数据结构与算法(二叉树)
2017-07-26 21:52
281 查看
这两天在跟着《零基础学算法》这本书学复杂数据结构,对于二叉树而言有三种历遍方式
1.前序历遍(DLR) 2.中序历遍(LDR) 3.后续历遍(LRD)
而对于三种历遍方式是基于递归的。
接下来我们观察他们是如何运作的
1.前序历遍(DLR)

我们看到对于前序历遍来说他的函数是这样的
操作流程:
1.oper(bt);
2.BinTree_DLR(bt->left,oper);
3.BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper);
而对于我们的前序历遍来说因为第一的执行的是oper这个函数也就是
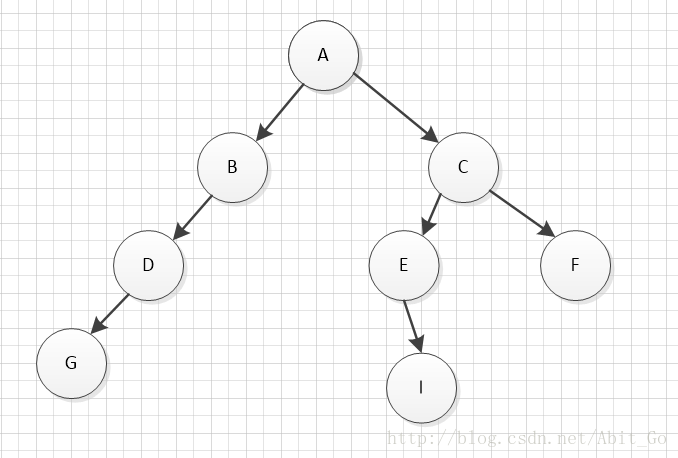
在执行完这个函数之后我们就发现函数递归到了B节点(看例1.png)再次执行oper函数再次递归,在递归到了G点时,发现bt=NULL于是我们又返回到了D这个位置的函数里面,接下来我们执行的是BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper);由此打印了H的值。
根据这个递归的思想我们可以将下列的例1.png的历遍顺序列出
A->B->D->G->H->C->E->I->F
2.中序历遍(LDR)
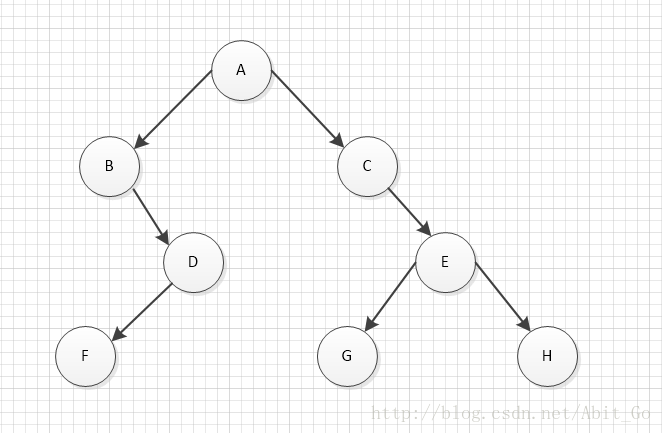
接下来我们继续中序历遍,因为中序历遍的第一个函数是递归左树,所以递归到B点,因为B点无左树我们只能执行oper来答应B数据。
B点因为执行完oper函数执行BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper);
所以我们执行到了D点,到了D点之后我们发现再一次执行了一次BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper); 到达了F点由此我们推理
中序历遍的顺序为:B->F->D->A->C->G->E->H
3.后续历遍(LRD)
我们继续沿用上面的树图,因为我们看到后续历遍的前两个函数都是递归,第三个才是oper函数,所以我们可以直接从A递归到D,F,再次之间没有经历过一次oper函数继而oper(F->D->B),因为到达A点的函数中我们看到继续递归下去,所以这个二叉树的历遍顺序为:F->D->B->G->H->E->C->A
在此我们总结经验
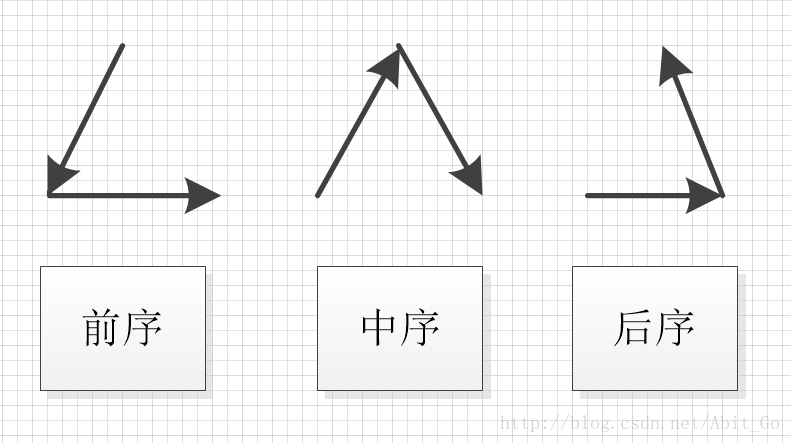
在根节点开始画图形(描绘三点),在三个点中如果有子树就顺着子树继续画图,遇到空缺的执行下一个描绘点直到历遍整个树。
以下是完整的二叉简易操作
以上是3-2链式.c的头文件
这里我们一定要注意,文件是.c文件,如果是.cpp则会报错
1.前序历遍(DLR) 2.中序历遍(LDR) 3.后续历遍(LRD)
而对于三种历遍方式是基于递归的。
接下来我们观察他们是如何运作的
1.前序历遍(DLR)

