TCP Three-way Handshake
2017-10-21 10:03
393 查看
TCP Connection Management
Out-of-Order and Duplication(复制) ProblemOld segment from previous connections to come
Use long sequence number (32-bits)
Establish randomly selected initial sequence number (ISN)
Accept sequence numbers from a small window(To allow the network to clear old segments from the network)
Enforces a time-out period at end of connection, called maximum segment lifetime (MSL), usually 2 minutes but round-trip delay dependent
TCP Header – Seq and Ack
Sequence NumberByte count
First byte in segment
32 bits long
0 <= SN <= 2^32-1
Initial sequence number (ISN) selected during connection setup (SYN flag bit is 1);
Acknowledgement Number
SN of next byte expected by receiver
Acknowledges that all prior bytes in stream have been received correctly
Valid if ACK flag is set
TCP Header – Control bits
Control6 bits
URG: urgent pointer flag
Urgent message end = SN + urgent pointer
ACK: ACK packet flag
PSH: override TCP buffering
RST: reset connection
Upon receipt of RST, connection is terminated and application layer notified(被通知)
SYN: establish connection
FIN: close connection
TCP Connection Management
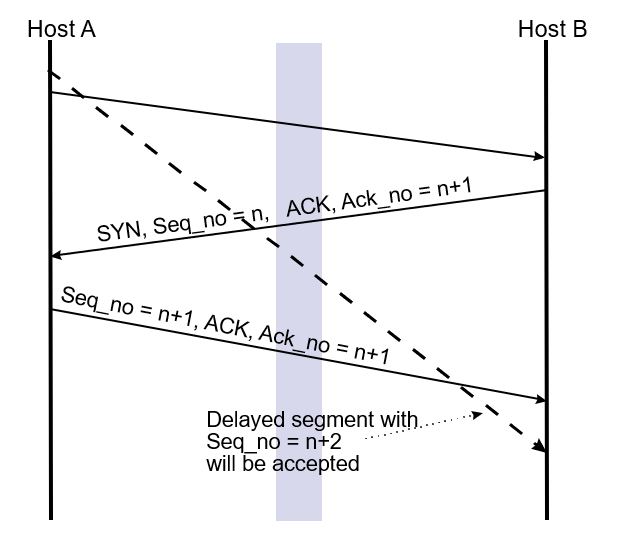
“Three-way Handshake”ISN’s protect against segments from prior connections

If host always uses the same ISN
TCP Connection Closing
“Graceful Close”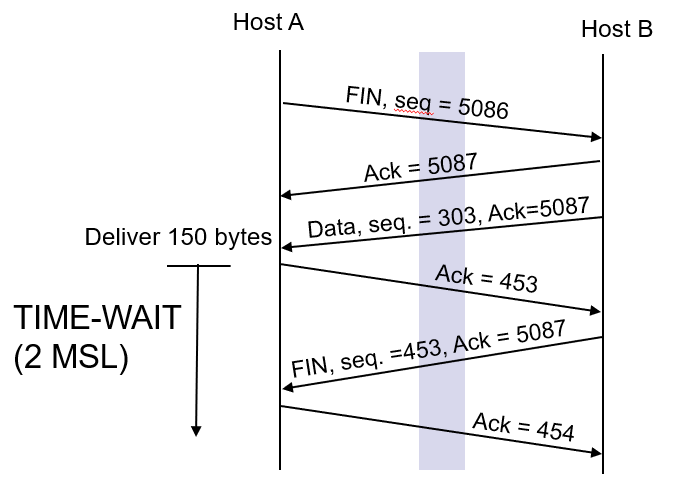
TCP Tree-way handshake
Establish connectionTransfer data
Close the connection
相关文章推荐
- TCP Three-Way handshake
- TCP Three-Way handshake
- [patch] fix WPA: Not enough entropy in random pool to proceed - reject first 4-way handshake
- TCP 3-Way Handshake (SYN,SYN-ACK,ACK)
- TCP三次握手过程详解(二) three way handshake of TCP
- socket 编程入门教程(三)TCP原理:5、TCP的三次握手(three-way handshake)
- 三次握手Three-way Handshake
- TCP 3次握手模式(3-WAY HANDSHAKE)
- 4 way handshake
- RSNA、802.1X及4-way handshake的关系
- 著名的三次握手(three-way handshake)
- WPA-PSK 4-way handshake 四次握手过程
- TCP三次握手(Three-way Handshake)
- 802.1X的wpa认证流程-------4-way handshake过程分析
- TCP 3 way handshake
- wpa的4-Way Handshake
- 三次握手Three-way Handshake
- socket 编程入门教程(三)TCP原理:5、TCP的三次握手(three-way handshake)
- TCP Three Way Handshake
- socket 编程入门教程(三)TCP原理:5、TCP的三次握手(three-way handshake)
