数据结构:点对之间最短距离--Floyd算法
2017-07-15 15:01
579 查看
Floyd算法
两点之间有边相连,weight(Vi,Vj)即是最小的。
通过另一点:中介点,两点相连,使weight(Vi,Vv)+weight(Vv,Vj)最小。
Min_Distance(Vi,Vj)=min{weight(Vi,Vj),weight(Vi,Vv)+weight(Vv,Vj)}。正是基于这种背后的逻辑,再加上动态规划的思想,构成了Floyd算法。故当Vv取完所有顶点后,Distance(Vi,Vj)即可达到最小。Floyd算法的起点就是图的邻接矩阵。
题外话:代码本身不重要,算法思想才是精髓。思想极难得到,而有了思想,稍加经验即可写出代码。向思想的开创者致敬!
思想很难,代码却比较简单,直接上代码
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
#define MAXWEIGHT 100
#undef INFINITY
#define INFINITY 1000
class Graph
{
private:
//顶点数
int numV;
//边数
int numE;
//邻接矩阵
int **matrix;
public:
Graph(int numV);
//建图
void createGraph(int numE);
//析构方法
~Graph();
//Floyd算法
void Floyd();
//打印邻接矩阵
void printAdjacentMatrix();
//检查输入
bool check(int, int, int);
};
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
//构造函数,指定顶点数目
Graph::Graph(int numV)
{
//对输入的顶点数进行检测
while (numV <= 0)
{
cout << "顶点数有误!重新输入 ";
cin >> numV;
}
this->numV = numV;
//构建邻接矩阵,并初始化
matrix = new int*[numV];
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
matrix[i] = new int[numV];
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
{
if (i == j)
matrix[i][i] = 0;
else
matrix[i][j] = INFINITY;
}
}
void Graph::createGraph(int numE)
{
/*
对输入的边数做检测
一个numV个顶点的有向图,最多有numV*(numV - 1)条边
*/
while (numE < 0 || numE > numV*(numV - 1))
{
cout << "边数有问题!重新输入 ";
cin >> numE;
}
this->numE = numE;
int tail, head, weight, i;
i = 0;
cout << "输入每条边的起点(弧尾)、终点(弧头)和权值" << endl;
while (i < numE)
{
cin >> tail >> head >> weight;
while (!check(tail, head, weight))
{
cout << "输入的边不正确!请重新输入 " << endl;
cin >> tail >> head >> weight;
}
matrix[tail][head] = weight;
i++;
}
}
Graph::~Graph()
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
delete[] matrix[i];
delete[]matrix;
}
/*
弗洛伊德算法
求各顶点对之间的最短距离
及其路径
*/
void Graph::Floyd()
{
//为了不修改邻接矩阵,多用一个二维数组
int **Distance = new int*[numV];
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
Distance[i] = new int[numV];
//初始化
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
Distance[i][j] = matrix[i][j];
//prev数组
int **prev = new int*[numV];
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
prev[i] = new int[numV];
//初始化prev
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
{
if (matrix[i][j] == INFINITY)
prev[i][j] = -1;
else
prev[i][j] = i;
}
int d, v;
for (v = 0; v < numV; v++)
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
{
d = Distance[i][v] + Distance[v][j];
if (d < Distance[i][j])
{
Distance[i][j] = d;
prev[i][j] = v;
}
}
//打印Distance和prev数组
cout << "Distance..." << endl;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
cout << setw(3) << Distance[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl <<
ce9f
; "prev..." << endl;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
cout << setw(3) << prev[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
//打印顶点对最短路径
stack<int> s;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
{
if (Distance[i][j] == 0);
else if (Distance[i][j] == INFINITY)
cout << "顶点 " << i << " 到顶点 " << j << " 无路径!" << endl;
else
{
s.push(j);
v = j;
do{
v = prev[i][v];
s.push(v);
} while (v != i);
//打印路径
cout << "顶点 " << i << " 到顶点 " << j << " 的最短路径长度是 "
<< Distance[i][j] << " ,其路径序列是...";
while (!s.empty())
{
cout << setw(3) << s.top();
s.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
//释放空间
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
delete[] Distance[i];
delete[] prev[i];
}
delete[]Distance;
delete[]prev;
}
//打印邻接矩阵
void Graph::printAdjacentMatrix()
{
int i, j;
cout.setf(ios::left);
cout << setw(7) << " ";
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
cout << setw(7) << i;
cout << endl;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
cout << setw(7) << i;
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
cout << setw(7) << matrix[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
}
bool Graph::check(int tail, int head, int weight)
{
if (tail < 0 || tail >= numV || head < 0 || head >= numV
|| weight <= 0 || weight >= MAXWEIGHT)
return false;
return true;
}
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
int main()
{
cout << "******Floyd***by David***" << endl;
int numV, numE;
cout << "建图..." << endl;
cout << "输入顶点数 ";
cin >> numV;
Graph graph(numV);
cout << "输入边数 ";
cin >> numE;
graph.createGraph(numE);
cout << endl << "Floyd..." << endl;
graph.Floyd();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
完整代码下载:Floyd算法
转载请注明出处,本文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/zhangxiangdavaid/article/details/38366923
若有所帮助,顶一个哦!
