机器学习(支持向量机-SVM)
2017-11-02 21:29
459 查看
一、深度学习的一般框架:
训练集->提取特征向量->结合一定算法(分类器:比如决策树,KNN)->得到结果
二、向量机的概念:
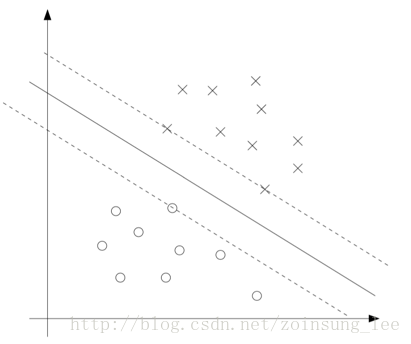
如图所示,就是一个二维几何空间中的分类。中间那条直线就是这个分类的超平面。我们不难发现,用来确定这条直线其实只需要两条虚线上的三个点就够了,其他距离很远的点,虽然是训练样本,但是因为特征太明显,不会引起歧义,也对我们分类的超平面的确定意义并不大。所以只要找到最靠近分类平面的这些点,我们就能够很好的确定出所需要的超平面。而这些点,在几何空间中也表示向量,那么就把这些能够用来确定超平面的向量称为支持向量(直接支持超平面的生成),于是该算法就叫做支持向量机了。所以这个算法的好处就很明显了,任你训练样本如何庞大,我只需要找到支持向量就能很好的完成任务了,计算量就大大缩小了。
SVM寻找区分两类的超平面,使边际最大,选取使边际最大的超平面,要做到超平面到一侧最近点的距离等于到另一侧最近点的距离,两侧两个超平面平行。
SVM分为线性可区分和线性不可分
三、定义与公式建立
1.超平面定义:
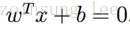
W = {w1,w2,w3…..wn}
W为权重向量,n是特征值的个数,X是训练实例,b是截距
2.线性分类
在训练数据中,每个数据都有n个的属性和一个二类类别标志,我们可以认为这些数据在一个n维空间里。我们的目标是找到一个n-1维的超平面,这个超平面可以将数据分成两部分,每部分数据都属于同一个类别。
其实这样的超平面有很多,我们要找到一个最佳的。因此,增加一个约束条件:这个超平面到每边最近数据点的距离是最大的。也成为最大间隔超平面。这个分类器也成为最大间隔分类器,支持向量机是一个二类分类器。
3.假设二维特征向量:X=(x1,x2)
把b想象为额外的weigh
超平面方程变为:
w0+w1*x1+w2**x2=0
所有超平面右上方的点满足:
w0+w1*x1+w2**x2>0
所有超平面左下方的点满足:
w0+w1*x1+w2**x2<0
调整weight,使超平面定义边际的两边:
H1:w0+w1*x1+w2**x2>=1 for y1=+1,
H1:w0+w1*x1+w2**x2<=-1 for y1=-1
综合以上两式,得:
yi(w0+w1*x1+w2**x2)>=1
所有坐落在边际两边的超平面上的被称作“支持向量”,分界的超平面和H1或H2上任意一点的距离为:
1/||w||
所以最大边际距离为:
2/||w||
3.如何找出最大边际的超平面:
利用一些数学推导,以上公式可变为有限制的凸优化问题
利用KKT条件和拉格朗日公式
使用sklearn模块中的svm调用支持向量机分类器:
(1)少量训练集:
运行结果:
2.训练集多的支持向量机代码实现:
运行结果:
运行结果绘图:

练习2(人脸识别分类):
运行结果:
运行效果可视化:

训练集->提取特征向量->结合一定算法(分类器:比如决策树,KNN)->得到结果
二、向量机的概念:

如图所示,就是一个二维几何空间中的分类。中间那条直线就是这个分类的超平面。我们不难发现,用来确定这条直线其实只需要两条虚线上的三个点就够了,其他距离很远的点,虽然是训练样本,但是因为特征太明显,不会引起歧义,也对我们分类的超平面的确定意义并不大。所以只要找到最靠近分类平面的这些点,我们就能够很好的确定出所需要的超平面。而这些点,在几何空间中也表示向量,那么就把这些能够用来确定超平面的向量称为支持向量(直接支持超平面的生成),于是该算法就叫做支持向量机了。所以这个算法的好处就很明显了,任你训练样本如何庞大,我只需要找到支持向量就能很好的完成任务了,计算量就大大缩小了。
SVM寻找区分两类的超平面,使边际最大,选取使边际最大的超平面,要做到超平面到一侧最近点的距离等于到另一侧最近点的距离,两侧两个超平面平行。
SVM分为线性可区分和线性不可分
三、定义与公式建立
1.超平面定义:
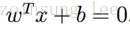
W = {w1,w2,w3…..wn}
W为权重向量,n是特征值的个数,X是训练实例,b是截距
2.线性分类
在训练数据中,每个数据都有n个的属性和一个二类类别标志,我们可以认为这些数据在一个n维空间里。我们的目标是找到一个n-1维的超平面,这个超平面可以将数据分成两部分,每部分数据都属于同一个类别。
其实这样的超平面有很多,我们要找到一个最佳的。因此,增加一个约束条件:这个超平面到每边最近数据点的距离是最大的。也成为最大间隔超平面。这个分类器也成为最大间隔分类器,支持向量机是一个二类分类器。
3.假设二维特征向量:X=(x1,x2)
把b想象为额外的weigh
超平面方程变为:
w0+w1*x1+w2**x2=0
所有超平面右上方的点满足:
w0+w1*x1+w2**x2>0
所有超平面左下方的点满足:
w0+w1*x1+w2**x2<0
调整weight,使超平面定义边际的两边:
H1:w0+w1*x1+w2**x2>=1 for y1=+1,
H1:w0+w1*x1+w2**x2<=-1 for y1=-1
综合以上两式,得:
yi(w0+w1*x1+w2**x2)>=1
所有坐落在边际两边的超平面上的被称作“支持向量”,分界的超平面和H1或H2上任意一点的距离为:
1/||w||
所以最大边际距离为:
2/||w||
3.如何找出最大边际的超平面:
利用一些数学推导,以上公式可变为有限制的凸优化问题
利用KKT条件和拉格朗日公式
使用sklearn模块中的svm调用支持向量机分类器:
