浅谈设计模式之简单工厂模式
2017-10-15 14:08
344 查看
简单工厂模式简介
简单工厂模式是属于创建型模式,又叫做静态工厂方法(Static Factory Method)模式,但不属于23种GOF设计模式之一。简单工厂模式是由一个工厂对象决定创建出哪一种产品类的实例。简单工厂模式是工厂模式家族中最简单实用的模式,可以理解为是不同工厂模式的一个特殊实现。(简而言之,就是有一个专门生产某个产品的类。比如下图中的鼠标工厂,专业生产鼠标,给参数0,生产戴尔鼠标,给参数1,生产惠普鼠标)简单工厂模式的UML类图
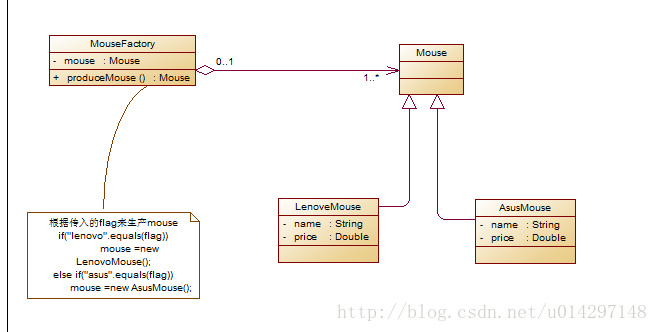
简单工厂模式简单实现
生产某个产品的工厂 如mouse鼠标工厂 MouseFactory/**
* @Description 鼠标工厂
* @Author xiaoqx <worldly_xuan@163.com>
* @Version V1.0.0
* @Since 1.0
* @Date 2018/1/27
*/
public class MouseFactory {
private static Mouse mouse;
//传入什么品牌就生产对应得品牌
public static Mouse produceMouse(String flag){
if("lenovo".equals(flag))
mouse =new LenovoMouse();
else if("asus".equals(flag))
mouse =new AsusMouse();
else
mouse =null;
return mouse;
}
}产品的抽象角色(如:鼠标mouse)
public abstract class Mouse{
}具体产品如联想鼠标LenoveMouse,华硕鼠标 AsusMouse
/**
* @Description 联想鼠标
* @Author xiaoqx <worldly_xuan@163.com>
* @Version V1.0.0
* @Since 1.0
* @Date 2018/1/27
*/
public class LenovoMouse extends Mouse{
private String name;
private Double price;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{\"LenovoMouse\":{"
+ "\"name\":\"" + name + "\""
+ ", \"price\":\"" + price + "\""
+ "}}";
}
}
/**
* @Description 华硕鼠标
* @Author xiaoqx <worldly_xuan@163.com>
* @Version V1.0.0
* @Since 1.0
* @Date 2018/1/27
*/
public class AsusMouse extends Mouse {
private String name;
private Double price;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{\"AsusMouse\":{"
+ "\"name\":\"" + name + "\""
+ ", \"price\":\"" + price + "\""
+ "}}";
}
}缺点
每增加一个具体产品,都需要修改源码,违反面向对象原则的开闭原则;所有的产品都是由 MouseFactory来生产的,比较臃肿比较难维护;
在jdk中的应用
/**
* Gets a calendar with the specified time zone and locale.
* The <code>Calendar</code> returned is based on the current time
* in the given time zone with the given locale.
*
* @param zone the time zone to use
* @param aLocale the locale for the week data
* @return a Calendar.
*/
public static Calendar getInstance(TimeZone zone,
Locale aLocale)
{
return createCalendar(zone, aLocale);
}
private static Calendar createCalendar(TimeZone zone,
Locale aLocale)
{
CalendarProvider provider =
LocaleProviderAdapter.getAdapter(CalendarProvider.class, aLocale)
.getCalendarProvider();
if (provider != null) {
try {
return provider.getInstance(zone, aLocale);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
// fall back to the default instantiation
}
}
Calendar cal = null;
//根据传入的aLocale来 new Calendar,采用简单工厂模式的实现
if (aLocale.hasExtensions()) {
String caltype = aLocale.getUnicodeLocaleType("ca");
if (caltype != null) {
switch (caltype) {
case "buddhist":
cal = new BuddhistCalendar(zone, aLocale);
break;
case "japanese":
cal = new JapaneseImperialCalendar(zone, aLocale);
break;
case "gregory":
cal = new GregorianCalendar(zone, aLocale);
break;
}
}
}
if (cal == null) {
// If no known calendar type is explicitly specified,
// perform the traditional way to create a Calendar:
// create a BuddhistCalendar for th_TH locale,
// a JapaneseImperialCalendar for ja_JP_JP locale, or
// a GregorianCalendar for any other locales.
// NOTE: The language, country and variant strings are interned.
if (aLocale.getLanguage() == "th" && aLocale.getCountry() == "TH") {
cal = new BuddhistCalendar(zone, aLocale);
} else if (aLocale.getVariant() == "JP" && aLocale.getLanguage() == "ja"
&& aLocale.getCountry() == "JP") {
cal = new JapaneseImperialCalendar(zone, aLocale);
} else {
cal = new GregorianCalendar(zone, aLocale);
}
}
return cal;
}
相关文章推荐
- 【浅谈设计模式】1 简单工厂模式
- 浅谈设计模式之一——简单工厂、工厂、抽象工厂
- 浅谈常见设计模式--单例模式 简单工厂模式
- 浅谈观察者、工厂、简单工厂设计模式
- 设计模式-简单工厂模式
- 【设计模式】简单工厂模式
- 设计模式:简单工厂、工厂方法、抽象工厂之小结与区别
- C++设计模式之一 工厂模式(简单工厂、工厂和抽象工厂)
- 设计模式:简单工厂、工厂方法、抽象工厂之小结与区别
- php设计模式之简单工厂模式
- 设计模式之—简单工厂设计模式
- 跟我学设计模式视频教程——面向对象理论,简单工厂,工厂方法
- 23大设计模式+简单工厂
- Java 设计模式之简单工厂模式
- 简单的计算器程序可以用到简单工厂的设计模式
- python设计模式(1)-Simple Factory(Static Factory)(简单工厂)
- 简单工厂模式——23种设计模式综合实例应用
- [设计模式]两种方法实现简单工厂模式
- 设计模式01 简单工厂模式
- 设计模式心得笔记--简单工厂
