SDN in Action: Practice NETCONF/RESTCONF and YANG with OpenDaylight and IOS XRv
2017-10-08 05:57
766 查看
SDN in Action: Practice NETCONF/RESTCONF and YANG with OpenDaylight and IOS XRv
薛国锋 xueguofeng2011@gmail.com
NETCONF provides mechanisms to install, manipulate and delete the configuration of network devices. It uses XML-based data encoding for the configuration data as well as the protocol messages with YANG modeling. NETCONF uses a simple RPC-based mechanism to facilitate communication between a client (SDN controller or Network Manager) and a server (router or switch); after reading the YANG models, the client can understand and communicate with the server accordingly. The underlying transport of NETCONF is connection-oriented and adopts SSH or TLS.
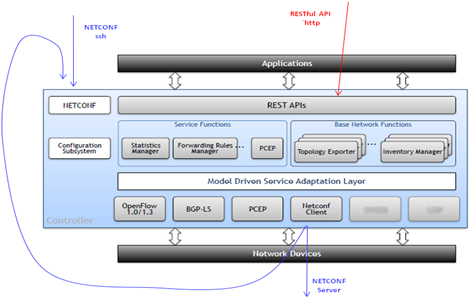
RESTCONF is a protocol that provides RESTful APIs over HTTP to access configure and operational data defined in YANG models and stored in data stores by the NETCONF southbound plugin and other modules of controller, and offers the simplified and friendly way for outside applications to communicate with the controller and network.
Recently we have seen more adoptions of NETCONF/RESTCONF and YANG in SDN solutions, such as SDN-WAN, SD-WAN and SDN-DCN, which deserves a hands-on practice to master how they actually work. Below is the physical and logical design:
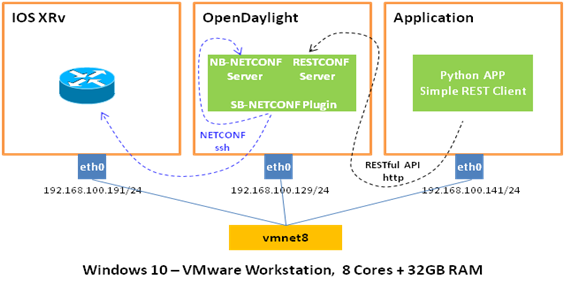
1 Set up the IOS XRv
Download IOS XRv – “iosxrv-k9-demo-5.3.3.ova”from the below web link:
https://github.com/plajjan/vrnetlab/tree/master/xrv
https://upload.cisco.com/cgi-bin/swc/fileexg/main.cgi?CONTYPES=Cisco-IOS-XRv
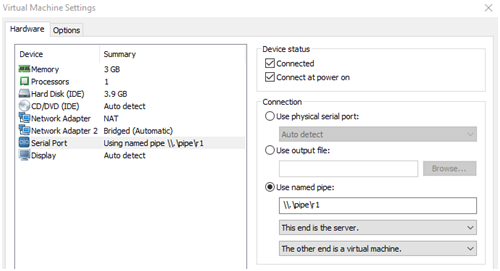
Open it with VMWare Workstation, add the serial port using the named pipe – “\\.\pipe\r1” and runthe IOS XRv:
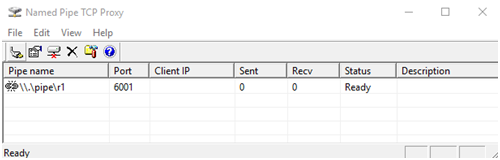
Install and run “NamedPipe TCP Proxy”, and map “\\.\pipe\r1” to “127.0.0.1:6001”:
Install “SecureCRT”, telnet 127.0.0.1:6001 and finish the follow configuration by CLI in the IOS XRv:
interface MgmtEth0/0/CPU0/0
ipv4 address 192.168.100.191 255.255.255.0
!
ssh server v2
ssh server netconf port 830
netconf-yang agent
ssh
Activate crypto keys for SSH by entering the following command in the IOS XRv:
crypto key generate dsa
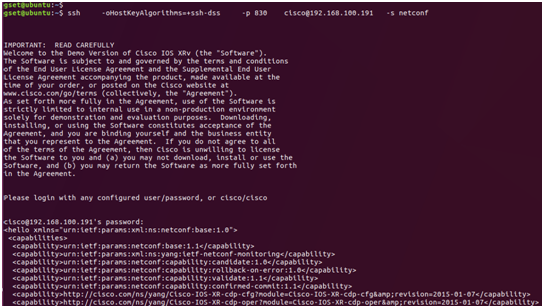
Make sure the NETCONF server feature in the IOS XRv is working properly by entering the below command in an Ubuntu host and check the result:
ssh -oHostKeyAlgorithms=+ssh-dss -p 830 cisco@192.168.100.191 -s netconf