(1)少量训练集:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- from sklearn import svm X = [[2,0],[1,1],[2,3]]#平面上的三个点 y = [0,0,1]#标记,第一个点和第二点属于第0类,第三个点属于第一类 clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')#linear为小写,线性核函数 clf.fit(X,y)#创建向量机模型 print(clf) print(clf.support_vectors_)#打印出支持向量 print(clf.support_)#打印出给出的向量中属于支持向量的向量的index下标 print(clf.n_support_)#打印出两个类中各自找出的支持向量的个数 print(clf.predict([[2,0],]))#必须传入一个嵌套列表
运行结果:
SVC(C=1.0, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, coef0=0.0, decision_function_shape='ovr', degree=3, gamma='auto', kernel='linear', max_iter=-1, probability=False, random_state=None, shrinking=True, tol=0.001, verbose=False) [[ 1. 1.] [ 2. 3.]] [1 2] [1 1] [0]
2.训练集多的支持向量机代码实现:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
print(__doc__)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pl #python中的绘图模块
from pylab import show
from sklearn import svm
np.random.seed(0) #随机固定随机值
X = np.r_[np.random.randn(20,2)-[2,2],np.random.randn(20,2)+[2,2]] #随机生成左下方20个点,右上方20个点
Y = [0]*20+[1]*20 #将前20个归为标记0,后20个归为标记1
#建立模型
clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
clf.fit(X,Y) #传入参数
#画出建立的超平面
w = clf.coef_[0] #取得w值,w中是二维的
a = -w[0]/w[1] #计算直线斜率
xx = np.linspace(-5,5) #随机产生连续x值
yy = a*xx-(clf.intercept_[0])/w[1] #根据随机x得到y值
#计算与直线相平行的两条直线
b = clf.support_vectors_[0]
yy_down = a*xx+(b[1]-a*b[0])
b = clf.support_vectors_[-1]
yy_up = a*xx+(b[1]-a*b[0])
print('w:',w)
print('a:',a)
print('support_vectors:',clf.support_vectors_)
print('clf.coef_',clf.coef_)
#画出三条直线
pl.plot(xx,yy,'k-')
pl.plot(xx,yy_down,'k--')
pl.plot(xx,yy_up,'k--')
pl.scatter(clf.support_vectors_[:,0],clf.support_vectors_[:,1],s=80,facecolors='none')
pl.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=Y, cmap=pl.cm.Paired)
pl.axis('tight')
pl.show()运行结果:
None w: [ 0.90230696 0.64821811] a: -1.39198047626 support_vectors: [[-1.02126202 0.2408932 ] [-0.46722079 -0.53064123] [ 0.95144703 0.57998206]] clf.coef_ [[ 0.90230696 0.64821811]]
运行结果绘图:

练习2(人脸识别分类):
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#兼容python2和python3的print函数
from __future__ import print_function
from time import time
import logging #打印日志
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #这个库具有绘图功能
#交叉验证模块
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_lfw_people
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.decomposition import RandomizedPCA
from sklearn.svm import SVC
print(__doc__)
#打印程序进展信息
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format='%(asctime)s %(message)s')#打印过程日志
lfw_people = fetch_lfw_people(min_faces_per_person=70,resize=0.4)#下载名人库的数据集
n_samples,h,w = lfw_people.images.shape #返回数据集的特征值
x = lfw_people.data #获取数据集特征向量的矩阵
n_features = x.shape[1] #获取数据集特征向量的维度
y = lfw_people.target #获取目标标记
