[Codeforces 817E] Choosing The Commander Trie树
2017-06-18 23:24
513 查看
E. Choosing The Commander
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
As you might remember from the previous round, Vova is currently playing a strategic game known as Rage of Empires.
Vova managed to build a large army, but forgot about the main person in the army - the commander. So he tries to hire a commander, and he wants to choose the person who will be respected by warriors.
Each warrior is represented by his personality — an integer number pi.
Each commander has two characteristics — his personality pjand
leadership lj (both
are integer numbers). Warrior i respects commander j only
if
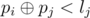
(
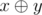
is
the bitwise excluding OR ofx and y).
Initially Vova's army is empty. There are three different types of events that can happen with the army:
1 pi —
one warrior with personality pi joins
Vova's army;
2 pi —
one warrior with personality pi leaves
Vova's army;
3 pi li —
Vova tries to hire a commander with personality pi and
leadership li.
For each event of the third type Vova wants to know how many warriors (counting only those who joined the army and haven't left yet)respect the commander he tries to hire.
Input
The first line contains one integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 100000)
— the number of events.
Then q lines follow. Each line describes the event:
1 pi (1 ≤ pi ≤ 108)
— one warrior with personality pi joins
Vova's army;
2 pi (1 ≤ pi ≤ 108)
— one warrior with personality pi leaves
Vova's army (it is guaranteed that there is at least one such warrior in Vova's army by this moment);
3 pi li (1 ≤ pi, li ≤ 108)
— Vova tries to hire a commander with personality pi and
leadership li.
There is at least one event of this type.
Output
For each event of the third type print one integer — the number of warriors who respect the commander Vova tries to hire in the event.
Example
input
output
Note
In the example the army consists of two warriors with personalities 3 and 4 after
first two events. Then Vova tries to hire a commander with personality 6 and leadership 3,
and only one warrior respects him (
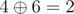
,
and 2 < 3, but
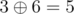
,
and 5 ≥ 3). Then warrior with personality 4 leaves,
and when Vova tries to hire that commander again, there are no warriors who respect him.
题解:
博主很菜啊,并没有什么码力,只能写写小水题辣!
xor相关,没有什么别的好的性质,于是考虑xor的原始定义-------->按位异或----------->于是可以想到01Trie树.
建立出01Trie树后,可以对于每个节点记录这个以这个节点为根的子树上的士兵总数,
从而可以O(logp)进行添加,删除和询问操作 (话说trie树把递归变成循环能快不少呢)
时间复杂度:O(qlogp).
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{int x=0;
char c=getchar();
while (c<'0'||c>'9') {c=getchar();}
while (c>='0'&&c<='9') {x=x*10+c-'0';c=getchar();}
return x;
}
struct trie
{int s,ch[2];
}t[3000005];
int cnt=1,rt=1;
inline void add(int x)
{int pos=1,i,tg;
t[pos].s++;
for (i=26;i>=0;i--)
{if (x&(1<<i)) {tg=1;}
else {tg=0;}
if (!t[pos].ch[tg])
{t[pos].ch[tg]=++cnt;}
pos=t[pos].ch[tg];
t[pos].s++;
}
return;
}
inline void del(int x)
{int pos=1,i,tg;
t[pos].s--;
for (i=26;i>=0;i--)
{if (x&(1<<i)) {tg=1;}
else {tg=0;}
pos=t[pos].ch[tg];
t[pos].s--;
}
return;
}
inline void ask(int x,int tar)
{int ans=0,pos=1,i,nt=0,ok;
for (i=26;i>=0;i--)
{if (nt+(1<<i)-1<tar)
{ok=1;nt=(nt+(1<<i));}
else
{ok=0;}
int p=x&(1<<i),tag;
if (p>0) {tag=0;}
else {tag=1;}
if (!ok) {tag^=1;}
else {ans+=t[t[pos].ch[tag^1]].s;}
pos=t[pos].ch[tag];
}
printf ("%d\n",ans);
return;
}
int main (){
int p,q,l,opt;
q=read();
while (q--)
{opt=read();
if (opt==1) {p=read();add(p);}
if (opt==2) {p=read();del(p);}
if (opt==3) {p=read();l=read();ask(p,l);}
}
return 0;
}
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
As you might remember from the previous round, Vova is currently playing a strategic game known as Rage of Empires.
Vova managed to build a large army, but forgot about the main person in the army - the commander. So he tries to hire a commander, and he wants to choose the person who will be respected by warriors.
Each warrior is represented by his personality — an integer number pi.
Each commander has two characteristics — his personality pjand
leadership lj (both
are integer numbers). Warrior i respects commander j only
if
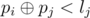
(
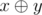
is
the bitwise excluding OR ofx and y).