专栏目录:
数据结构与算法目录
c指针
Floyd算法
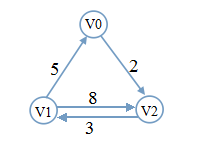
Dijkstra算法是用于解决单源最短路径问题的,Floyd算法则是解决点对之间最短路径问题的。Floyd算法的设计策略是动态规划,而Dijkstra采取的是贪心策略。当然,贪心算法就是动态规划的特例。算法思想
点对之间的最短路径只会有两种情况:两点之间有边相连,weight(Vi,Vj)即是最小的。
通过另一点:中介点,两点相连,使weight(Vi,Vv)+weight(Vv,Vj)最小。
Min_Distance(Vi,Vj)=min{weight(Vi,Vj),weight(Vi,Vv)+weight(Vv,Vj)}。正是基于这种背后的逻辑,再加上动态规划的思想,构成了Floyd算法。故当Vv取完所有顶点后,Distance(Vi,Vj)即可达到最小。Floyd算法的起点就是图的邻接矩阵。
题外话:代码本身不重要,算法思想才是精髓。思想极难得到,而有了思想,稍加经验即可写出代码。向思想的开创者致敬!
思想很难,代码却比较简单,直接上代码
代码
类定义[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
#define MAXWEIGHT 100
#undef INFINITY
#define INFINITY 1000
class Graph
{
private:
//顶点数
int numV;
//边数
int numE;
//邻接矩阵
int **matrix;
public:
Graph(int numV);
//建图
void createGraph(int numE);
//析构方法
~Graph();
//Floyd算法
void Floyd();
//打印邻接矩阵
void printAdjacentMatrix();
//检查输入
bool check(int, int, int);
};
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
#define MAXWEIGHT 100
#undef INFINITY
#define INFINITY 1000
class Graph
{
private:
//顶点数
int numV;
//边数
int numE;
//邻接矩阵
int **matrix;
public:
Graph(int numV);
//建图
void createGraph(int numE);
//析构方法
~Graph();
//Floyd算法
void Floyd();
//打印邻接矩阵
void printAdjacentMatrix();
//检查输入
bool check(int, int, int);
};类实现[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
//构造函数,指定顶点数目
Graph::Graph(int numV)
{
//对输入的顶点数进行检测
while (numV <= 0)
{
cout << "顶点数有误!重新输入 ";
cin >> numV;
}
this->numV = numV;
//构建邻接矩阵,并初始化
matrix = new int*[numV];
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
matrix[i] = new int[numV];
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
{
if (i == j)
matrix[i][i] = 0;
else
matrix[i][j] = INFINITY;
}
}
void Graph::createGraph(int numE)
{
/*
对输入的边数做检测
一个numV个顶点的有向图,最多有numV*(numV - 1)条边
*/
while (numE < 0 || numE > numV*(numV - 1))
{
cout << "边数有问题!重新输入 ";
cin >> numE;
}
this->numE = numE;
int tail, head, weight, i;
i = 0;
cout << "输入每条边的起点(弧尾)、终点(弧头)和权值" << endl;
while (i < numE)
{
cin >> tail >> head >> weight;
while (!check(tail, head, weight))
{
cout << "输入的边不正确!请重新输入 " << endl;
cin >> tail >> head >> weight;
}
matrix[tail][head] = weight;
i++;
}
}
Graph::~Graph()
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
delete[] matrix[i];
delete[]matrix;
}
/*
弗洛伊德算法
求各顶点对之间的最短距离
及其路径
*/
void Graph::Floyd()
{
//为了不修改邻接矩阵,多用一个二维数组
int **Distance = new int*[numV];
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
Distance[i] = new int[numV];
//初始化
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
Distance[i][j] = matrix[i][j];
//prev数组
int **prev = new int*[numV];
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
prev[i] = new int[numV];
//初始化prev
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
{
if (matrix[i][j] == INFINITY)
prev[i][j] = -1;
else
prev[i][j] = i;
}
int d, v;
for (v = 0; v < numV; v++)
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
{
d = Distance[i][v] + Distance[v][j];
if (d < Distance[i][j])
{
Distance[i][j] = d;
prev[i][j] = v;
}
}
//打印Distance和prev数组
cout << "Distance..." << endl;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