target_names = lfw_people.target_names #获取目标标记的类别值
n_classes = target_names.shape[0] #返回数据集中有多少类,有多少个人
print('Total dataSet size:')
print("n_samples:%d"%n_samples)
print("n_futures:%d"%n_features)
print("n_classes:%d"%n_classes)
#将数据集拆分为训练集和测试集
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.25)
n_components = 150 #组成元素的数量
print("Extracting the top %d eigenfaces from %d faces"%(n_components,x_train.shape[0]))
#每一步的时间
t0 = time()
#使用pca对数据集进行降维处理
pca = RandomizedPCA(n_components=n_components,whiten=True).fit(x_train)
print("done in %0.3fs"%(time()-t0))
#提取人脸图片中的特征值
eigenfaces = pca.components_.reshape((n_components,h,w))
print("projecting the input data on the eigenfaces orthonormal basis ")
t0 = time()
x_train_pca = pca.transform(x_train) #将特征向量进行降维操作
x_test_pca = pca.transform(x_test) #将测试集数据集降维
print("done in %0.3fs"%(time()-t0))
print("Fitting the classifier to the trainning set")
t0 = time()
#c为权重,对错误进行惩罚,根据降维之后的数据结合分类器进行分类
#gamma为核函数的不同表现,表示有多少特征能够被表示,表示比例
param_grid = {'C':[1e3,5e5,1e4,5e4,1e5],
'gamma':[0.0001,0.0005,0.001,0.005,0.01,0.1],}
#建立分类器模型,找出表现最好的核函数
clf = GridSearchCV(SVC(kernel='rbf',class_weight='balanced'),param_grid)
#训练模型
clf = clf.fit(x_train_pca,y_train) #获取使边际最大的超平面
print("done in %0.3fs"%(time()-t0))
print("Best estimator found by grid search:")
print(clf.best_estimator_) #打印分类器的信息
print("Predicting people's names on the test set")
t0 = time()
#进行预测
y_pred = clf.predict(x_test_pca)
print("done in %0.3fs"%(time()-t0))
#将标签值的真实值与预测值之间的比较情况
print(classification_report(y_test,y_pred,target_names=target_names))
#将结果整合在矩阵中
print(confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred,labels=range(n_classes)))
#将结果可视化
def plot_gallery(images,titles,h,w,n_row=3,n_col=4):
plt.figure(figsize=(1.8*n_col,2.4*n_row))
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0,left=0.01,right=0.99,top=0.90,hspace=0.35)
for i in range(n_row * n_col):
plt.subplot(n_row,n_col,i+1)
plt.imshow(images[i].reshape((h,w)),cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.title(titles[i],size=12)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
def title(y_pred,y_test,target_names,i):
pred_name = target_names[y_pred[i]].rsplit(' ',1)[-1]
true_name = target_names[y_test[i]].rsplit(' ',1)[-1]
return "predicted: %s\nture: %s"%(pred_name,true_name)
prediction_titles = [title(y_pred, y_test, target_names, i)
for i in range(y_pred.shape[0])]
plot_gallery(x_test,prediction_titles,h,w)
eigenface_titles = ["eigenface %d"% i for i in range(eigenfaces.shape[0])]
plot_gallery(eigenfaces,eigenface_titles,h,w)
plt.show()运行结果:
