hdu6171 双向搜索+hash
2017-08-26 22:02
225 查看
Suppose that you are an admiral of a famous naval troop. Our naval forces have got 21 battleships. There are 6 types of battleships.
First, we have got one flagship in which the admiral must be and it is denoted by number 0. Others are denoted by number from 1 to 5, each of them has 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ships of its kind. So, we have got 21 battleships in total and we must take a giant battle against
the enemy. Hence, the correct strategy of how to arrange each type of battleships is very important to us.
The shape of the battlefield is like the picture that is shown below.
To simplify the problem, we consider all battleships have the same rectangular shape.
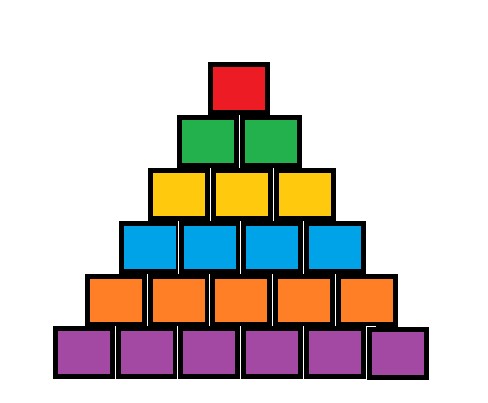
Fortunately, we have already known the optimal state of battleships.
As you can see, the battlefield consists of 6 rows. And we have 6 types of battleship, so the optimal state is that all the battleships denoted by number i are located at the i-th row. Hence, each type of battleship corresponds to different color.
You are given the initial state of battlefield as input. You can change the state of battlefield by changing the position of flagship with adjacent battleship.
Two battleships are considered adjacent if and only if they are not in the same row and share parts of their edges. For example, if we denote the cell which is at i-th row and j-th position from the left as (i,j), then the cell (2,1) is adjacent to the cells
(1,0), (1,1), (3,1), (3,2).
Your task is to change the position of the battleships minimum times so as to reach the optimal state.
Note: All the coordinates are 0-base indexed.
Input
The first line of input contains an integer T (1 <= T <= 10), the number of test cases.
Each test case consists of 6 lines. The i-th line of each test case contains i integers, denoting the type of battleships at i-th row of battlefield, from left to right.
Output
For each test case, if you can’t reach the goal in no more than 20 moves, you must output “too difficult” in one line. Otherwise, you must output the answer in one line.
Sample Input
1
1
2 0
2 1 2
3 3 3 3
4 4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5 5
Sample Output
3
Source
2017 Multi-University Training Contest - Team 10
题意:给出一个图,问我们能否经过最多20步的转移达到
0
1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3 3
4 4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5 5
这种,但是只能拿0和他四个方向的单元换(左上,上,下,右下)
思路:直接搜索的话20步,没个10秒,完不成的,所以可以双向搜索,因为我们知道如果可以的话最终图的形态肯定是
0
1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3 3
4 4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5 5
所以我们 可以先根据结果预先倒着搜10步,并将中间的状态压缩,并记录到达中间状态的步数
然后我们在从0所在的位置正面搜索10步,如果搜到的状态与预处理的相同的话,就是一条完整的路线,在这个过程中维护最小值
中间状态压缩用字符串hash的方式,把整个中间图压缩成一个字符串然后map记录步数
ac代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
map<unsigned long long int,int>ss,ss2;
unsigned long long int h[45];
struct node
{
int x,y,step;
char temp[25];
}now,nex;
int a[8][8];
int output;
int poss[8][8];
int fx[4]={1,-1,1,-1};
int fy[4]={0,0,1,-1};
int get
4000
pos(int x,int y)
{
return poss[x][y];
}
unsigned long long int Getval(char s[])
{
int n=strlen(s);
unsigned long long int x=1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
h[i]=h[i-1]+x*(s[i]-'0');
x=x*31;
}
return h[n-1];
}
void Bfs()
{
queue<node>s;
now.x=1;
now.y=1;
now.step=0;
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
poss[i][j]=cnt;
now.temp[cnt++]=i+'0'-1;
}
}
now.temp[cnt]='\0';
s.push(now);
while(!s.empty())
{
now=s.front();s.pop();
ss[Getval(now.temp)]=now.step;