Initially Vova's army is empty. There are three different types of events that can happen with the army:
1 pi —
one warrior with personality pi joins
Vova's army;
2 pi —
one warrior with personality pi leaves
Vova's army;
3 pi li —
Vova tries to hire a commander with personality pi and
leadership li.
For each event of the third type Vova wants to know how many warriors (counting only those who joined the army and haven't left yet)respect the commander he tries to hire.
Input
The first line contains one integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 100000)
— the number of events.
Then q lines follow. Each line describes the event:
1 pi (1 ≤ pi ≤ 108)
— one warrior with personality pi joins
Vova's army;
2 pi (1 ≤ pi ≤ 108)
— one warrior with personality pi leaves
Vova's army (it is guaranteed that there is at least one such warrior in Vova's army by this moment);
3 pi li (1 ≤ pi, li ≤ 108)
— Vova tries to hire a commander with personality pi and
leadership li.
There is at least one event of this type.
Output
For each event of the third type print one integer — the number of warriors who respect the commander Vova tries to hire in the event.
Example
input
5 1 3 1 4 3 6 3 2 4 3 6 3
output
1 0
Note
In the example the army consists of two warriors with personalities 3 and 4 after
first two events. Then Vova tries to hire a commander with personality 6 and leadership 3,
and only one warrior respects him (
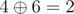
,
and 2 < 3, but
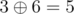
,
and 5 ≥ 3). Then warrior with personality 4 leaves,
and when Vova tries to hire that commander again, there are no warriors who respect him.
题解:
博主很菜啊,并没有什么码力,只能写写小水题辣!
xor相关,没有什么别的好的性质,于是考虑xor的原始定义-------->按位异或----------->于是可以想到01Trie树.
建立出01Trie树后,可以对于每个节点记录这个以这个节点为根的子树上的士兵总数,
从而可以O(logp)进行添加,删除和询问操作 (话说trie树把递归变成循环能快不少呢)
时间复杂度:O(qlogp).
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{int x=0;
char c=getchar();
while (c<'0'||c>'9') {c=getchar();}
while (c>='0'&&c<='9') {x=x*10+c-'0';c=getchar();}
return x;
}
struct trie
{int s,ch[2];
}t[3000005];
int cnt=1,rt=1;
inline void add(int x)
{int pos=1,i,tg;
t[pos].s++;
for (i=26;i>=0;i--)
{if (x&(1<<i)) {tg=1;}
else {tg=0;}
if (!t[pos].ch[tg])
{t[pos].ch[tg]=++cnt;}
pos=t[pos].ch[tg];
t[pos].s++;
}
return;
}
inline void del(int x)
{int pos=1,i,tg;
t[pos].s--;
for (i=26;i>=0;i--)
{if (x&(1<<i)) {tg=1;}
else {tg=0;}
pos=t[pos].ch[tg];
t[pos].s--;
}
return;
}
inline void ask(int x,int tar)
{int ans=0,pos=1,i,nt=0,ok;
for (i=26;i>=0;i--)
{if (nt+(1<<i)-1<tar)
{ok=1;nt=(nt+(1<<i));}
else
{ok=0;}
int p=x&(1<<i),tag;
if (p>0) {tag=0;}
else {tag=1;}
if (!ok) {tag^=1;}
else {ans+=t[t[pos].ch[tag^1]].s;}
pos=t[pos].ch[tag];
}
printf ("%d\n",ans);
return;
}
int main (){
int p,q,l,opt;
q=read();
while (q--)
{opt=read();
if (opt==1) {p=read();add(p);}
if (opt==2) {p=read();del(p);}
if (opt==3) {p=read();l=read();ask(p,l);}
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- codeforces 817E 字典树计数
- Codeforces 4C Registration System map的应用
- Codeforces 501D Misha and Permutations Summation (康托展开+平衡树优化)
- 【CodeForces】[1A]Theatre Square
- Codeforces 716C[数论][构造]
- CodeForces - 792C Divide by Three(思路)(分类讨论)
- Codeforces 794F - Leha and security system [线段树-区间更新]【数据结构】
- codeforces 251A Points on Line 二分 or 单调队列
- CodeForces 546A Soldier and Bananas
- Codeforces 660C Hard Process【二分 Or 尺取】
- [codeforces] 2B - The least round way
- Codeforces 796D Police Stations 构造+BFS
- CodeForces - 859E Desk Disorder 思维 + 并查集判环
- Codeforces 341
- CodeForces 554B(扫房间)
- Codeforces 630Q Pyramids
- Codeforces 719B B. Anatoly and Cockroaches
- Codeforces 740D Alyona and a tree 二分+树上差分
- Codeforces 863D 模拟
- codeforces 191 E (树状数组+二分)