D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\cross_validation.py:41: DeprecationWarning: This module was deprecated in version 0.18 in favor of the model_selection module into which all the refactored classes and functions are moved. Also note that the interface of the new CV iterators are different from that of this module. This module will be removed in 0.20. "This module will be removed in 0.20.", DeprecationWarning) D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\grid_search.py:42: DeprecationWarning: This module was deprecated in version 0.18 in favor of the model_selection module into which all the refactored classes and functions are moved. This module will be removed in 0.20. DeprecationWarning) None Total dataSet size: n_samples:1288 n_futures:1850 n_classes:7 Extracting the top 150 eigenfaces from 966 faces D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\utils\deprecation.py:58: DeprecationWarning: Class RandomizedPCA is deprecated; RandomizedPCA was deprecated in 0.18 and will be removed in 0.20. Use PCA(svd_solver='randomized') instead. The new implementation DOES NOT store whiten ``components_``. Apply transform to get them. warnings.warn(msg, category=DeprecationWarning) done in 0.137s projecting the input data on the eigenfaces orthonormal basis done in 0.021s Fitting the classifier to the trainning set done in 21.104s Best estimator found by grid search: SVC(C=1000.0, cache_size=200, class_weight='balanced', coef0=0.0, decision_function_shape='ovr', degree=3, gamma=0.005, kernel='rbf', max_iter=-1, probability=False, random_state=None, shrinking=True, tol=0.001, verbose=False) Predicting people's names on the test set done in 0.059s precision recall f1-score support Ariel Sharon 0.75 0.60 0.67 15 Colin Powell 0.75 0.80 0.78 56 Donald Rumsfeld 0.93 0.84 0.88 31 George W Bush 0.85 0.95 0.90 136 Gerhard Schroeder 0.90 0.83 0.86 23 Hugo Chavez 1.00 0.75 0.86 24 Tony Blair 0.94 0.81 0.87 37 avg / total 0.86 0.86 0.86 322 [[ 9 1 0 5 0 0 0] [ 1 45 1 8 0 0 1] [ 0 3 26 2 0 0 0] [ 1 5 1 129 0 0 0] [ 0 0 0 4 19 0 0] [ 1 4 0 0 0 18 1] [ 0 2 0 3 2 0 30]]
运行效果可视化:

相关文章推荐
- 机器学习第十课:支持向量机SVM(一)线性可分(硬间隔)SVM
- 斯坦福大学Andrew Ng - 机器学习笔记(5) -- 支持向量机(SVM)
- 机器学习(八)支持向量机svm终结篇
- 机器学习(五):SVM支持向量机_Python
- 机器学习 ——支持向量机SVM
- 【机器学习实战-python3】支持向量机(Support Vecrtor Machines SVM)
- 机器学习中的算法(2)-支持向量机(SVM)基础
- 机器学习中的算法(2)-支持向量机(SVM)基础
- 机器学习中的算法-支持向量机(SVM)基础
- 【机器学习】推导支持向量机SVM二分类
- opencv3/C++ 机器学习-支持向量机SVM
- 机器学习——支持向量机(SVM)
- 机器学习--SVM支持向量机
- 机器学习中的算法(2)-支持向量机(SVM)基础
- 机器学习中的算法(2)-支持向量机(SVM)基础
- 机器学习——支持向量机SVM之核函数
- 林轩田--机器学习技法--SVM笔记1--线性支持向量机(linear+SVM)
- 机器学习实战之支持向量机SVM-1
- 机器学习——支持向量机SVM在R中的实现
- 机器学习中的算法-支持向量机(SVM)基础
