多线程实现互斥访问对象的方法
2017-11-29 23:21
351 查看
场景说明
假设有 A、B 两个线程都去调用对象 α 的方法 method1(),并且要求 A、B 两个线程是互斥调用 method1 的。具体来说,假设 method1 中有 4 个命令,一旦 A 调用了 method1,在执行 method1 中有 4 个命令的时候,B 不会调用 method1 方法,反之,依然。利用 java的同步机制
在 JAVA 中的 Object 类型中,都是带有一个内存锁的,在有线程获取该内存锁后,其它线程无法访问该内存,从而实现JAVA中简单的同步、互斥操作。具体到代码中,涉及到三个关键字:synchronize:这个关键字会实现对象的方法互斥的执行
notify:通知另外一个正在等待进程可以申请资源
wait:本线程主动释放资源
notify、wait 实现了线程间的通信
经常被锁的资源为:
字节码:对象的 class,例如,A.class
类中的 static 类型的对象
或者在 main 方法中 new 一个对象
第一种代码的实现
package wyf.org.concurrent.KeyWord;
public class Word implements Runnable {
private String name ;
private int count = 0 ;
public Object o ;
public Word(String name, Object o){
this.name = name;
this.o = o ;
}
public void output() throws InterruptedException{
synchronized(o){
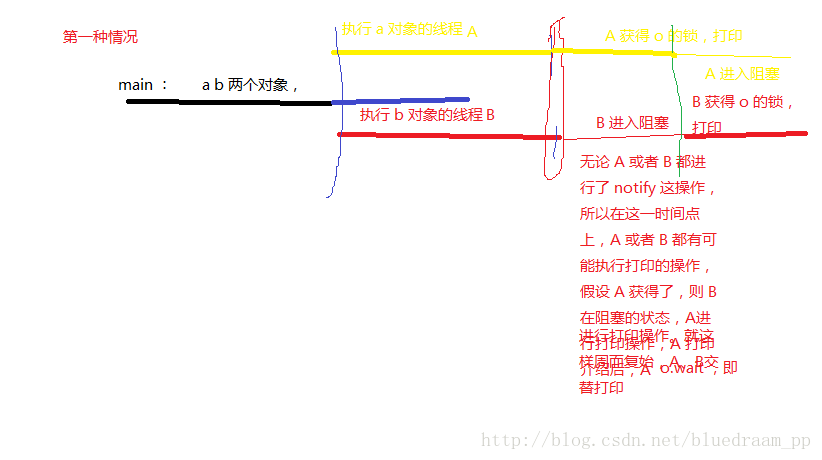
o.notify();//当程序走到这里,会先执行 notify 的操作,无论是 a 或者 b 都会得到 o 的锁并且执行下面的 5 行代码,最后 wait 主动让出 o 的锁
System.out.println(name + " 1, thread run ");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(name + " 2, thread run ");
System.out.println(name + " 3, thread run ");
System.out.println(" ");
o.wait();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 使用一个 object 来作为同步的的临界值,哪个线程得了 object 的锁就能,活得 synchronized 中代码的执行资源
* */
Object o = new Object();
Word a = new Word("A",o);
Word b = new Word("B",o);
new Thread(a).start();
new Thread(b).start();
}
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
this.output();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}下面是程序运行的时序图:
第二种代码的实现
