java里面的运行异常与普通异常的区别以及spring boot统一异常处理
2017-11-07 14:22
453 查看
java提供两种错误的异常类,一种是Error,一种是Exception.Error表示在运行期间发生的非常严重的错误,并且错误是不可恢复的,这是属于jvm层次的严重错误,这种错误会导致程序终止执行。内存溢出,进程停止都是错误。
Exception表示可恢复的异常,是编译器可以捕捉到的,包括检查异常和运行时异常
1、IO和sql异常在编译的时候就把异常代码放在try块中,,这种异常不会导致程序错误,处理后可继续执行后续操作。
2、运行时异常,编译器没有提示你要抛出异常,比方空指针异常,类型转换异常、数组越界、缓冲区溢出异常、算术异常等。发生异常后,程序会把异常往上抛,直到出现处理代码为止,多线程用Thread.run()方法抛出,单线程用main()方法抛出。抛出后如果是线程线程退出,如果是主程序,程序就结束了。
注:java异常处理用到了多态,在书写异常处理时,要先写子类异常,在写基类异常。
3统一异常处理
需求:假设我们有一个user表,表里面有一个id字段,我们要实现id不同范围输出不同的提示语句到浏览器上面。
设计:方法1:在业务逻辑层service层里面写一个接口方法,并写出它的实现类
public String getAge(Integer id);
}
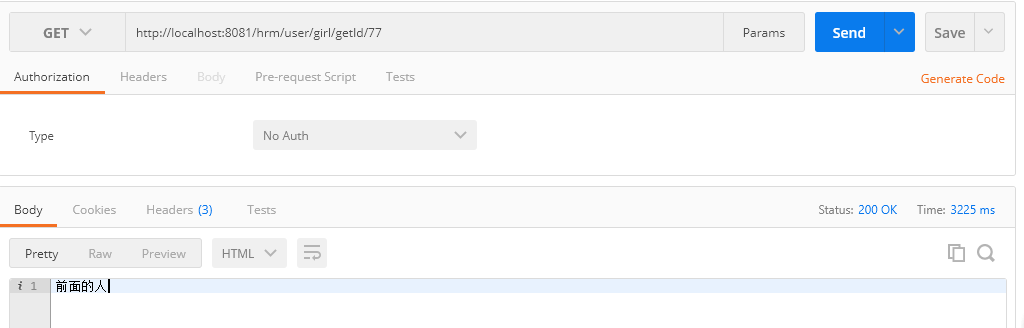
然后在controler里面写方法,再用postman调试如下图所示
这样写是可以处理简单的符合判断语句就出提示语句。可是如果业务加大,满足条件又有其他一系列的操作,就不行了,我就将代码修改成
方法二
service层
controler
这样可以满足我们的需求,可是代码过于繁琐,在service里面判断了一次,在controler里面又要做一次判断。
方法三
这时候需要用我们的统一异常处理
service层如下所示,往外抛异常,异常向上抛,抛到controler层
controler层继续抛异常
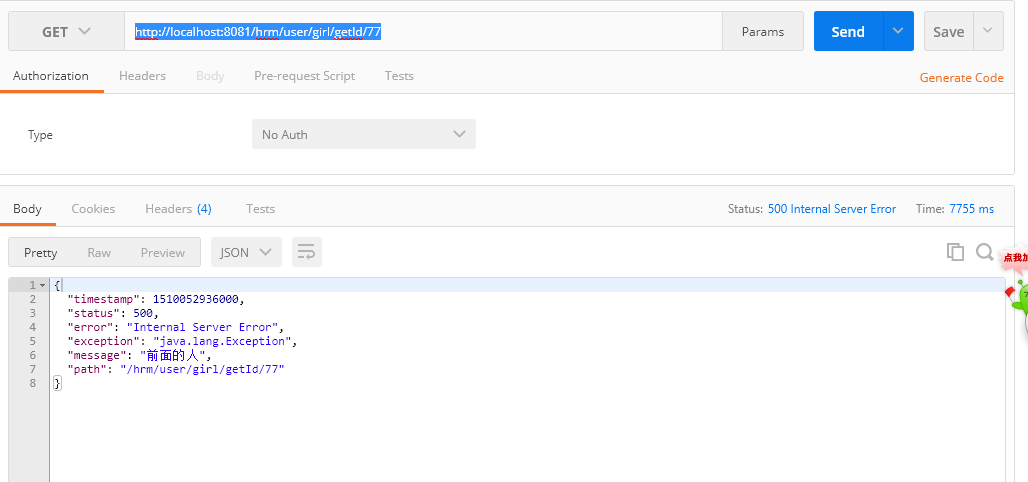
可是这个结果不是我们想要的,我们想要的是显示三部分,分别是code,data,message
于是我们写一个json实体
在写一个json结果工具类
在写一个异常处理类,然后显示json格式的结果了,可是又有一个问题出现了,我两异常对应的code都是100,而Exception里面又只能写一个message。
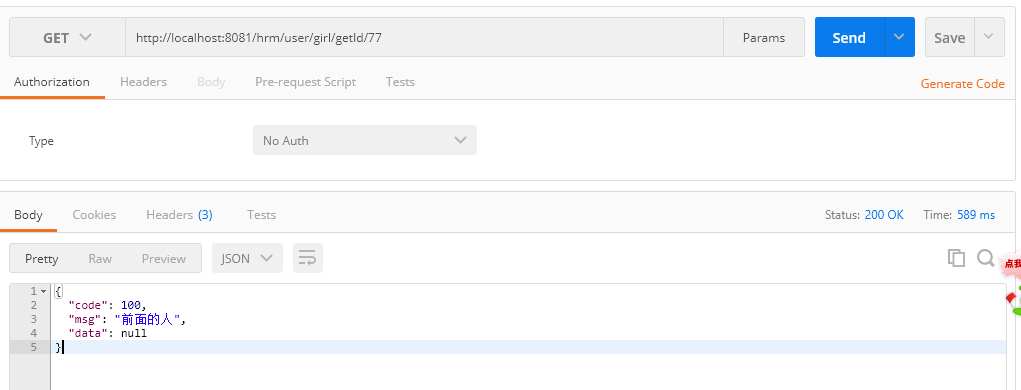
这里我们重新写一个异常方法,这里我们重新写一个继承RuntimeException的子类。不能只继承Exception,不然事务不会回滚。
ExceptionHandle和Service如下
现在又出现一个新问题了,我的code和message都是随机写的,如果业务加大,很容易出现重复的。怎么统一管理呢
这就用到了枚举
方法4:将code和message用枚举显示