if(now.step>=10)break;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
nex=now;
nex.x+=fx[i];
nex.y+=fy[i];
nex.step++;
if(nex.x>=1&&nex.x<=6&&nex.y>=1&&nex.y<=nex.x)
{
int pos1=getpos(now.x,now.y);
int pos2=getpos(nex.x,nex.y);
swap(nex.temp[pos1],nex.temp[pos2]);
unsigned long long int nexval=Getval(nex.temp);
if(ss[nexval]==0)
{
ss[nexval]=nex.step;
s.push(nex);
}
}
}
}
}
void Bfs2()
{
ss2.clear();
queue<node>s;
output=40;
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
now.temp[cnt++]=a[i][j]+'0';
if(a[i][j]==0)
{
now.x=i;
now.y=j;
now.step=0;
}
}
}
now.temp[cnt]='\0';
s.push(now);
while(!s.empty())
{
now=s.front();s.pop();
ss2[Getval(now.temp)]=now.step;
if(now.step>=10)break;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
nex=now;
nex.x+=fx[i];
nex.y+=fy[i];
nex.step++;
if(nex.x>=1&&nex.x<=6&&nex.y>=1&&nex.y<=nex.x)
{
int pos1=getpos(now.x,now.y);
int pos2=getpos(nex.x,nex.y);
swap(nex.temp[pos1],nex.temp[pos2]);
unsigned long long int nexval=Getval(nex.temp);
if(ss2[nexval]==0)
{
ss2[nexval]=nex.step;
s.push(nex);
}
if(ss[nexval]>0)
{
output=min(output,nex.step+ss[nexval]);
}
}
}
}
if(output==40)printf("too difficult\n");
else printf("%d\n",output);
}
int main()
{
ss.clear();
Bfs();
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
int len=0;
char bb[55];
char aa[55];
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
bb[len]=i-1+'0';
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
aa[len++]=a[i][j]+'0';
}
}
bb[len]='\0';
aa[len]='\0';
if(strcmp(aa,bb)==0)
{
printf("0\n");
continue;
}
int anssss=ss[Getval(aa)];
if(anssss==0)
{
Bfs2();
}
else printf("%d\n",anssss);
}
}
First, we have got one flagship in which the admiral must be and it is denoted by number 0. Others are denoted by number from 1 to 5, each of them has 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ships of its kind. So, we have got 21 battleships in total and we must take a giant battle against
the enemy. Hence, the correct strategy of how to arrange each type of battleships is very important to us.
The shape of the battlefield is like the picture that is shown below.
To simplify the problem, we consider all battleships have the same rectangular shape.

Fortunately, we have already known the optimal state of battleships.
As you can see, the battlefield consists of 6 rows. And we have 6 types of battleship, so the optimal state is that all the battleships denoted by number i are located at the i-th row. Hence, each type of battleship corresponds to different color.
You are given the initial state of battlefield as input. You can change the state of battlefield by changing the position of flagship with adjacent battleship.
Two battleships are considered adjacent if and only if they are not in the same row and share parts of their edges. For example, if we denote the cell which is at i-th row and j-th position from the left as (i,j), then the cell (2,1) is adjacent to the cells
(1,0), (1,1), (3,1), (3,2).
Your task is to change the position of the battleships minimum times so as to reach the optimal state.
Note: All the coordinates are 0-base indexed.
Input
The first line of input contains an integer T (1 <= T <= 10), the number of test cases.
Each test case consists of 6 lines. The i-th line of each test case contains i integers, denoting the type of battleships at i-th row of battlefield, from left to right.
Output
For each test case, if you can’t reach the goal in no more than 20 moves, you must output “too difficult” in one line. Otherwise, you must output the answer in one line.