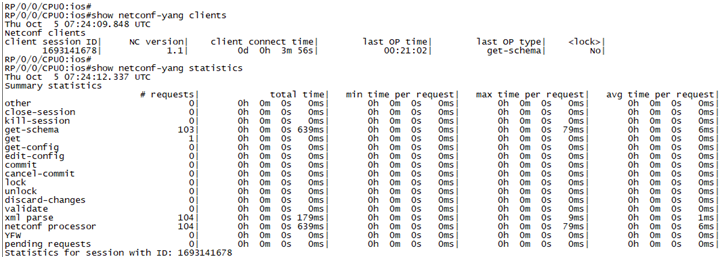
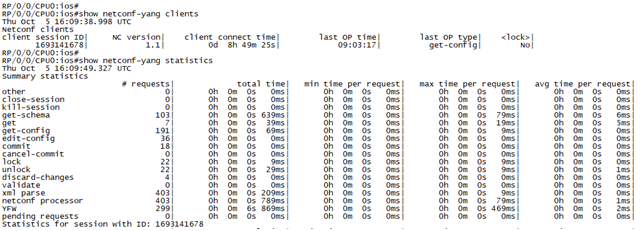
Try the following commands in IOS XRv and check the result:
show netconf-yang clients
show netconf-yang statistics
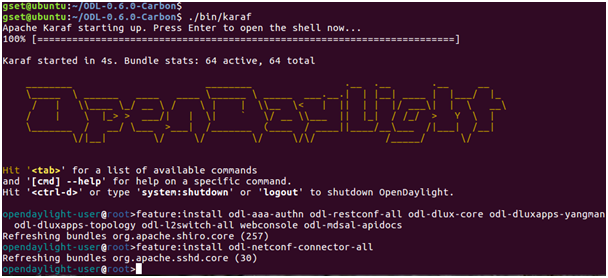
2 Run OpenDaylight and install the necessary features
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-aaa-authn
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-restconf-all
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-dlux-core
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-dluxapps-yangman
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-dluxapps-topology
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-l2switch-all
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installwebconsole
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-mdsal-apidocs
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-netconf-connector-all
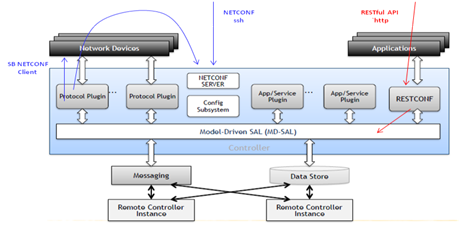
OpenDaylight supports the NETCONF protocol as a northbound server for config-subsystem as well as a southbound plugin connecting remote NETCONF devices. After installing “odl-netconf-connector-all”,a single instance of netconf-connector called “controller-config” is created by OpenDaylight and connected to the NETCONF northbound server in a loopback fashion. The NETCONF northbound server for config-subsystem allows users to spawn/reconfigure/destroy modules or applications in OpenDaylight; the netconf-connector mounts the NETCONF northbound server in order to enable RESTCONF protocol for config-subsystem as well, which is more user-friendly than using NETCONF over SSH directly. More details can befound by the below web link:
http://docs.opendaylight.org/en/stable-carbon/user-guide/netconf-user-guide.html#netconf-user-guide
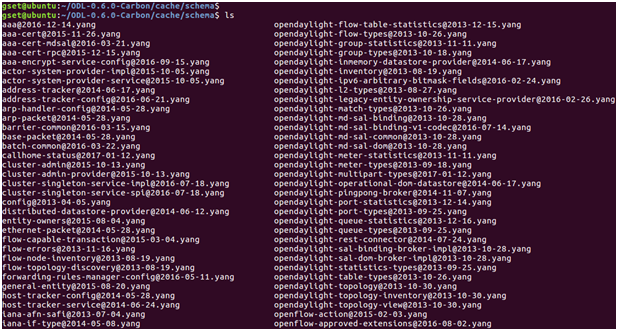
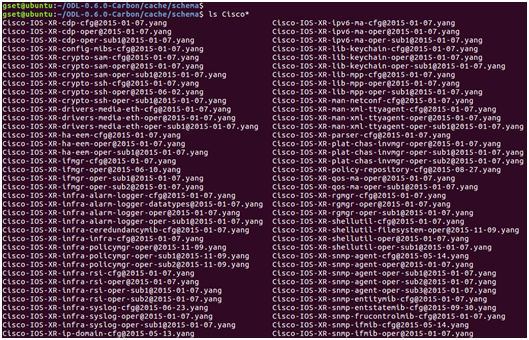
After the NETCONF northbound server is mounted, all the YANG models it supports are downloaded by OpenDaylight using the get-schema operation and put into “/cache/schema”:
With the controller-config netconf-connector, we can directly communicate with the NETCONF northbound server using RESTCONF instead SSH.
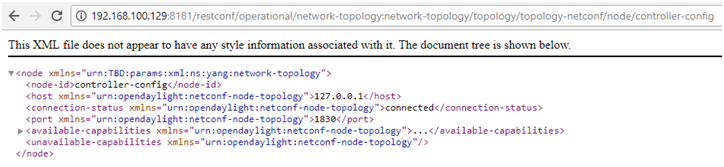
Read the entire content of configure datastore from the NETCONF northbound server:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/controller-config/yang-ext:mount