我们看到对于前序历遍来说他的函数是这样的
void BinTree_DLR(ChainBinTree *bt,void (*oper)(ChainBinTree *p))
{
if(bt)
{
oper(bt);//处理节点的数据
BinTree_DLR(bt->left,oper);
BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper);
}
return;
}操作流程:
1.oper(bt);
2.BinTree_DLR(bt->left,oper);
3.BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper);
而对于我们的前序历遍来说因为第一的执行的是oper这个函数也就是
void oper(ChainBinTree *p)
{
printf("%c",p->data);
return;
}在执行完这个函数之后我们就发现函数递归到了B节点(看例1.png)再次执行oper函数再次递归,在递归到了G点时,发现bt=NULL于是我们又返回到了D这个位置的函数里面,接下来我们执行的是BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper);由此打印了H的值。
根据这个递归的思想我们可以将下列的例1.png的历遍顺序列出
A->B->D->G->H->C->E->I->F

2.中序历遍(LDR)
void BinTree_LDR(ChainBinTree *bt,void (*oper)(ChainBinTree *p))
{
if(bt)
{
BinTree_DLR(bt->left,oper);
oper(bt);//处理节点的数据
BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper);
}
return;
}接下来我们继续中序历遍,因为中序历遍的第一个函数是递归左树,所以递归到B点,因为B点无左树我们只能执行oper来答应B数据。
B点因为执行完oper函数执行BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper);
所以我们执行到了D点,到了D点之后我们发现再一次执行了一次BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper); 到达了F点由此我们推理
中序历遍的顺序为:B->F->D->A->C->G->E->H

3.后续历遍(LRD)
void BinTree_LRD(ChainBinTree *bt,void (*oper)(ChainBinTree *p))
{
if(bt)
{
BinTree_DLR(bt->left,oper);
BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper);
oper(bt);//处理节点的数据
}
return;
}我们继续沿用上面的树图,因为我们看到后续历遍的前两个函数都是递归,第三个才是oper函数,所以我们可以直接从A递归到D,F,再次之间没有经历过一次oper函数继而oper(F->D->B),因为到达A点的函数中我们看到继续递归下去,所以这个二叉树的历遍顺序为:F->D->B->G->H->E->C->A
在此我们总结经验

