集体智慧编程第十一章---用java编写(小部分)
2017-06-26 14:37
369 查看
<<集体智慧编程>>的第十一章是有关遗传编程的话题,书中提到本章将考查一种截然不同的问题解决方法。与先前遇到一个问题就选择一种算法的思路不同,我们将编写一个程序,尝试自动构造出解决某一问题的最佳程序。因而从本质上,我们将要构造的是一个能够构造算法的算法。
本章最后实现了一个能人机对战的AI,虽然比较粗糙,但还是觉得挺有趣,于是想自己实现一次里面的代码。书中代码是用python编写的,但是想试下用不同的语言实现同一个机器学习算法,举一反三,之前接触的机器学习算法都是用python,没试过java,于是打算用java编写一次。
此算法需要先构造一棵程序解析树。
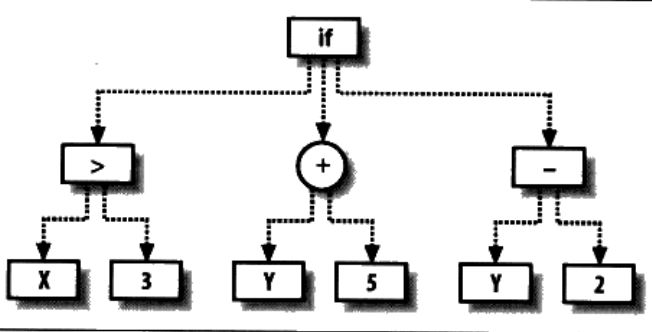
相当于
def func(x,y)
if x > 3:
return y + 5
else:
return y - 2
书中的Python2代码:
个别类的说明
fwrapper
一个封装类,对应于“函数型”节点上的函数。其成员变量包括了函数名称、函数本身,以及该函数接受的参数个数
node
对应于函数型节点(即带子节点的节点)。我们以一个fwrapper类对其进行初始化。当evaluate被调用时,我们会对各个子节点进行求值运算,然后再将函数本身应用于求得的结果
paramnode
这个类对应的节点只返回传递给程序的某个参数。其evaluate方法返回的是由idx指定的函数
constnode
返回常量值的节点。其evaluate方法返回该类初始化时所传入的值
程序运行代码结果:
>>>import gp
>>>exampletree = gp.exampletree()
>&g
9c12
t;>exampletree.evaluate([2,3])
1
>>>exampletree.evaluate([5,3])
8
>>>exampletree.display()
if
isgreater
p0
3
add
p1
5
subtract
p1
2
java代码:
java代码里的class和方法基本和python里的class和函数对应,这样写其实意义不大...代码比较烂,但是也从中学到一点java反射的知识,尤其是Method类的invoke。
运行结果也一样
请输入参数X,Y :
5
3
exampletree.evaluate([5,3])
8
exampletree.display()
if
isgreater
p0
3
add
p1
5
subtract
p1
2
这次没有完整实现整章的算法,但以上的内容是本章后面的算法的基础。
本章最后实现了一个能人机对战的AI,虽然比较粗糙,但还是觉得挺有趣,于是想自己实现一次里面的代码。书中代码是用python编写的,但是想试下用不同的语言实现同一个机器学习算法,举一反三,之前接触的机器学习算法都是用python,没试过java,于是打算用java编写一次。
此算法需要先构造一棵程序解析树。

相当于
def func(x,y)
if x > 3:
return y + 5
else:
return y - 2
书中的Python2代码:
from random import random,randint,choice
from copy import deepcopy
from math import log
class fwrapper:
def __init__(self,function,childcount,name):
self.function=function
self.childcount=childcount
self.name=name
class node:
def __init__(self,fw,children):
self.function=fw.function
self.name=fw.name
self.children=children
def evaluate(self,inp):
results=[n.evaluate(inp) for n in self.children]
return self.function(results)
def display(self,indent=0):
print ((' '*indent)+self.name)
for c in self.children:
c.display(indent+1)
class paramnode:
def __init__(self,idx):
self.idx=idx
def evaluate(self,inp):
return inp[self.idx]
def display(self,indent=0):
print ('%sp%d' % (' '*indent,self.idx))
class constnode:
def __init__(self,v):
self.v=v
def evaluate(self,inp):
return self.v
def display(self,indent=0):
print ('%s%d' % (' '*indent,self.v))
addw=fwrapper(lambda l:l[0]+l[1],2,'add')
subw=fwrapper(lambda l:l[0]-l[1],2,'subtract')
mulw=fwrapper(lambda l:l[0]*l[1],2,'multiply')
def iffunc(l):
if l[0]>0: return l[1]
else: return l[2]
ifw=fwrapper(iffunc,3,'if')
def isgreater(l):
if l[0]>l[1]: return 1
else: return 0
gtw=fwrapper(isgreater,2,'isgreater')
flist=[addw,mulw,ifw,gtw,subw]
def exampletree():
return node(ifw,[
node(gtw,[paramnode(0),constnode(3)]),
node(addw,[paramnode(1),constnode(5)]),
node(subw,[paramnode(1),constnode(2)]),
]
)个别类的说明
fwrapper
一个封装类,对应于“函数型”节点上的函数。其成员变量包括了函数名称、函数本身,以及该函数接受的参数个数
node
对应于函数型节点(即带子节点的节点)。我们以一个fwrapper类对其进行初始化。当evaluate被调用时,我们会对各个子节点进行求值运算,然后再将函数本身应用于求得的结果
paramnode
这个类对应的节点只返回传递给程序的某个参数。其evaluate方法返回的是由idx指定的函数
constnode
返回常量值的节点。其evaluate方法返回该类初始化时所传入的值
程序运行代码结果:
>>>import gp
>>>exampletree = gp.exampletree()
>&g
9c12
t;>exampletree.evaluate([2,3])
1
>>>exampletree.evaluate([5,3])
8
>>>exampletree.display()
if
isgreater
p0
3
add
p1
5
subtract
p1
2
java代码:
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Chapter11Test {
private FWrapper addw ,subw ,mulw ,ifw , gtw ;
private List<FWrapper> flist ;
private static Chapter11Test obj = new Chapter11Test();
int addfunc(List<Integer> l){
return l.get(0)+l.get(1);
}
int subfunc(List<Integer> l){
return l.get(0)-l.get(1);
}
int mulfunc(List<Integer> l){
return l.get(0)*l.get(1);
}
int iffunc(List<Integer> l){
if(l.get(0) > 0) return l.get(1);
else return l.get(2);
}
int isgreater(List<Integer> l){
if(l.get(0) > l.get(1)) return 1;
else return 0;
}
private Node exampletree(){