cout << setw(3) << Distance[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl <<
ce9f
; "prev..." << endl;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
cout << setw(3) << prev[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
//打印顶点对最短路径
stack<int> s;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
{
if (Distance[i][j] == 0);
else if (Distance[i][j] == INFINITY)
cout << "顶点 " << i << " 到顶点 " << j << " 无路径!" << endl;
else
{
s.push(j);
v = j;
do{
v = prev[i][v];
s.push(v);
} while (v != i);
//打印路径
cout << "顶点 " << i << " 到顶点 " << j << " 的最短路径长度是 "
<< Distance[i][j] << " ,其路径序列是...";
while (!s.empty())
{
cout << setw(3) << s.top();
s.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
//释放空间
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
delete[] Distance[i];
delete[] prev[i];
}
delete[]Distance;
delete[]prev;
}
//打印邻接矩阵
void Graph::printAdjacentMatrix()
{
int i, j;
cout.setf(ios::left);
cout << setw(7) << " ";
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
cout << setw(7) << i;
cout << endl;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
cout << setw(7) << i;
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
cout << setw(7) << matrix[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
}
bool Graph::check(int tail, int head, int weight)
{
if (tail < 0 || tail >= numV || head < 0 || head >= numV
|| weight <= 0 || weight >= MAXWEIGHT)
return false;
return true;
}
//构造函数,指定顶点数目
Graph::Graph(int numV)
{
//对输入的顶点数进行检测
while (numV <= 0)
{
cout << "顶点数有误!重新输入 ";
cin >> numV;
}
this->numV = numV;
//构建邻接矩阵,并初始化
matrix = new int*[numV];
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
matrix[i] = new int[numV];
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
{
if (i == j)
matrix[i][i] = 0;
else
matrix[i][j] = INFINITY;
}
}
void Graph::createGraph(int numE)
{
/*
对输入的边数做检测
一个numV个顶点的有向图,最多有numV*(numV - 1)条边
*/
while (numE < 0 || numE > numV*(numV - 1))
{
cout << "边数有问题!重新输入 ";
cin >> numE;
}
this->numE = numE;
int tail, head, weight, i;
i = 0;
cout << "输入每条边的起点(弧尾)、终点(弧头)和权值" << endl;
while (i < numE)
{
cin >> tail >> head >> weight;
while (!check(tail, head, weight))
{
cout << "输入的边不正确!请重新输入 " << endl;
cin >> tail >> head >> weight;
}
matrix[tail][head] = weight;
i++;
}
}
Graph::~Graph()
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
delete[] matrix[i];
delete[]matrix;
}
/*
弗洛伊德算法
求各顶点对之间的最短距离
及其路径
*/
void Graph::Floyd()
{
//为了不修改邻接矩阵,多用一个二维数组
int **Distance = new int*[numV];
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
Distance[i] = new int[numV];
//初始化
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
Distance[i][j] = matrix[i][j];
//prev数组
int **prev = new int*[numV];
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
prev[i] = new int[numV];
//初始化prev
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
{
if (matrix[i][j] == INFINITY)
prev[i][j] = -1;
else
prev[i][j] = i;
}
int d, v;
for (v = 0; v < numV; v++)
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
{
d = Distance[i][v] + Distance[v][j];