1)新建一个枚举类
2)异常类改为
运行后就可以显示统一管理后返回的json值了。
Exception表示可恢复的异常,是编译器可以捕捉到的,包括检查异常和运行时异常
1、IO和sql异常在编译的时候就把异常代码放在try块中,,这种异常不会导致程序错误,处理后可继续执行后续操作。
2、运行时异常,编译器没有提示你要抛出异常,比方空指针异常,类型转换异常、数组越界、缓冲区溢出异常、算术异常等。发生异常后,程序会把异常往上抛,直到出现处理代码为止,多线程用Thread.run()方法抛出,单线程用main()方法抛出。抛出后如果是线程线程退出,如果是主程序,程序就结束了。
注:java异常处理用到了多态,在书写异常处理时,要先写子类异常,在写基类异常。
3统一异常处理
需求:假设我们有一个user表,表里面有一个id字段,我们要实现id不同范围输出不同的提示语句到浏览器上面。
设计:方法1:在业务逻辑层service层里面写一个接口方法,并写出它的实现类
public String getAge(Integer id);
public String getAge(Integer id) {
Users user=userRepository.findOne(id);
Integer age=user.getId();
if(age<100){
return "前面的人";
}
else if(age>100&&age<200){
return "中间的人";
}
return "后面的人";}
然后在controler里面写方法,再用postman调试如下图所示
@GetMapping(value="girl/getId/{id}")
@ResponseBody
public String getId(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return userService.getAge(id);
}
这样写是可以处理简单的符合判断语句就出提示语句。可是如果业务加大,满足条件又有其他一系列的操作,就不行了,我就将代码修改成
方法二
service层
public Integer getAge(Integer id) {
Users user=userRepository.findOne(id);
Integer age=user.getId();
if(age<100){
return 1;
}
else if(age>100&&age<200){
return 2;
}
return 0;
}controler
@GetMapping(value="girl/getId/{id}")
public void getId(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
Integer a=userService.getAge(id);
if(a.equals(1)){
//...
}
else if(a.equals(2)){
//...