Read the entire content of operational datastore from the NETCONF northboundserver:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/operational/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/controller-config/yang-ext:mount
Read the configure datastore of the controller-config netconf-connector:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/controller-config
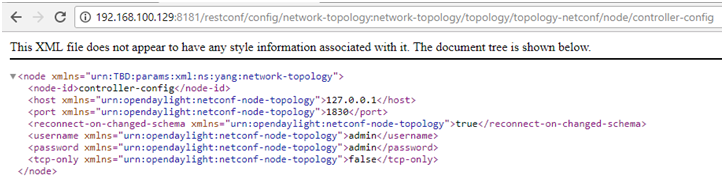
Read the operational datastore of the controller-config netconf-connector:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/operational/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/controller-config
3 Mount IOS XRv in OpenDaylight
Now we can configure the new netconf-connector and mount IOS XRv directly through MD-SAL with the usage ofthe network-topology model.
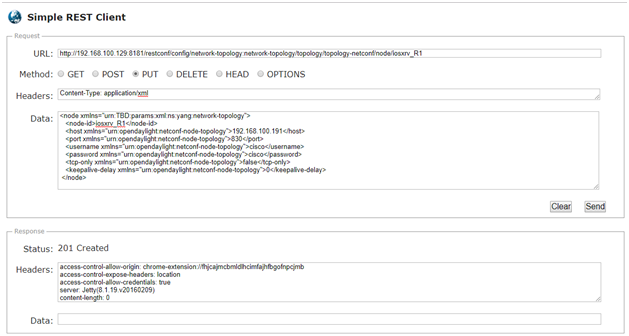
Send the following request (PUT) to OpenDaylight with Simple REST Client:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1
Content-Type: application/xml
<nodexmlns="urn:TBD:params:xml:ns:yang:network-topology">
<node-id>iosxrv_R1</node-id>
<hostxmlns="urn:opendaylight:netconf-node-topology">192.168.100.191</host>
<port xmlns="urn:opendaylight:netconf-node-topology">830</port>
<usernamexmlns="urn:opendaylight:netconf-node-topology">cisco</username>
<passwordxmlns="urn:opendaylight:netconf-node-topology">cisco</password>
<tcp-onlyxmlns="urn:opendaylight:netconf-node-topology">false</tcp-only>
<keepalive-delayxmlns="urn:opendaylight:netconf-node-topology">0</keepalive-delay>
</node>
After the IOS XRv is mounted,all the following YANG models are retrieved from it and put into “/cache/schema”:
With the new netconf-connector– iosxrv_R1, we can invoke RPC(POST, yang-ext:mount/<module>:<operation>) and receive notifications from the IOS XRv, and accordingly get/set/modify its configuration and obtain operational details.
Read the entire content of configure datastore from the IOS XRv:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1/yang-ext:mount
Read the entire content of operational datastore from the the IOSXRv:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/operational/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1/yang-ext:mount
Read the configure datastore of the iosxrv_R1 netconf-connector:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1
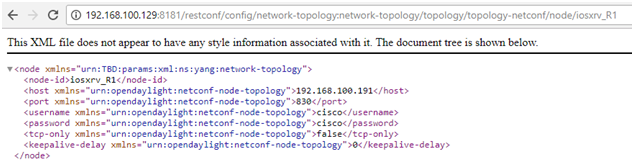
Read the operational datastore of the iosxrv_R1 netconf-connector:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/operational/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1

