《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(九)
2017-11-17 11:27
337 查看
当interrupt方法遇到wait方法
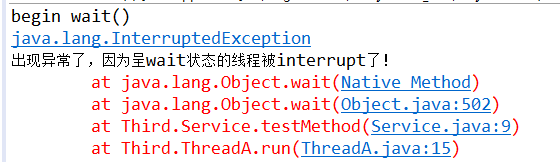
当线程呈wait()状态时,调用线程对象的interrupt()会出现InterruptedException异常
package Third;
public class Service {
public void testMethod(Object lock) {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("begin wait()");
lock.wait();
System.out.println(" end wait()");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("出现异常了,因为呈wait状态的线程被interrupt了!");
}
}
}
package Third;
public class ThreadA extends Thread {
private Object lock;
public ThreadA(Object lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Service service = new Service();
service.testMethod(lock);
}
}
package Third;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Object lock = new Object();
ThreadA a = new ThreadA(lock);
a.start();
Thread.sleep(5000);
a.interrupt();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

只通知一个线程
调用方法notify()一次只随机通知一个线程进行唤醒
package Third;
public class Service {
public void testMethod(Object lock) {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
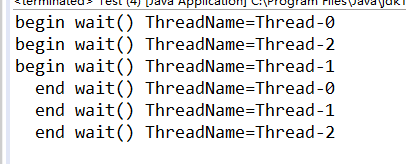
System.out.println("begin wait() ThreadName="
+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
lock.wait();
System.out.println(" end wait() ThreadName="
+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package Third;
public class ThreadA extends Thread {
private Object lock;
public ThreadA(Object lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Service service = new Service();
service.testMethod(lock);
}
}
package Third;
public class ThreadB extends Thread {
private Object lock;
public ThreadB(Object lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Service service = new Service();
service.testMethod(lock);
}
}
package Third;
public class ThreadC extends Thread {
private Object lock;
public ThreadC(Object lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Service service = new Service();
service.testMethod(lock);
}
}
package Third;
public class NotifyThread extends Thread {
private Object lock;
public NotifyThread(Object lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
lock.notify();
}
}
}
package Third;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Object lock = new Object();
ThreadA a = new ThreadA(lock);
a.start();
ThreadB b = new ThreadB(lock);
b.start();
ThreadC c = new ThreadC(lock);
c.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
NotifyThread notifyThread = new NotifyThread(lock);
notifyThread.start();
}
}

唤醒所有线程
package Third;
public class NotifyThread extends Thread {
private Object lock;
public NotifyThread(Object lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}

wait(long)的使用
功能是等待某一时间内是否有线程对锁进行唤醒,如果超过这个时间则自动唤醒

当然也可以由其他线程进行唤醒
package Third;
public class MyRunnable {
static private Object lock = new Object();
static private Runnable runnable1 = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("wait begin timer="
+ System.currentTimeMillis());
lock.wait(5000);
System.out.println("wait end timer="
+ System.currentTimeMillis());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
static private Runnable runnable2 = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("notify begin timer="
+ System.currentTimeMillis());
lock.notify();
System.out.println("notify end timer="
+ System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(runnable1);
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(3000);
Thread t2 = new Thread(runnable2);
t2.start();
}
}

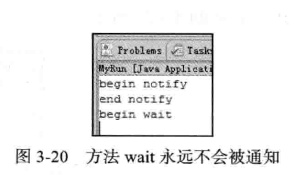
通知过早
package Third;
public class MyRun {
private String lock = new String("");
private Runnable runnableA = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("begin wait");
lock.wait();
System.out.println("end wait");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
private Runnable runnableB = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("begin notify");
lock.notify();
System.out.println("end notify");
}
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRun run = new MyRun();
Thread a = new Thread(run.runnableA);
a.start();
Thread b = new Thread(run.runnableB);
b.start();
}
}