package wyf.org.concurrent.KeyWord;
public class SynchroniseWord implements Runnable{
private String name = "";
public SynchroniseWord(String name){
this.name = name ;
}
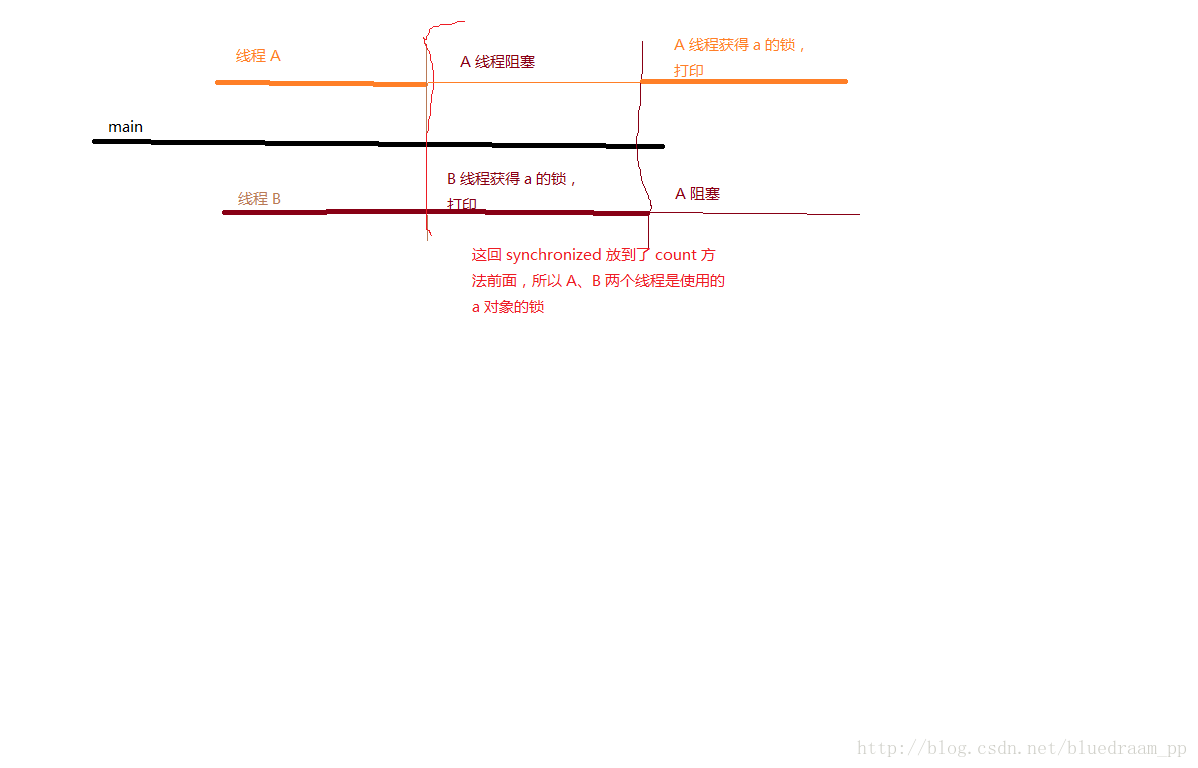
public synchronized void Count() throws InterruptedException{
System.out.println(name + " 1, thread run ");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(name + " 2, thread run ");
System.out.println(name + " 3, thread run ");
System.out.println(" ");
}
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
this.Count();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynchroniseWord sw = new SynchroniseWord("A");
new Thread(sw).start();
new Thread(sw).start();
}
}程序运行的时序图:
相关文章推荐
- ATL学习笔记(2): ATL对象多线程访问临界锁的实现
- PHP实现在对象之外访问其私有属性private及保护属性protected的方法
- Java多线程编程之访问共享对象和数据的方法
- Windows多线程编程实现数据互斥访问的几个方法
- Java中多线程互斥访问的实现
- 在iOS中有几种方法来解决多线程访问同一个内存地址的互斥同步问题
- java多线程之-----对象及变量的并发访问1(synchronized同步方法)
- ATL学习笔记(2): ATL对象多线程访问临界锁的实现
- 使用临界区CRITICAL_SECTION结构对象保护多线程互斥地访问共享资源
- 【Java面试题】26 多线程有几种实现方法?同步有几种实现方法? 当一个线程进入一个对象的一个synchronized方法后,其它线程是否可进入此对象的其它方法?
- 多线程访问共享对象和数据方法
- VC++中数据访问互斥的简单实现方法
- 面向对象,类的组合关系,继承,实现,方法重写,方法重载,this的使用,抽象方法和抽象类的比较,父类构造方法存在的意义,多态的是用和解析,各种访问修饰符
- 能用foreach遍历访问的对象需要实现 ________________接口或声明________________方法的类型。
- C++接口定义,实现,继承接口类的子类,实例对象访问方法问题
- 使用等待对象的方法,实现多线程的同步处理。。
- 能用foreach遍历访问的对象需要实现____接口或声明____方法的类型
- 能用foreach遍历访问的对象需要实现____接口或声明____方法的类型
- oc 面向对象特性(接口,实现,方法发送,访问成员变量)
- Bakery Algorithm的c#实现用于多线程互斥访问临界资源
