【Java基础】——线程Thread VS Runnable
2017-10-13 00:00
357 查看
进程和线程的关系
多个线程构成一个进程,线程是进程中的一个元素,例如QQ.exe查看电脑进程的时候发现只有一个进程,但是我们可以同时和多个用户聊天交流,而且可以一边聊天,刷空间之类。对每一个用户的聊天就是一个线程,多个用户的互动构成进程。演示一个不使用多线程的Demo,也就是单线程
public class SingleDemo{ public static void main(String[] args){ MyThread myThread = new MyThread(); myThread.run(); while(true){ System.out.println("Main方法在运行"); } } } class MyThread{ public void run(){ while (true){ System.out.println("MyThread类的run()方法在运行"); } } }根据demo可以知道mian中的run方法永远都不可能被执行
一张图说明何为单线程和多线程!
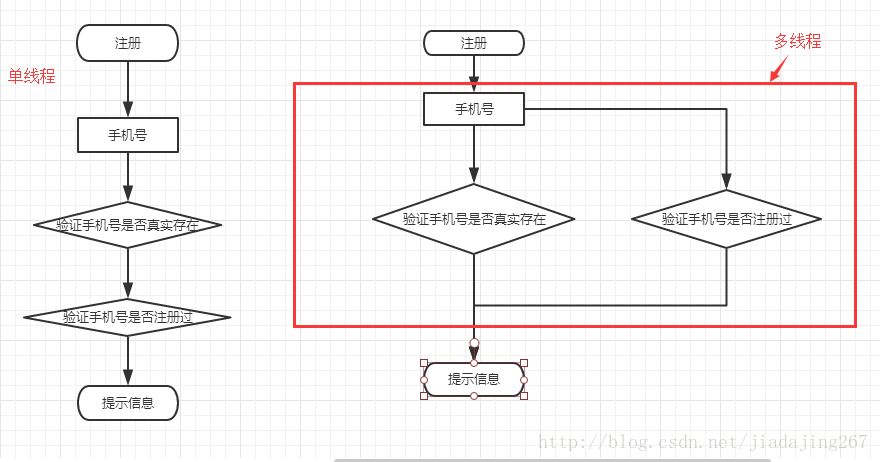
从图中很清晰表明我们使用多线程的原因
继承Thread创建多线程
public class DemoThread{ public static void main(String[] args){ MyThread myThread = new MyThread(); myThread.start(); while(true){ System.out.println("run()方法在运行"); } } } class MyThread extends Thread { public void run(){ while(true){ System.out.println("MyThread类的run()方法在运行"); } } }显示结果
实现Runnable接口创建多线程
public class DemoRunnable{ public static void main(String[] args){ RunnableDemo runnable = new RunnableDemo(); Thread mythread = new Thread(runnable); mythread.start(); while(true){ System.out.println("main类的run()方法在运行"); } } } class RunnableDemo implements Runnable{ public void run(){ while(true){ System.out.println("RunnableDemo类的run()方法在运行"); } } }显示结果
Runnable的实现机制
其实是利用Thread(Runnable target)这个构造函数实现的,Runnable是一个接口其中只有一个run()方法,在调用Thread时,其实实现的是接口Runnable中的方法。Thread VS Runnable两者的不同
先说一个例子,火车站售票会牵扯到一个资源共享的问题,资源就是车票,每个售票都相当与一个线程,假如有100张票,每张票理论上都只能买一个人,下面看Thread和Runnable的处理方式继承Thread
public class DemoExceple{ public static void main(String[] args){ new TicketWindow().start(); new TicketWindow().start(); new TicketWindow().start(); new TicketWindow().start(); } } class TicketWindow extends Thread{ private int tickets = 100; public void run(){ while(true){ if(tickets>0){ Thread th = Thread.currentThread(); String name = th.getName(); System.out.println(name+"正在发售第"+tickets--+"张票"); } } } }运行结果
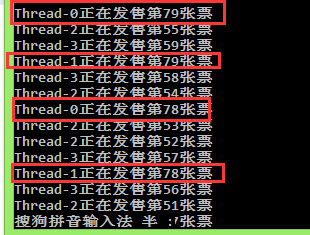
根据这个运行结果,发现每一张票都被重复卖了四次,明显这种多线程的方式并不太适合资源共享的问题。
实现Runnable接口
public class RunnableDemoTest{ public static void main(String[] args){ TicketWindow tw = new TicketWindow(); new Thread(tw,"窗口1").start(); new Thread(tw,"窗口2").start(); new Thread(tw,"窗口3").start(); new Thread(tw,"窗口4").start(); } } class TicketWindow implements Runnable{ private int tickets = 100; public void run(){ while(true){ if(tickets>0){ Thread th = Thread.currentThread(); String th_name = th.getName(); System.out.println(th_name+"正在发售第"+tickets--+"张票"); } } } }运行结果
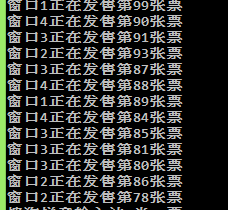
根据运行结果发现使用Runnable接口刚好能解决我们资源共享的问题。
结论
根据上述两种情况的对比,发现Runnable接口相对Thread更实用一些。1、Runnable适合多个相同的代码线程去处理同一个资源的情况,把线程同程序代码做了很好的隔离,更接近面向对象的思想,解决资源共享的问题。
2、Runnable可以避免Java中单继承的局限性,一个子类继承父类,不能在继承Thread实现多线程,Runnable接口刚好是完美的解决方案。
整体上来说,大部分应用程序会采用Runnable的方式来创建多线程。
小编也是刚刚开始学习,如有错误之处还请指出,不胜感激!
相关文章推荐
- Java线程基础(一):Thread和Runnable
- JAVA与多线程开发(线程基础、继承Thread类来定义自己的线程、实现Runnable接口来解决单继承局限性、控制多线程程并发)
- java线程基础巩固---策略模式在Thread和Runnable中的应用分析
- java基础知识回顾之java Thread类--java线程实现常见的两种方式实现Runnable接口(二)
- 2015年11月25 Java基础系列(二)Thread Runnable线程初级讲解
- java 线程 --- Thread,Runnable,Callable 基础学习
- 【Java基础_(线程篇_第一篇)】继承Thread;实现runnable;sleep、wait用法和区别;Thread和Runnable区别;线程停止
- Java线程——Thread与Runnable、start()与run()
- Java线程演示样例 - 继承Thread类和实现Runnable接口
- Java多线程基础-2-简单继承Thread,实现Runnable例子
- Java.线程.Thread类.Runnable接口.start().setDaemon().join()
- 多线程编程(三)--创建线程之Thread VS Runnable
- java 实现线程的三种方式 Thread 、Runnable、 Callable Future
- Java多线程Thread VS Runnable详解
- java线程基础巩固---多线程与JVM内存结构的关系及Thread构造函数StackSize的理解
- Java Thread线程基础总结
- java创建线程implement runnable 和 extends thread 比较
- java入门教程-7.4Java创建线程(Runnable接口和Thread类)
- java中的通过继承Thread和实现Runnable接口实现的线程
- 【转】java线程系列---Runnable和Thread的区别