4 Making API Calls on OpenDaylight to configure the IOS XRv
First let’s use Simple REST Client and send the following request (POST) to OpenDaylight and create the logical interface –loopback1:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1/yang-ext:mount/Cisco-IOS-XR-ifmgr-cfg:interface-configurations
Content-Type:application/xml
<interface-configurationxmlns="http://cisco.com/ns/yang/Cisco-IOS-XR-ifmgr-cfg">
<active>act</active>
<interface-name>Loopback1</interface-name>
<interface-virtual/>
<ipv4-networkxmlns="http://cisco.com/ns/yang/Cisco-IOS-XR-ipv4-io-cfg">
<addresses>
<primary>
<netmask>255.255.255.255</netmask>
<address>1.1.1.1</address>
</primary>
</addresses>
</ipv4-network>
</interface-configuration>
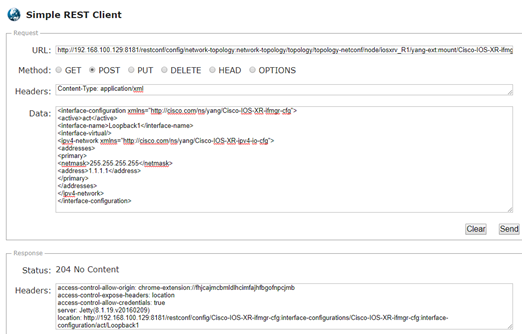
Now we write a Python APP and send the request (POST) to OpenDaylight:
/////////////////////////////////////// command.xml
<interface-configuration xmlns="http://cisco.com/ns/yang/Cisco-IOS-XR-ifmgr-cfg">
<active>act</active>
<interface-name>Loopback2</interface-name>
<interface-virtual/>
<ipv4-networkxmlns="http://cisco.com/ns/yang/Cisco-IOS-XR-ipv4-io-cfg">
<addresses>
<primary>
<netmask>255.255.255.255</netmask>
<address>1.1.1.2</address>
</primary>
</addresses>
</ipv4-network>
</interface-configuration>
/////////////////////////////////////// application.py
import requests
from xml.etree importElementTree
header = {'content-type': 'application/xml','Accept':'application/xml'}
# getting the entire content of configure datastore from the IOS XRv:
r = requests.get( url = 'http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1/yang-ext:mount', headers = header,auth=('admin','admin'))
print(str(r.status_code))
print(r.url)
print("\n")
root = ElementTree.fromstring(r.text)
print(root.tag)
for child in root:
print(child.tag)
for node in root[2]:
print(node[1].text)
print("\n")
# Sending the request to add the logical interface of loopback2 in the IOS XRv:
with open('command.xml') asfile_object:
contents = file_object.read()
r = requests.post( url ='http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1/yang-ext:mount/Cisco-IOS-XR-ifmgr-cfg:interface-configurations',headers = header, data = contents, auth =('admin','admin'))
print(str(r.status_code))
print(r.url)
print("\n")
# getting the entire content of configure data storefrom the IOS XRv:
r = requests.get( url = 'http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1/yang-ext:mount', headers = header,auth=('admin','admin'))
print(str(r.status_code))
print(r.url)
print("\n")
root = ElementTree.fromstring(r.text)
print(root.tag)
for child in root:
print(child.tag)
for node in root[2]:
print(node[1].text)
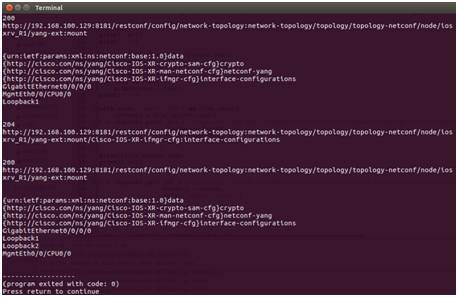
Check the running status of IOS XRv by CLI:
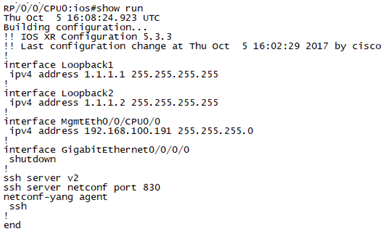
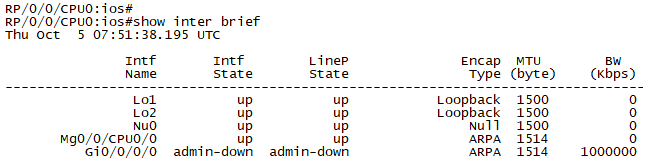
Main takeaways
This test is very simple, the SDN controller only provides the gateway function between RESTCONF/HTTP and NETCONF/SSH – a fancy form of NMS. The commercial SDN solutions can offer more intelligence, such multi-layer or area orchestration, multi-vendor deployment, traffic engineering and service automation, etc.
From this test, we also have a better understanding regarding to the architecture of OpenDaylight and the functionalities of key components: MD-SAL provides infrastructure services - DataStore, RPC / Service routing, notification subscription and publish services, and unifies both northbound and southbound APIs and the data structures for all the modules in OpenDaylight to cooperate with each other by native Java API calls,for which YANG modeling plays a critical role; while RESTCONF extends such capabilities to outside applications, allowing them to interact efficiently with the modules inside OpenDaylight.
薛国锋 xueguofeng2011@gmail.com
NETCONF provides mechanisms to install, manipulate and delete the configuration of network devices. It uses XML-based data encoding for the configuration data as well as the protocol messages with YANG modeling. NETCONF uses a simple RPC-based mechanism to facilitate communication between a client (SDN controller or Network Manager) and a server (router or switch); after reading the YANG models, the client can understand and communicate with the server accordingly. The underlying transport of NETCONF is connection-oriented and adopts SSH or TLS.
RESTCONF is a protocol that provides RESTful APIs over HTTP to access configure and operational data defined in YANG models and stored in data stores by the NETCONF southbound plugin and other modules of controller, and offers the simplified and friendly way for outside applications to communicate with the controller and network.
Recently we have seen more adoptions of NETCONF/RESTCONF and YANG in SDN solutions, such as SDN-WAN, SD-WAN and SDN-DCN, which deserves a hands-on practice to master how they actually work. Below is the physical and logical design:

1 Set up the IOS XRv
Download IOS XRv – “iosxrv-k9-demo-5.3.3.ova”from the below web link:
https://github.com/plajjan/vrnetlab/tree/master/xrv
https://upload.cisco.com/cgi-bin/swc/fileexg/main.cgi?CONTYPES=Cisco-IOS-XRv
Open it with VMWare Workstation, add the serial port using the named pipe – “\\.\pipe\r1” and runthe IOS XRv:

Install and run “NamedPipe TCP Proxy”, and map “\\.\pipe\r1” to “127.0.0.1:6001”:

Install “SecureCRT”, telnet 127.0.0.1:6001 and finish the follow configuration by CLI in the IOS XRv:
interface MgmtEth0/0/CPU0/0
ipv4 address 192.168.100.191 255.255.255.0
!
ssh server v2
ssh server netconf port 830
netconf-yang agent
ssh
Activate crypto keys for SSH by entering the following command in the IOS XRv:
crypto key generate dsa
Make sure the NETCONF server feature in the IOS XRv is working properly by entering the below command in an Ubuntu host and check the result:
ssh -oHostKeyAlgorithms=+ssh-dss -p 830 cisco@192.168.100.191 -s netconf

Try the following commands in IOS XRv and check the result:
show netconf-yang clients
show netconf-yang statistics