}
}这样可以满足我们的需求,可是代码过于繁琐,在service里面判断了一次,在controler里面又要做一次判断。
方法三
这时候需要用我们的统一异常处理
service层如下所示,往外抛异常,异常向上抛,抛到controler层
public void getAge(Integer id) throws Exception;
public Users insert(Users user){
return userRepository.save(user);
}
public void getAge(Integer id) throws Exception {
Users user=userRepository.findOne(id);
Integer age=user.getId();
if(age<100){
throw new Exception("前面的人");
}
else if(age>100&&age<200){
throw new Exception("中间的人");
}
}controler层继续抛异常
@GetMapping(value="girl/getId/{id}")
public void getId(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) throws Exception{
userService.getAge(id);
}
可是这个结果不是我们想要的,我们想要的是显示三部分,分别是code,data,message
于是我们写一个json实体
public class Result<T> {
private Integer code;
private String msg;
private T data;
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public T getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
}在写一个json结果工具类
public class ResultUtil {
public static Result success(Object object) {
Result result=new Result();
result.setCode(0);
result.setMsg("成功");
result.setData(object);
return result;
}
public static Result success() {
return success(null);
}
public static Result error(Integer code,String msg) {
Result result=new Result();
result.setCode(code);
result.setMsg(msg);
return result;
}
}在写一个异常处理类,然后显示json格式的结果了,可是又有一个问题出现了,我两异常对应的code都是100,而Exception里面又只能写一个message。
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionHandle {
@ExceptionHandler(value=Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public Result handle(Exception e){
return ResultUtil.error(100,e.getMessage());
}
}
这里我们重新写一个异常方法,这里我们重新写一个继承RuntimeException的子类。不能只继承Exception,不然事务不会回滚。
public class UserException extends RuntimeException {
private Integer code;
public UserException(String message, Integer code) {
super(message);
this.code = code;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
}ExceptionHandle和Service如下
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionHandle {
@ExceptionHandler(value=Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public Result handle(Exception e){
if(e instanceof UserException){
UserException userException=(UserException)e;
return ResultUtil.error(userException.getCode(),userException.getMessage());
}
return ResultUtil.error(-1,"未知错误");
}
}public void getAge(Integer id) throws UserException {
Users user=userRepository.findOne(id);
Integer age=user.getId();
if(age<100){
throw new UserException("前面的人",100);
}
else if(age>100&&age<200){
throw new UserException("中间的人",101);
}
}现在又出现一个新问题了,我的code和message都是随机写的,如果业务加大,很容易出现重复的。怎么统一管理呢
这就用到了枚举
方法4:将code和message用枚举显示
1)新建一个枚举类
package com.example.demo.enums;
/**
* @Author :zhanglu
* @Description:
* @Date :Created in 14:02 2017/11/8
* @Modified By:
*/
public enum ResultEnums {
UNKOWN_ERROR(-1,"未知错误"),
SUCCESS(0,"成功"),
PRIMARY_SCHOOL(100,"前面的数据"),
MIDDLE_SCHOOL(101,"中间的数据")
;
private Integer code;
private String msg;
ResultEnums(Integer code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
}2)异常类改为
package com.example.demo.Exception;
import com.example.demo.enums.ResultEnums;
/**
* @Author :zhanglu
* @Description:
* @Date :Created in 19:41 2017/11/7
* @Modified By:
*/
//RuntimeExcetion可以进行事务回滚,Exception不会进行事务回滚
public class UserException extends RuntimeException {
private Integer code;
public UserException(ResultEnums resultEnums) {
super(resultEnums.getMsg());
this.code = resultEnums.getCode();
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
}3)service方法改为
public void getAge(Integer id) throws UserException {
Users user=userRepository.findOne(id);
Integer age=user.getId();
if(age<100){
throw new UserException(ResultEnums.PRIMARY_SCHOOL);
}
else if(age>100&&age<200){
throw new UserException(ResultEnums.MIDDLE_SCHOOL);
}
}运行后就可以显示统一管理后返回的json值了。
相关文章推荐
- Java运行时异常与普通异常的区别
- Java_error与Exception的区别,以及受控异常与运行时异常的区别
- java的运行时异常和普通异常有什么区别(TODO)
- Java_error与Exception的区别,以及受控异常与运行时异常的区别
- RuntimeException和Exception区别(运行时异常和普通异常)
- Java之运行时异常与编译时异常区别
- Java异常类简介以及throws,try,catch,throw,finally的区别
- java 运行时异常 RuntimeException 和编译时异常的区别
- Java异常-一般异常和运行时异常的区别
- JAVA 错误 运行时异常 一般异常 区别
- 解决浙大PAT用JAVA返回非零以及运行超时异常
- java的两种异常类型,以及区别。
- 【Java面试题】20 运行时异常和一般异常有何区别
- java运行时异常和编译时异常的区别
- Java之运行时异常与编译时异常区别
- java自定义异常以及throws和throw的区别
- Java的编译时异常和运行时异常的区别
- BeanUtils与PropertyUtils区别以及java.util.Date发生异常问题
- Java运行时异常与一般异常以及错误的异同
- java中一般异常和运行时异常的区别