return new Node(ifw,new Object[]{
new Node(gtw,new Object[]{new ParamNode(0),new ConstNode(3)}),
new Node(addw,new Object[]{new ParamNode(1),new ConstNode(5)}),
new Node(subw,new Object[]{new ParamNode(1),new ConstNode(2)})
});
}
private void beginTest() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
addw = new FWrapper(obj.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("addfunc",List.class), 2 ,"add");
subw = new FWrapper(obj.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("subfunc",List.class), 2 ,"subtract");
mulw = new FWrapper(obj.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("mulfunc",List.class), 2 ,"multiply");
ifw = new FWrapper(obj.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("iffunc",List.class), 3 ,"if");
gtw = new FWrapper(obj.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("isgreater",List.class), 2 ,"isgreater");
flist = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(addw,subw,mulw,ifw,gtw));
Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入参数X,Y :");
int X = reader.nextInt();
int Y = reader.nextInt();
System.out.println("exampletree.evaluate(["+X+","+Y+"])");
System.out.println(exampletree().evaluate(new int[]{X,Y}));
System.out.println("exampletree.display()");
exampletree().display(0);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
obj.beginTest();
}
class FWrapper{
Method function;
int childcount;
String name;
FWrapper(Method function,int childcount,String name){
this.function = function;
this.childcount = childcount;
this.name = name;
}
}
class Node{
//private Method function;
private FWrapper fw;
private Object[] children;
private String name;
Node(FWrapper fw,Object[] children){
this.fw = fw;
this.name = fw.name;
this.children = children;
}
public int evaluate(int[] inp) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException {
List<Integer> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
int result = (Integer)children[i].getClass().getDeclaredMethod("evaluate",Class.forName("[I")).invoke(children[i],inp);
results.add(result);
}
return (Integer)fw.function.invoke(obj,results);
}
public void display(int indent) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
String indents="";
for (int i = 0; i < indent; i++)
indents+=" ";
System.out.println(indents + name);
for(Object c: children)
c.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("display",int.class).invoke(c,indent+1);
}
}
class ParamNode{
private int idx;
ParamNode(int idx){
this.idx = idx;
}
public int evaluate(int[] inp){
return inp[idx];
}
public void display(int indent){
String indents="";
for (int i = 0; i < indent; i++)
indents+=" ";
System.out.println(indents+"p"+idx);
}
}
class ConstNode{
private int v ;
ConstNode(int v){
this.v = v;
}
public int evaluate(int[] inp){
return v;
}
public void display(int indent){
String indents="";
for (int i = 0; i < indent; i++)
indents+=" ";
System.out.println(indents+v);
}
}
}java代码里的class和方法基本和python里的class和函数对应,这样写其实意义不大...代码比较烂,但是也从中学到一点java反射的知识,尤其是Method类的invoke。
运行结果也一样
请输入参数X,Y :
5
3
exampletree.evaluate([5,3])
8
exampletree.display()
if
isgreater
p0
3
add
p1
5
subtract
p1
2
这次没有完整实现整章的算法,但以上的内容是本章后面的算法的基础。
相关文章推荐
- 编写多线程的 Java 应用程序 如何避免当前编程中最常见的问题
- 3D编程指南第一部分:快速进入移动JAVA 3D编程世界
- 如何使用Java编写多线程程序-Java基础-Java-编程开发
- Java 编程的动态性,第 1 部分: 类和类装入
- 编写高性能 Java 数据访问应用程序之 2 :内联方法编程风格简介
- Java编程 的动态性,第 2部分: 引入反射
- 疯狂JAVA讲义---第十一章(中):AWT编程-常用组件和事件处理
- 编写一个JAVA的队列类-Java基础-Java-编程开发
- 编写跨平台Java程序注意事项-Java基础-Java-编程开发
- 利用Java技术进行XML编程,第2部分(续)
- 3D编程指南第一部分:快速进入移动JAVA 3D编程世界
- Java动画编程基础第四部分
- 什么是 Enterprise JavaBeans 组件?第二部分:EJB 编程模型
- Java咖啡馆(6)——编写猜数字游戏-Java基础-Java-编程开发
- Java动画编程基础第三部分
- 程序安装,升级及卸载核心部分(java编写)
- Java网络编程---I/O部分学习笔记整理
- 编写高效的JAVA程序-编程规范 (基本篇 )
- 如何轻松编写一个强大的字符串分解器-Java基础-Java-编程开发
- 疯狂JAVA讲义---第十一章(上):AWT编程-布局管理器