2 Run OpenDaylight and install the necessary features
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-aaa-authn
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-restconf-all
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-dlux-core
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-dluxapps-yangman
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-dluxapps-topology
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-l2switch-all
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installwebconsole
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-mdsal-apidocs
opendaylight-user@root>feature:installodl-netconf-connector-all

OpenDaylight supports the NETCONF protocol as a northbound server for config-subsystem as well as a southbound plugin connecting remote NETCONF devices. After installing “odl-netconf-connector-all”,a single instance of netconf-connector called “controller-config” is created by OpenDaylight and connected to the NETCONF northbound server in a loopback fashion. The NETCONF northbound server for config-subsystem allows users to spawn/reconfigure/destroy modules or applications in OpenDaylight; the netconf-connector mounts the NETCONF northbound server in order to enable RESTCONF protocol for config-subsystem as well, which is more user-friendly than using NETCONF over SSH directly. More details can befound by the below web link:
http://docs.opendaylight.org/en/stable-carbon/user-guide/netconf-user-guide.html#netconf-user-guide
After the NETCONF northbound server is mounted, all the YANG models it supports are downloaded by OpenDaylight using the get-schema operation and put into “/cache/schema”:

With the controller-config netconf-connector, we can directly communicate with the NETCONF northbound server using RESTCONF instead SSH.
Read the entire content of configure datastore from the NETCONF northbound server:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/controller-config/yang-ext:mount
Read the entire content of operational datastore from the NETCONF northboundserver:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/operational/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/controller-config/yang-ext:mount
Read the configure datastore of the controller-config netconf-connector:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/controller-config

Read the operational datastore of the controller-config netconf-connector:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/operational/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/controller-config

3 Mount IOS XRv in OpenDaylight
Now we can configure the new netconf-connector and mount IOS XRv directly through MD-SAL with the usage ofthe network-topology model.
Send the following request (PUT) to OpenDaylight with Simple REST Client:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1
Content-Type: application/xml
<nodexmlns="urn:TBD:params:xml:ns:yang:network-topology">
<node-id>iosxrv_R1</node-id>
<hostxmlns="urn:opendaylight:netconf-node-topology">192.168.100.191</host>
<port xmlns="urn:opendaylight:netconf-node-topology">830</port>
<usernamexmlns="urn:opendaylight:netconf-node-topology">cisco</username>
<passwordxmlns="urn:opendaylight:netconf-node-topology">cisco</password>
<tcp-onlyxmlns="urn:opendaylight:netconf-node-topology">false</tcp-only>
<keepalive-delayxmlns="urn:opendaylight:netconf-node-topology">0</keepalive-delay>
</node>

After the IOS XRv is mounted,all the following YANG models are retrieved from it and put into “/cache/schema”:

With the new netconf-connector– iosxrv_R1, we can invoke RPC(POST, yang-ext:mount/<module>:<operation>) and receive notifications from the IOS XRv, and accordingly get/set/modify its configuration and obtain operational details.
Read the entire content of configure datastore from the IOS XRv:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1/yang-ext:mount
Read the entire content of operational datastore from the the IOSXRv:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/operational/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1/yang-ext:mount
Read the configure datastore of the iosxrv_R1 netconf-connector:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1

Read the operational datastore of the iosxrv_R1 netconf-connector:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/operational/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1

4 Making API Calls on OpenDaylight to configure the IOS XRv
First let’s use Simple REST Client and send the following request (POST) to OpenDaylight and create the logical interface –loopback1:
http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1/yang-ext:mount/Cisco-IOS-XR-ifmgr-cfg:interface-configurations
Content-Type:application/xml
<interface-configurationxmlns="http://cisco.com/ns/yang/Cisco-IOS-XR-ifmgr-cfg">
<active>act</active>
<interface-name>Loopback1</interface-name>
<interface-virtual/>
<ipv4-networkxmlns="http://cisco.com/ns/yang/Cisco-IOS-XR-ipv4-io-cfg">
<addresses>
<primary>
<netmask>255.255.255.255</netmask>
<address>1.1.1.1</address>
</primary>
</addresses>
</ipv4-network>
</interface-configuration>