package Third;
public class MyRun {
private String lock = new String("");
private Runnable runnableA = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("begin wait");
lock.wait();
System.out.println("end wait");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
private Runnable runnableB = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("begin notify");
lock.notify();
System.out.println("end notify");
}
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRun run = new MyRun();
Thread a = new Thread(run.runnableA);
a.start();
Thread.sleep(100);
Thread b = new Thread(run.runnableB);
b.start();
}
}
如果先通知了,则wait方法也就没有必要执行了
package Third;
public class MyRun {
private String lock = new String("");
private boolean isFirstRunB = false;
private Runnable runnableA = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
while (isFirstRunB == false) {
System.out.println("begin wait");
lock.wait();
System.out.println("end wait");
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
private Runnable runnableB = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("begin notify");
lock.notify();
System.out.println("end notify");
isFirstRunB = true;
}
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRun run = new MyRun();
Thread b = new Thread(run.runnableB);
b.start();
Thread.sleep(100);
Thread a = new Thread(run.runnableA);
a.start();
}
}

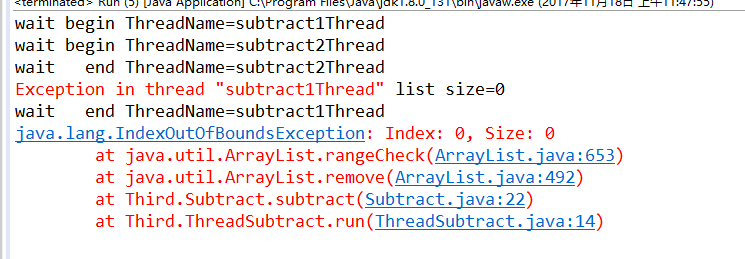
等待wait条件发生变化
在使用wait/notify模式时,还需要注意另外一种情况。也就是wait等待的条件发生了变化,也容易造成程序逻辑混乱
package Third;
public class Add {
private String lock;
public Add(String lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
public void add() {
synchronized (lock) {
ValueObject.list.add("anyString");
lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
package Third;
public class Subtract {
private String lock;
public Subtract(String lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
public void subtract() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
if (ValueObject.list.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("wait begin ThreadName="
+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
lock.wait();
System.out.println("wait end ThreadName="
+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
ValueObject.list.remove(0);
System.out.println("list size=" + ValueObject.list.size());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package Third;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ValueObject {
public static List list = new ArrayList();
}
package Third;
public class ThreadAdd extends Thread {
private Add p;
public ThreadAdd(Add p) {
super();
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public void run() {
p.add();
}
}
package Third;
public class ThreadSubtract extends Thread {
private Subtract r;
public ThreadSubtract(Subtract r) {
super();
this.r = r;
}
@Override
public void run() {
r.subtract();
}
}
package Third;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
String lock = new String("");
Add add = new Add(lock);
Subtract subtract = new Subtract(lock);
ThreadSubtract subtract1Thread = new ThreadSubtract(subtract);
subtract1Thread.setName("subtract1Thread");
subtract1Thread.start();
ThreadSubtract subtract2Thread = new ThreadSubtract(subtract);
subtract2Thread.setName("subtract2Thread");
subtract2Thread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
ThreadAdd addThread = new ThreadAdd(add);
addThread.setName("addThread");
addThread.start();
}
}

package Third;
public class Subtract {
private String lock;
public Subtract(String lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
public void subtract() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
while (ValueObject.list.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("wait begin ThreadName="
+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
lock.wait();
System.out.println("wait end ThreadName="
+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
ValueObject.list.remove(0);
System.out.println("list size=" + ValueObject.list.size());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