if (d < Distance[i][j])
{
Distance[i][j] = d;
prev[i][j] = v;
}
}
//打印Distance和prev数组
cout << "Distance..." << endl;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
cout << setw(3) << Distance[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl << "prev..." << endl;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
cout << setw(3) << prev[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
//打印顶点对最短路径
stack<int> s;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
{
if (Distance[i][j] == 0);
else if (Distance[i][j] == INFINITY)
cout << "顶点 " << i << " 到顶点 " << j << " 无路径!" << endl;
else
{
s.push(j);
v = j;
do{
v = prev[i][v];
s.push(v);
} while (v != i);
//打印路径
cout << "顶点 " << i << " 到顶点 " << j << " 的最短路径长度是 "
<< Distance[i][j] << " ,其路径序列是...";
while (!s.empty())
{
cout << setw(3) << s.top();
s.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
//释放空间
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
delete[] Distance[i];
delete[] prev[i];
}
delete[]Distance;
delete[]prev;
}
//打印邻接矩阵
void Graph::printAdjacentMatrix()
{
int i, j;
cout.setf(ios::left);
cout << setw(7) << " ";
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
cout << setw(7) << i;
cout << endl;
for (i = 0; i < numV; i++)
{
cout << setw(7) << i;
for (j = 0; j < numV; j++)
cout << setw(7) << matrix[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
}
bool Graph::check(int tail, int head, int weight)
{
if (tail < 0 || tail >= numV || head < 0 || head >= numV
|| weight <= 0 || weight >= MAXWEIGHT)
return false;
return true;
}主函数[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
int main()
{
cout << "******Floyd***by David***" << endl;
int numV, numE;
cout << "建图..." << endl;
cout << "输入顶点数 ";
cin >> numV;
Graph graph(numV);
cout << "输入边数 ";
cin >> numE;
graph.createGraph(numE);
cout << endl << "Floyd..." << endl;
graph.Floyd();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int main()
{
cout << "******Floyd***by David***" << endl;
int numV, numE;
cout << "建图..." << endl;
cout << "输入顶点数 ";
cin >> numV;
Graph graph(numV);
cout << "输入边数 ";
cin >> numE;
graph.createGraph(numE);
cout << endl << "Floyd..." << endl;
graph.Floyd();
system("pause");
return 0;
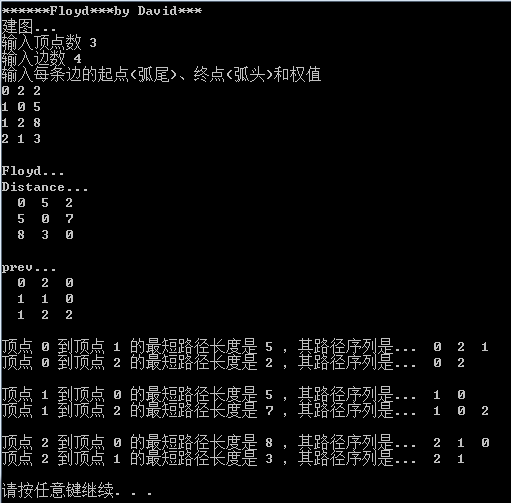
}运行

小结
Floyd算法代码看似很长,其实并不难。代码中很多都是用于准备工作和输出,关键代码就是三层for循环。完整代码下载:Floyd算法
转载请注明出处,本文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/zhangxiangdavaid/article/details/38366923
若有所帮助,顶一个哦!
专栏目录:
数据结构与算法目录
c指针
相关文章推荐
- 数据结构:点对之间最短距离--Floyd算法
- (1.2.6.7)点对之间最短距离--Floyd算法
- Floyd算法(求每一对顶点之间的最短距离)
- UVa:567 Risk (Floyd算法求所有顶点之间的最短距离模版题)
- Floyd算法,求图中两个点之间的最短距离
- 数据结构:点之间的最短距离--Floyd算法
- Floyd算法(各对顶点之间的最短距离)
- 每对顶点间的最短距离——floyd算法
- poj 3608(旋转卡壳求解两凸包之间的最短距离)
- 菜鸟上路 杭电OJ 1007 求平面上两点之间最短距离--分而治之以及关键点的考虑
- 城市之间的最短总距离(最小生成树算法)
- 坐标象限法判断矩形之间最短的距离
- 任意两节点之间最短距离
- uva 11280 求2点之间最短距离(图中不超过k个节点)
- 计算两个坐标点之间走最短距离有多少种走法
- 给出每个站点之间的最短距离,求出最短路径,用unordered_map来实现,让你实现find_cheapest_transform函数
- hdu 2544 最短路 图论-求两点之间的最短距离 Dijkstra
- Java数据结构----图--最短路径解法Dijkstra算法和Floyd算法
- 用FLOYD算法求特殊图的任意两点之间的距离
- 所有顶点之间的最短路径算法:Floyd算法。
