Codeforces 785D Anton and School - 2 (范德蒙恒等式+ 乘法逆元)
2017-08-25 00:44
323 查看
D. Anton and School - 2
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
As you probably know, Anton goes to school. One of the school subjects that Anton studies is Bracketology. On the Bracketology lessons students usually learn different sequences that consist of round brackets (characters "("
and ")" (without quotes)).
On the last lesson Anton learned about the regular simple bracket sequences (RSBS). A bracket sequence s of length n is
an RSBS if the following conditions are met:
It is not empty (that is n ≠ 0).
T
4000he length of the sequence is even.
First

charactes
of the sequence are equal to "(".
Last

charactes
of the sequence are equal to ")".
For example, the sequence "((()))" is an RSBS but the sequences "((())"
and "(()())" are not RSBS.
Elena Ivanovna, Anton's teacher, gave him the following task as a homework. Given a bracket sequence s. Find the number of its distinct
subsequences such that they are RSBS. Note that a subsequence of s is a string that can be obtained from s by
deleting some of its elements. Two subsequences are considered distinct if distinct sets of positions are deleted.
Because the answer can be very big and Anton's teacher doesn't like big numbers, she asks Anton to find the answer modulo 109 + 7.
Anton thought of this task for a very long time, but he still doesn't know how to solve it. Help Anton to solve this task and write a program that finds the answer for it!
Input
The only line of the input contains a string s — the bracket sequence given in Anton's homework. The string consists only of characters
"(" and ")" (without quotes). It's guaranteed that the
string is not empty and its length doesn't exceed 200 000.
Output
Output one number — the answer for the task modulo 109 + 7.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
In the first sample the following subsequences are possible:
If we delete characters at the positions 1 and 5 (numbering
starts with one), we will get the subsequence "(())".
If we delete characters at the positions 1, 2, 3 and 4,
we will get the subsequence "()".
If we delete characters at the positions 1, 2, 4 and 5,
we will get the subsequence "()".
If we delete characters at the positions 1, 2, 5 and 6,
we will get the subsequence "()".
If we delete characters at the positions 1, 3, 4 and 5,
we will get the subsequence "()".
If we delete characters at the positions 1, 3, 5 and 6,
we will get the subsequence "()".
The rest of the subsequnces are not RSBS. So we got 6 distinct subsequences that are RSBS, so the answer is 6.
题解:
遇到右括号,记录, 遇到左括号 组合计算, 应用范德蒙式化简:
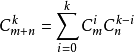
在 利用乘法逆元 计算组合数 :
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include <vector>
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define findx(x) lower_bound(b+1,b+1+bn,x)-b
#define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin)
#define FOUT freopen("output.txt","w",stdout)
#define S1(n) scanf("%d",&n)
#define S2(n,m) scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)
#define Pr(n) printf("%d\n",n)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double PI=acos(-1);
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double esp=1e-6;
const int maxn=1e6+5;
const int MOD=1e9+7;
const int mod=1e9+7;
int dir[5][2]={0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0};
ll inv[maxn*2],fac[maxn];
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){ return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
ll exgcd(ll a,ll b,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){x=1;y=0;return a;}ll ans=exgcd(b,a%b,x,y);ll temp=x;x=y;y=temp-a/b*y;return ans;}
ll lcm(ll a,ll b){ return b/gcd(a,b)*a;}
ll qpow(ll x,ll n){ll res=1;for(;n;n>>=1){if(n&1)res=(res*x)%MOD;x=(x*x)%MOD;}return res;}
void INV(){inv[1] = 1;for(int i = 2; i < maxn; i++) inv[i] = (MOD - MOD / i) * inv[MOD % i] % MOD;}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){ x=1; y=0; d=a; }else{ ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x); y-=x*(a/b);}}
void Fac(){fac[0]=1;for(int i=1;i<=maxn;i++)fac[i]=(fac[i-1]*i)%MOD;}
ll inv_exgcd(ll a,ll n){ll d,x,y;ex_gcd(a,n,d,x,y);return d==1?(x+n)%n:-1;}
ll inv1(ll b){return b==1?1:(MOD-MOD/b)*inv1(MOD%b)%MOD;}
ll inv2(ll b){return qpow(b,MOD-2);}
ll cal(ll m,ll n){if(m<n)return 0;return (fac[m]*inv[fac
]%MOD)%MOD*inv[fac[m-n]]%MOD;}
ll cals(ll m,ll n){if(m<n)return 0;return (fac[m]*inv1(fac
)%MOD)%MOD*inv1(fac[m-n])%MOD;}
char str[maxn];
int main()
{
Fac();
scanf("%s",&str);
c674
int len=strlen(str);
int le=0,ri=0;
ll ans=0;
ll res=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
if(str[i]==')')
++ri;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(str[i]=='(')
{
++le;
ans=(ans+cals(le+ri-1,le))%mod;
}
else
ri--;
}
Pr(ans);
return 0;
}
/*
((((()(()))()))))))(()(
*/
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
As you probably know, Anton goes to school. One of the school subjects that Anton studies is Bracketology. On the Bracketology lessons students usually learn different sequences that consist of round brackets (characters "("
and ")" (without quotes)).
On the last lesson Anton learned about the regular simple bracket sequences (RSBS). A bracket sequence s of length n is
an RSBS if the following conditions are met:
It is not empty (that is n ≠ 0).
T
4000he length of the sequence is even.
First