Now we write a Python APP and send the request (POST) to OpenDaylight:
/////////////////////////////////////// command.xml
<interface-configuration xmlns="http://cisco.com/ns/yang/Cisco-IOS-XR-ifmgr-cfg">
<active>act</active>
<interface-name>Loopback2</interface-name>
<interface-virtual/>
<ipv4-networkxmlns="http://cisco.com/ns/yang/Cisco-IOS-XR-ipv4-io-cfg">
<addresses>
<primary>
<netmask>255.255.255.255</netmask>
<address>1.1.1.2</address>
</primary>
</addresses>
</ipv4-network>
</interface-configuration>
/////////////////////////////////////// application.py
import requests
from xml.etree importElementTree
header = {'content-type': 'application/xml','Accept':'application/xml'}
# getting the entire content of configure datastore from the IOS XRv:
r = requests.get( url = 'http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1/yang-ext:mount', headers = header,auth=('admin','admin'))
print(str(r.status_code))
print(r.url)
print("\n")
root = ElementTree.fromstring(r.text)
print(root.tag)
for child in root:
print(child.tag)
for node in root[2]:
print(node[1].text)
print("\n")
# Sending the request to add the logical interface of loopback2 in the IOS XRv:
with open('command.xml') asfile_object:
contents = file_object.read()
r = requests.post( url ='http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1/yang-ext:mount/Cisco-IOS-XR-ifmgr-cfg:interface-configurations',headers = header, data = contents, auth =('admin','admin'))
print(str(r.status_code))
print(r.url)
print("\n")
# getting the entire content of configure data storefrom the IOS XRv:
r = requests.get( url = 'http://192.168.100.129:8181/restconf/config/network-topology:network-topology/topology/topology-netconf/node/iosxrv_R1/yang-ext:mount', headers = header,auth=('admin','admin'))
print(str(r.status_code))
print(r.url)
print("\n")
root = ElementTree.fromstring(r.text)
print(root.tag)
for child in root:
print(child.tag)
for node in root[2]:
print(node[1].text)

Check the running status of IOS XRv by CLI:



Main takeaways
This test is very simple, the SDN controller only provides the gateway function between RESTCONF/HTTP and NETCONF/SSH – a fancy form of NMS. The commercial SDN solutions can offer more intelligence, such multi-layer or area orchestration, multi-vendor deployment, traffic engineering and service automation, etc.
From this test, we also have a better understanding regarding to the architecture of OpenDaylight and the functionalities of key components: MD-SAL provides infrastructure services - DataStore, RPC / Service routing, notification subscription and publish services, and unifies both northbound and southbound APIs and the data structures for all the modules in OpenDaylight to cooperate with each other by native Java API calls,for which YANG modeling plays a critical role; while RESTCONF extends such capabilities to outside applications, allowing them to interact efficiently with the modules inside OpenDaylight.


相关文章推荐
- SDN in Action: Practice SDN/OpenFlow with LINC-Switch and OpenDaylight
- OpenDaylight: Programming Flows with the REST Interface and cURL
- ASP.NET MVC – Create easy REST API with JSON and XML(转)
- SDN in Action: Build a mini-lab environment and practice SDN-IP/ONOS with GNS3, Mininet and VMware
- CDH flume ETL with morpnline conf and write into solr
- Creating a REST API with Spring Boot and MongoDB
- Static Libs With Support to iOS 5 and Arm64
- SDN in Action: Prepare for OpenDaylight Code
- WCF REST Configuration for ASP.NET AJAX and plain REST Services
- Active Directory Authentication in ASP.NET MVC 5 with Forms Authentication and Group-Based Authorization
- Wrestling with Status Bars and Navigation Bars on iOS 7(在处理iOS7中的Status Bar和Navigation Bar时的挣扎)
- Cool Tips and Tricks with ASP.NET 2.0 posted by Scott
- 推荐一篇好文《NHibernate Best Practices with ASP.NET and Generics》
- How and Where Concurrent Asynchronous I/O with ASP.NET Web API 对异步编程分析的非常的好
- Caution with using asp.net session timeout and FormsAuthentication timeout together
- Applying Domain-Driven Design and Patterns: With Examples in C# and .NET
- Advanced Data Access with ADO.NET and Oracle
- How to create iOS 8 Today extension and share data with containing app – tutorial
- REST on ASP.Net MVC (and Future)
- 《Semantic image segmentation with deep convolution nets and fully connected CRFs》学习总结(deeplabV1)