在根节点开始画图形(描绘三点),在三个点中如果有子树就顺着子树继续画图,遇到空缺的执行下一个描绘点直到历遍整个树。
以下是完整的二叉简易操作
/*
Name: 二叉树的基本操作
Copyright:
Author: abit
Date: 26/07/17 20:50
Description:
*/
//file_name:3-2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define max 50
typedef char DATA;
typedef struct ChainTree
{
DATA data;
struct ChainTree *left;
struct ChainTree *right;
}ChainBinTree;
ChainBinTree *BinTreeInit(ChainBinTree *node)
{
if(node!=NULL)//若node不为空,则返回该节点指针的值作为二叉树的根节点
return node;
else
return NULL;
}
int BinTreeAddNode(ChainBinTree *bt,ChainBinTree *node,int n)//bt父节点,node子节点,1->左子树,2->右子树
{
if(bt==NULL)
{
printf("父节点不在,请先设置父节点\n");
return 0;
}
switch(n)
{
case 1:
if(bt->left)
{
printf("左子树节点不为空\n");
return 0;
}else
bt->left=node;
break;
case 2:
if(bt->left)
{
printf("右子树节点不为空\n");
return 0;
}else
bt->right=node;
break;
default:
printf("参数错误\n");
break;
}
return 1;
}
ChainBinTree *BinTreeLeft(ChainBinTree *bt)
{
if(bt)
return bt->left;
else
return NULL;
}
ChainBinTree *BinTreeRight(ChainBinTree *bt)
{
if(bt)
return bt->right;
else
return NULL;
}
int BinTreeIsEmpty(ChainBinTree *bt)
{
if(bt)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
int BinTreeDepth(ChainBinTree *bt)
{
int dep1,dep2;
if(bt==NULL)
return 0;
else
{
dep1=BinTreeDepth(bt->left);//左子树
dep2=BinTreeDepth(bt->right);//右子树
if(dep1>dep2)
return dep1+1;
else
return dep2+1;
}
}
ChainBinTree *BinTreeFind(ChainBinTree *bt,DATA data)
{
ChainBinTree *p;
if(bt==NULL)
return NULL;
else{
if(bt->data==data)
return bt;
else{
if(p=BinTreeFind(bt->left,data))
return p;
else if(p=BinTreeFind(bt->right,data))
return p;
else
return NULL;
}
}
}
void BinTreeClear(ChainBinTree *bt)
{
if(bt)
{
BinTreeClear(bt->left);//清空左子树
BinTreeClear(bt->right);//清空右子树
free(bt);//防止还有子树
bt=NULL;
}
return;
}
void BinTree_DLR(ChainBinTree *bt,void (*oper)(ChainBinTree *p)) { if(bt) { oper(bt);//处理节点的数据 BinTree_DLR(bt->left,oper); BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper); } return; }
void BinTree_LDR(ChainBinTree *bt,void (*oper)(ChainBinTree *p)) { if(bt) { BinTree_DLR(bt->left,oper); oper(bt);//处理节点的数据 BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper); } return; }
void BinTree_LRD(ChainBinTree *bt,void (*oper)(ChainBinTree *p)) { if(bt) { BinTree_DLR(bt->left,oper); BinTree_DLR(bt->right,oper); oper(bt);//处理节点的数据 } return; }
void BinTree_Level(ChainBinTree *bt,void (*oper)(ChainBinTree *p))
{
ChainBinTree *p;
ChainBinTree *q[max];
int head=0;
int tail=0;
if(bt)
{
tail=(tail+1)%max;
q[tail]=bt;
}
while(head!=tail)
{
head=(head+1)%max;
p=q[head];
oper(p);
if(p->left!=NULL)
{
tail=(tail+1)%max;
q[tail]=p->left;
}
if(p->right!=NULL)
{
tail=(tail+1)%max;
q[tail]=p->right;
}
}
return;
}
以上是3-2链式.c的头文件
这里我们一定要注意,文件是.c文件,如果是.cpp则会报错
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include "3-2.c"
void oper(ChainBinTree *p) { printf("%c",p->data); return; }
ChainBinTree *InitRoot()
{
ChainBinTree *node;
if(node=(ChainBinTree *)malloc(sizeof(ChainBinTree)))
{
printf("\n输入根节点数据:");
scanf("%s",&node->data);
node->left=NULL;
node->right=NULL;
return node;
}
return NULL;
}
void AddNode(ChainBinTree *bt)
{
ChainBinTree *node,*parent;
DATA data;
char select;
if(node=(ChainBinTree *)malloc(sizeof(ChainBinTree)))
{
printf("\n输入二叉书节点数据:");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%s",&node->data);
node->left=NULL;
node->right=NULL;
printf("输入父节点的数据:");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%s",&data);
parent=BinTreeFind(bt,data);
if(!parent)
{
printf("未找到父节点\n");
free(node);
return;
}
printf("1.添加到左子树\n2.添加到右子树\n");
do{
select=getch();
select-='0';
if(select==1 || select==2)
BinTreeAddNode(parent,node,select);
}while(select!=1 && select !=2);
}
return ;
}
int main(void)
{
ChainBinTree *root=NULL;
char select;
void (*oper1)();
oper1=oper;
do{
printf("\n1.设置二叉根元素 2.添加二叉树节点\n");
printf("3.先序历遍 4.中序历遍\n");
printf("5.后序历遍 6.按层历遍\n");
printf("7.二叉树深度 0.退出\n");
select=getch();
switch(select)
{
case '1':
root=InitRoot();
break;
case '2':
AddNode(root);
break;
case '3':
printf("\n先序历遍的结果:");
BinTree_DLR(root,oper1);
printf("\n");
break;
case '4':
printf("\n中序历遍的结果:");
BinTree_LDR(root,oper1);
printf("\n");
break;
case '5':
printf("\n后序历遍的结果:");
BinTree_LRD(root,oper1);
printf("\n");
break;
case '6':
printf("\n按层历遍的结果:");
BinTree_Level(root,oper1);
printf("\n");
break;
case '7':
printf("\n二叉树的深度为:%d\n",BinTreeDepth(root));
break;
case '0':
break;
}
}while(select!='0');
BinTreeClear(root);
root=NULL;
getch();
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 数据结构与算法-第12章二叉树和其他树-001遍历
- [数据结构与算法]二叉树与二叉树遍历
- 数据结构与算法Java版——二叉树及其遍历
- 数据结构与算法-二叉树
- 数据结构与算法简记:非递归遍历二叉树
- 数据结构与算法(C#)--树和二叉树
- 数据结构与算法-第12章二叉树和其他树-002克隆二叉树
- 数据结构与算法—论证任意二叉树度数为2的节点的个数等于叶节点个数减1
- 研磨数据结构与算法-13删除二叉树节点
- 数据结构与算法 -- 二叉树 ADT
- 数据结构与算法(二):二叉树前序,中序,后序遍历详解
- java数据结构与算法-二叉树
- 数据结构与算法--二叉树
- 数据结构与算法-第12章二叉树和其他树-003求二叉树的高度
- 5. C#数据结构与算法 -- 非线性结构(树,二叉树,二叉查找树)
- Java数据结构与算法---二叉树
- 数据结构与算法简记:通过前序中序或中序后序构建二叉树
- 数据结构与算法(C#实现)---二叉树
- 我的软考之路(四)——数据结构与算法(2)之树与二叉树
- 数据结构与算法之树&二叉树的定义