charactes
of the sequence are equal to "(".
Last

charactes
of the sequence are equal to ")".
For example, the sequence "((()))" is an RSBS but the sequences "((())"
and "(()())" are not RSBS.
Elena Ivanovna, Anton's teacher, gave him the following task as a homework. Given a bracket sequence s. Find the number of its distinct
subsequences such that they are RSBS. Note that a subsequence of s is a string that can be obtained from s by
deleting some of its elements. Two subsequences are considered distinct if distinct sets of positions are deleted.
Because the answer can be very big and Anton's teacher doesn't like big numbers, she asks Anton to find the answer modulo 109 + 7.
Anton thought of this task for a very long time, but he still doesn't know how to solve it. Help Anton to solve this task and write a program that finds the answer for it!
Input
The only line of the input contains a string s — the bracket sequence given in Anton's homework. The string consists only of characters
"(" and ")" (without quotes). It's guaranteed that the
string is not empty and its length doesn't exceed 200 000.
Output
Output one number — the answer for the task modulo 109 + 7.
Examples
input
)(()()
output
6
input
()()()
output
7
input
)))
output
0
Note
In the first sample the following subsequences are possible:
If we delete characters at the positions 1 and 5 (numbering
starts with one), we will get the subsequence "(())".
If we delete characters at the positions 1, 2, 3 and 4,
we will get the subsequence "()".
If we delete characters at the positions 1, 2, 4 and 5,
we will get the subsequence "()".
If we delete characters at the positions 1, 2, 5 and 6,
we will get the subsequence "()".
If we delete characters at the positions 1, 3, 4 and 5,
we will get the subsequence "()".
If we delete characters at the positions 1, 3, 5 and 6,
we will get the subsequence "()".
The rest of the subsequnces are not RSBS. So we got 6 distinct subsequences that are RSBS, so the answer is 6.
题解:
遇到右括号,记录, 遇到左括号 组合计算, 应用范德蒙式化简:
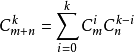
在 利用乘法逆元 计算组合数 :
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include <vector>
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define findx(x) lower_bound(b+1,b+1+bn,x)-b
#define FIN freopen("input.txt","r",stdin)
#define FOUT freopen("output.txt","w",stdout)
#define S1(n) scanf("%d",&n)
#define S2(n,m) scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)
#define Pr(n) printf("%d\n",n)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double PI=acos(-1);
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double esp=1e-6;
const int maxn=1e6+5;
const int MOD=1e9+7;
const int mod=1e9+7;
int dir[5][2]={0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0};
ll inv[maxn*2],fac[maxn];
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){ return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
ll exgcd(ll a,ll b,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){x=1;y=0;return a;}ll ans=exgcd(b,a%b,x,y);ll temp=x;x=y;y=temp-a/b*y;return ans;}
ll lcm(ll a,ll b){ return b/gcd(a,b)*a;}
ll qpow(ll x,ll n){ll res=1;for(;n;n>>=1){if(n&1)res=(res*x)%MOD;x=(x*x)%MOD;}return res;}
void INV(){inv[1] = 1;for(int i = 2; i < maxn; i++) inv[i] = (MOD - MOD / i) * inv[MOD % i] % MOD;}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){ x=1; y=0; d=a; }else{ ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x); y-=x*(a/b);}}
void Fac(){fac[0]=1;for(int i=1;i<=maxn;i++)fac[i]=(fac[i-1]*i)%MOD;}
ll inv_exgcd(ll a,ll n){ll d,x,y;ex_gcd(a,n,d,x,y);return d==1?(x+n)%n:-1;}
ll inv1(ll b){return b==1?1:(MOD-MOD/b)*inv1(MOD%b)%MOD;}
ll inv2(ll b){return qpow(b,MOD-2);}
ll cal(ll m,ll n){if(m<n)return 0;return (fac[m]*inv[fac
]%MOD)%MOD*inv[fac[m-n]]%MOD;}
ll cals(ll m,ll n){if(m<n)return 0;return (fac[m]*inv1(fac
)%MOD)%MOD*inv1(fac[m-n])%MOD;}
char str[maxn];
int main()
{
Fac();
scanf("%s",&str);
c674
int len=strlen(str);
int le=0,ri=0;
ll ans=0;
ll res=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
if(str[i]==')')
++ri;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(str[i]=='(')
{
++le;
ans=(ans+cals(le+ri-1,le))%mod;
}
else
ri--;
}
Pr(ans);
return 0;
}
/*
((((()(()))()))))))(()(
*/
相关文章推荐
- Codeforces 521C 组合数取模(乘法逆元)
- Codeforces 543D. Road Improvement (树dp + 乘法逆元)
- Codeforces 543D Road Improvement(树形DP + 乘法逆元)
- CodeForces - 937D Sleepy Game (乘法逆元)
- CodeForces-696C Please(数学题,快速幂取模,乘法逆元)
- Codeforces 711E ZS and The Birthday Paradox(乘法逆元)
- CodeForces 300C Beautiful Numbers (乘法逆元+快速幂(含乘法逆元的讲解))
- codeforces 300C 乘法逆元 (乘法逆元模为素数的模板)
- Codeforces 300C Beautiful Numbers 乘法逆元
- Codeforces 327C 乘法逆元 + 费马小定理 || 等比数列二分求和取模
- CodeForces - 617B Chocolate (规律)
- 【CodeForces】458A - Golden System(数论 & 模拟)
- Codeforces 368B Sereja and Suffixes 线段树按值建树
- Codeforces 628D Magic Numbers 【数位dp】
- Codeforces 919D - Substring 【有向图判环+DP】
- codeforces 782C Andryusha and Colored Balloons【构造】
- Codeforces_841_B Godsend(思路|简单博弈)
- CodeForces 593B Anton and Lines【数学+排序】
- CodeForces 589 I Lottery
- [Codeforces] 158C - Cd and pwd commands