生产者/消费者模式实现
1、一生产与一消费:操作值
package Third;
//生产者
public class P {
private String lock;
public P(String lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
public void setValue() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
if (!ValueObject.value.equals("")) {
lock.wait();
}
String value = System.currentTimeMillis() + "_"
+ System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("set的值是" + value);
ValueObject.value = value;
lock.notify();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package Third;
//消费者
public class C {
private String lock;
public C(String lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
public void getValue() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
if (ValueObject.value.equals("")) {
lock.wait();
}
System.out.println("get的值是" + ValueObject.value);
ValueObject.value = "";
lock.notify();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package Third;
public class ValueObject {
public static String value = "";
}
package Third;
public class ThreadP extends Thread {
private P p;
public ThreadP(P p) {
super();
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
p.setValue();
}
}
}
package Third;
public class ThreadC extends Thread {
private C r;
public ThreadC(C r) {
super();
this.r = r;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
r.getValue();
}
}
}
package Third;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String lock = new String("");
P p = new P(lock);
C r = new C(lock);
ThreadP pThread = new ThreadP(p);
ThreadC rThread = new ThreadC(r);
pThread.start();
rThread.start();
}
}

在控制台中打印的日志get和set是交替运行的
2、多生产与多消费:操作值-假死
“”假死“”的现象其实就是线程进入waiting等待状态,如果全部线程都进入waiting状态,则程序就不再执行任何业务功能了,整个项目呈停止状态
package Third;
//消费者
public class C {
private String lock;
public C(String lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
public void getValue() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
while (ValueObject.value.equals("")) {
System.out.println("消费者 "
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + " WAITING了☆");
lock.wait();
}
System.out.println("消费者 " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " RUNNABLE了");
ValueObject.value = "";
lock.notify();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package Third;
//生产者
public class P {
private String lock;
public P(String lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
public void setValue() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
while (!ValueObject.value.equals("")) {
System.out.println("生产者 "
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + " WAITING了★");
lock.wait();
}
System.out.println("生产者 " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " RUNNABLE了");
String value = System.currentTimeMillis() + "_"
+ System.nanoTime();
ValueObject.value = value;
lock.notify();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package Third;
public class ValueObject {
public static String value = "";
}
package Third;
public class ThreadP extends Thread {
private P p;
public ThreadP(P p) {
super();
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
p.setValue();
}
}
}
package Third;
public class ThreadC extends Thread {
private C r;
public ThreadC(C r) {
super();
this.r = r;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
r.getValue();
}
}
}
package Third;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
String lock = new String("");
P p = new P(lock);
C r = new C(lock);
ThreadP[] pThread = new ThreadP[2];
ThreadC[] rThread = new ThreadC[2];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
pThread[i] = new ThreadP(p);
pThread[i].setName("生产者" + (i + 1));
rThread[i] = new ThreadC(r);
rThread[i].setName("消费者" + (i + 1));
pThread[i].start();
rThread[i].start();
}
Thread.sleep(5000);
Thread[] threadArray = new Thread[Thread.currentThread()
.getThreadGroup().activeCount()];
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().enumerate(threadArray);
for (int i = 0; i < threadArray.length; i++) {
System.out.println(threadArray[i].getName() + " "
+ threadArray[i].getState());
}
}
}


假死出现的主要原因是有可能连续唤醒同类
多生产与多消费:操作值
将上面项目的P.java和C.java文件中的notify()改成notifyAll()即可,不光通知同类线程,也包括异类
相关文章推荐
- 《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(十一)
- 《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(十三)
- 《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感
- 《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(一)
- 《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(二)
- 《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(十六)
- 《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(十七)
- 《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(四)
- 《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(十八)
- 《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(七)
- 《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(八)
- 算法导论读后感-之树的旋转(维护红黑树的性质)
- 《最好的告别》读后感
- 《精通Spring4.X企业应用开发实战》读后感第四章(Java反射)
- 三国历史读后感
- 《伪装的艺术》读后感
- 代码整洁之道Clean Code 读后感After Reading
- 《区块链:从数字货币到信用社会》-读后感
- 《Redis入门指南(第2版)》读后感
- 学习JAVA多线程编程 --- 《JAVA多线程编程核心技术》第2章 对象及变量的并发访问 笔记
