HDU2489--Minimal Ratio Tree(最小生成树)
2017-08-14 19:00
441 查看
Do more with less
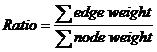
Given a complete graph of n nodes with all nodes and edges weighted, your task is to find a tree, which is a sub-graph of the original graph, with m nodes and whose ratio is the smallest among all the trees of m nodes in the graph.
All the weights of both nodes and edges (except for the ones on the diagonal of the matrix) are integers and in the range of [1, 100].
The figure below illustrates the first test case in sample input. Node 1 and Node 3 form the minimal ratio tree.
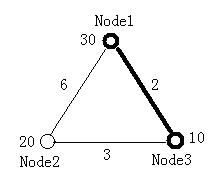
30 20 10
0 6 2
6 0 3
2 3 0
2 2
1 1
0 2
2 0
0 0
1 2
给的数据说明图中结点两两相连
所以只需要N个节点中枚举M个,求出他们的最小生成树,即可算出这M个结点最小权值
比较所以的权值即可得出最小
Description
For a tree, which nodes and edges are all weighted, the ratio of it is calculated according to the following equation.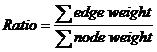
Given a complete graph of n nodes with all nodes and edges weighted, your task is to find a tree, which is a sub-graph of the original graph, with m nodes and whose ratio is the smallest among all the trees of m nodes in the graph.
Input
Input contains multiple test cases. The first line of each test case contains two integers n (2<=n<=15) and m (2<=m<=n), which stands for the number of nodes in the graph and the number of nodes in the minimal ratio tree. Two zeros end the input. The next line contains n numbers which stand for the weight of each node. The following n lines contain a diagonally symmetrical n×n connectivity matrix with each element shows the weight of the edge connecting one node with another. Of course, the diagonal will be all 0, since there is no edge connecting a node with itself.All the weights of both nodes and edges (except for the ones on the diagonal of the matrix) are integers and in the range of [1, 100].
The figure below illustrates the first test case in sample input. Node 1 and Node 3 form the minimal ratio tree.

Output
For each test case output one line contains a sequence of the m nodes which constructs the minimal ratio tree. Nodes should be arranged in ascending order. If there are several such sequences, pick the one which has the smallest node number; if there’s a tie, look at the second smallest node number, etc. Please note that the nodes are numbered from 1 .Sample Input
3 230 20 10
0 6 2
6 0 3
2 3 0
2 2
1 1
0 2
2 0
0 0
Sample Output
1 31 2
#
根据上面的公式,找M个结点连成的权值最小的树思路
要找权值最小的m个连点连成的树给的数据说明图中结点两两相连
所以只需要N个节点中枚举M个,求出他们的最小生成树,即可算出这M个结点最小权值
比较所以的权值即可得出最小
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 1 << 25;
int n, m;
int map[30][30];
int wei[30];
int v[30];
int book[30];
int res[30];
double minall = INF;
void prim()
{
int lowcost[30];
int vis[30];
int x = v[1];
int sum = 0;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
lowcost[v[i]] = map[x][v[i]];
vis[x] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
{
int minx = INF;
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j ++)
{
if(!vis[v[j]] && lowcost[v[j]] < minx)
{
x = v[j];
minx = lowcost[v[j]];
}
}
vis[x] = 1;
if(minx != INF)
sum += minx;
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j ++)
{
if(!vis[v[j]] && lowcost[v[j]] > map[x][v[j]])
lowcost[v[j]] = map[x][v[j]];
}
}
int sumn = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
sumn += wei[v[i]];
double minthis = (sum*1.0) / (sumn*1.0);
if(minthis < minall)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
res[i] = v[i];
minall = minthis;
}
}
void dfs(int x,int cnt)
{
if(x == m + 1)
{
prim();
return ;
}
for(int i = cnt;i <= n;i++)
{
if( !book[i] )
{
book[i] = 1;
v[x] = i;
dfs( x+1,i+1);
book[i] = 0;
}
}
}
int main()
{
while(cin >> n >> m && n | m)
{
minall = INF;
memset(book,0,sizeof(book));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
cin >> wei[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++)
cin >> map[i][j];
dfs(1,1);
sort(res + 1, res + m + 1);
for(int i = 1; i < m; i ++)
cout << res[i] << " ";
cout << res[m] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree【最小生成树】
- hdu 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(dfs枚举 + 最小生成树)~~~
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(最小生成树)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(dfs+最小生成树-Prim)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree (暴力枚举+最小生成树)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(图论-最小生成树)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(dfs+最小生成树)
- hdu 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree 枚举+最小生成树
- hdu-2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(DFS+最小生成树)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree (dfs+Prim最小生成树)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(dfs枚举+最小生成树)
- hdu 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree 最小生成树+枚举
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(暴力+最小生成树)(2008 Asia Regional Beijing)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree 最小生成树+DFS
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(DFS+Kruskal最小生成树)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree (DFS枚举+最小生成树Prim)
- hdu 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree 最小生成树+状态压缩
- 文章标题 HDU 2489 : Minimal Ratio Tree (最小生成树+状态压缩二进制思想)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(dfs+最小生成树-Prim)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(数据结构-最小生成树)
