不能单独使用。
一个输入流链或输出流链中一定有且只有一个节点流;可以没有,也可以有多个过滤流。
过滤流和节点流的套接:
InputStream in;
in=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("test.txt"));
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
BufferedReader in2 = new BufferedReader(new inputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file),"utf-8"));
s = in2.readLine();
[b]标准输入输出流和错误流
1.System.out: -PrintStream类型
把输出送到缺省的显示(通常是显示器)
2.System.in - InputStream类型
从标准输入获取输入(通常是键盘)
3.System.err - PrintStream类型
out的用法大家已熟知了,err的用法与out一样
System是final类,in,out,err是System的静态成员变量,因此可以用System.in等形式直接使用。
由于System,.in是InputStream类型,因此需要包装 :
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); br.readLine();
注:
1.输入/输出流的方法会抛出异常,因此必须进行异常处理。
2.标准输入/输出/错误流对象System.in, System.out、 System.err 始终存在 ,不需要实例化,也 不需要关闭。
最后附上两张图
1、常用节点流:

2.常用过滤流:

相关文章推荐
- java输入输出流,字节流,字符流
- Java笔记(7)-输入、输出流、File类、InputStream、Reader、文件字节流、文件字符流、缓冲流、随机流、数据流、对象流、序列化和对象克隆、Scanner解析文件、Console流
- Java学习笔记之输入输出流(一) File、文件字节流、文件字符流
- JAVA输入/输出流(字节流、字符流、缓冲流)
- java中的io流(输入输出流,序列化与反序列化,字节流 , 字符流,包装流,缓冲流)
- 牛客网Java刷题知识点之输入流、输出流、字节流、字符流、字节流的抽象基类(InputStream、OutputStream)、字符流的抽象基类(Reader、Writer)、FileWriter、FileReader
- java--IO流-LineNumberReader,读取键盘录入,字符字节流转换,改变标准输入输出设备,异常的日志信息,系统信息
- JavaIO 总结笔记<三> 基本字节字符输入输出流和文件复制
- Java 字节流与字符流(字符输出流:Writer)
- Java基础知识回顾-4 字符输入输出流
- java输入输出流、字符字节流
- java基础6:io流对象之字符输入输出流
- Java语言基础-IO流(输入输出流) 字节流、转换流
- Java之字节流(文件输入、输出流)
- java中字符输入输出流在输出结果的结尾多一个乱码字符:'?'
- JAVA输入/输出流程序例题(文件和目录、字节流、字符流)
- 自己动手写java 字节流输入输出流
- Java语言基础-IO流(输入输出流) 字符流
- Java 字节流与字符流(字节输出流:OutputStream)
- Java中的字节输入出流和字符输入输出流