Sample Input
1
1
2 0
2 1 2
3 3 3 3
4 4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5 5
Sample Output
3
Source
2017 Multi-University Training Contest - Team 10
题意:给出一个图,问我们能否经过最多20步的转移达到
0
1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3 3
4 4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5 5
这种,但是只能拿0和他四个方向的单元换(左上,上,下,右下)
思路:直接搜索的话20步,没个10秒,完不成的,所以可以双向搜索,因为我们知道如果可以的话最终图的形态肯定是
0
1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3 3
4 4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5 5
所以我们 可以先根据结果预先倒着搜10步,并将中间的状态压缩,并记录到达中间状态的步数
然后我们在从0所在的位置正面搜索10步,如果搜到的状态与预处理的相同的话,就是一条完整的路线,在这个过程中维护最小值
中间状态压缩用字符串hash的方式,把整个中间图压缩成一个字符串然后map记录步数
ac代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
map<unsigned long long int,int>ss,ss2;
unsigned long long int h[45];
struct node
{
int x,y,step;
char temp[25];
}now,nex;
int a[8][8];
int output;
int poss[8][8];
int fx[4]={1,-1,1,-1};
int fy[4]={0,0,1,-1};
int get
4000
pos(int x,int y)
{
return poss[x][y];
}
unsigned long long int Getval(char s[])
{
int n=strlen(s);
unsigned long long int x=1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
h[i]=h[i-1]+x*(s[i]-'0');
x=x*31;
}
return h[n-1];
}
void Bfs()
{
queue<node>s;
now.x=1;
now.y=1;
now.step=0;
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
poss[i][j]=cnt;
now.temp[cnt++]=i+'0'-1;
}
}
now.temp[cnt]='\0';
s.push(now);
while(!s.empty())
{
now=s.front();s.pop();
ss[Getval(now.temp)]=now.step;
if(now.step>=10)break;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
nex=now;
nex.x+=fx[i];
nex.y+=fy[i];
nex.step++;
if(nex.x>=1&&nex.x<=6&&nex.y>=1&&nex.y<=nex.x)
{
int pos1=getpos(now.x,now.y);
int pos2=getpos(nex.x,nex.y);
swap(nex.temp[pos1],nex.temp[pos2]);
unsigned long long int nexval=Getval(nex.temp);
if(ss[nexval]==0)
{
ss[nexval]=nex.step;
s.push(nex);
}
}
}
}
}
void Bfs2()
{
ss2.clear();
queue<node>s;
output=40;
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
now.temp[cnt++]=a[i][j]+'0';
if(a[i][j]==0)
{
now.x=i;
now.y=j;
now.step=0;
}
}
}
now.temp[cnt]='\0';
s.push(now);
while(!s.empty())
{
now=s.front();s.pop();
ss2[Getval(now.temp)]=now.step;
if(now.step>=10)break;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
nex=now;
nex.x+=fx[i];
nex.y+=fy[i];
nex.step++;
if(nex.x>=1&&nex.x<=6&&nex.y>=1&&nex.y<=nex.x)
{
int pos1=getpos(now.x,now.y);
int pos2=getpos(nex.x,nex.y);
swap(nex.temp[pos1],nex.temp[pos2]);
unsigned long long int nexval=Getval(nex.temp);
if(ss2[nexval]==0)
{
ss2[nexval]=nex.step;
s.push(nex);
}
if(ss[nexval]>0)
{
output=min(output,nex.step+ss[nexval]);
}
}
}
}
if(output==40)printf("too difficult\n");
else printf("%d\n",output);
}
int main()
{
ss.clear();
Bfs();
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
int len=0;
char bb[55];
char aa[55];
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
bb[len]=i-1+'0';
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
aa[len++]=a[i][j]+'0';
}
}
bb[len]='\0';
aa[len]='\0';
if(strcmp(aa,bb)==0)
{
printf("0\n");
continue;
}
int anssss=ss[Getval(aa)];
if(anssss==0)
{
Bfs2();
}
else printf("%d\n",anssss);
}
}
相关文章推荐
- POJ 1840 双向搜索 +Hash
- 双向搜索+hash
- 162_超大背包问题 (双向搜索)
- 双向搜索法 ------推箱子算法简要分析
- 双向广度搜索
- poj 3131 双向搜索+hash判重
- POJ 3131 双向搜索 解题报告
- hdu 1151 - > 双向路径搜索解决覆盖问题
- 八数码问题——双向广度优先搜索解决
- poj 1186 方程的解数 (hash+双向dfs)
- 相似图片搜索原理一(ahash—c++实现)
- [POJ] 2785 4 Values whose Sum is 0(双向搜索)
- 折半枚举(双向搜索)
- hdu6171 Admiral 双向宽搜
- 八数码难题 双向搜索(codevs 1225)
- geohash:用字符串实现附近地点搜索
- hdu 1043(搜索 + 康拓展开hash)
- hdu 1151 - > 双向路径搜索解决覆盖问题
- 八数码问题——双向广度优先搜索解决
- POJ 3126 Prime Path(筛法,双向搜索)
