OPENGL—编码裁剪(Cohen-Sutherland)法裁剪图
2017-06-01 18:36
666 查看
//编码裁剪(Cohen-Sutherland)法裁剪图
#include"stdafx.h"
#include<Gl/glut.h>
#include <process.h>
class wcPt2D {
public:
float x, y;
};
const int winLeftBitCode = 0x1;
const int winRightBitCode = 0x2;
const int winBottomBitCode = 0x4;
const int winTopBitCode = 0x8;
GLubyte encode(wcPt2D pt, wcPt2D winMin, wcPt2D winMax) { //进行编码
GLubyte code = 0x00;
if (pt.x < winMin.x) //D0=1,否则为0
code = code | winLeftBitCode;
if (pt.x > winMax.x) //D1=1,否则为0
code = code | winRightBitCode;
if (pt.y < winMin.y) //D2=1,否则为0
code = code | winBottomBitCode;
if (pt.y > winMax.y) //D3=1,否则为0
code = code | winTopBitCode;
return (code);
}
inline int inside(int code) { //在内部,inside=1
return int(!code);
}
inline int reject(int code1, int code2) { //code1&code2不等于0,“简弃”,reject=true
return int(code1 & code2);
}
inline int accept(int code1, int code2) { //code1|code2等于0,“简取”,accept=true
return int(!(code1 | code2));
}
void swapPts(wcPt2D *p1, wcPt2D *p2) { //交换坐标值
wcPt2D tmp;
tmp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = tmp;
}
void swapCodes(GLubyte *c1, GLubyte *c2) { //交换编码
GLubyte tmp;
tmp = *c1;
*c1 = *c2;
*c2 = tmp;
}
void lineClip(wcPt2D winMin, wcPt2D winMax, wcPt2D p1, wcPt2D p2) //裁剪
{
GLubyte code1, code2;
int done = false, plotLine = false;
float m;
while (!done) //保证用新的P1P2重新进行计算
{
code1 = encode(p1, winMin, winMax); //对p1、p2进行编码,分别为code1、code2
code2 = encode(p2, winMin, winMax);
if (accept(code1, code2)) //对直线P1P2“简取”之
{
done = true;
plotLine = true;
}
else if (reject(code1, code2)) //对直线P1P2“简弃”之
{
done = true;
}
else //否则
{
if (inside(code1)) //若P1在窗口内,则交换P1和P2的坐标值和编码
{
swapPts(&p1, &p2);
swapCodes(&code1, &code2);
}
//判断P1在窗口外哪一侧,然后求出两者的交点,并用交点的值替代P1的坐标值,以达到去掉P1S线段的目的
if (p2.x != p1.x)
m = (p2.y - p1.y) / (p2.x - p1.x);
if (code1 & winLeftBitCode)
{
p1.y += (winMin.x - p1.x) * m;
p1.x = winMin.x;
}
else if (code1 & winRightBitCode)
{
p1.y += (winMax.x - p1.x) * m;
p1.x = winMax.x;
}
else if (code1 & winBottomBitCode)
{
if (p2.x != p1.x)
p1.x += (winMin.y - p1.y) / m;
p1.y = winMin.y;
}
else if (code1 & winTopBitCode)
{
if (p2.x != p1.x)
p1.x = (winMax.y - p1.y) / m;
p1.y = winMax.y;
}
}
}
//重新绘制当前的直线段P1P2
if (plotLine)
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glColor3f(1, 0, 0);
glVertex2f(p1.x, p1.y);
glVertex2f(p2.x, p2.y);
glEnd();
}
void drawpolygon(double cd[])
{
glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); //绘制直线
glLineWidth(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i = i + 2) {
glVertex2f(cd[i], cd[i + 1]);
}
glEnd();
}
void drawline(double cd[])
{
glBegin(GL_LINES); //绘制点
glLineWidth(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i = i + 2) {
glVertex2f(cd[i], cd[i + 1]);
}
glEnd();
}
void myKeyBoard(unsigned char key, int x, int y) //处理按键信息
{
wcPt2D winMin = {200, 200};
wcPt2D winMax = {400, 400};
wcPt2D p1 = {100, 0};
wcPt2D p2 = {500, 500};
if (key == 13) //按下Enter键
lineClip(winMin, winMax, p1, p2);
glFlush();
if (key == 27) //按下ESC键
exit(0);
}
void display(void)
{
double re[8] = {200, 200, 400, 200, 400, 400, 200, 400}; //按照比例输出
double line[4] = {100,0 , 500, 500};
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
glViewport(0, 0, 600, 600);
glColor3f(0, 0, 0);
//绘制
drawpolygon(re);
drawline(line);
glFlush();
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//初始化
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RED);
glutInitWindowSize(600, 600);
glutInitWindowPosition(100, 100);
glutCreateWindow("Cohen-Sutherland算法");
glClearColor(1, 1, 1, 0.0);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
gluOrtho2D(0.0, 600.0, 0.0, 600.0);
glutKeyboardFunc(myKeyBoard); //键盘输入控制
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
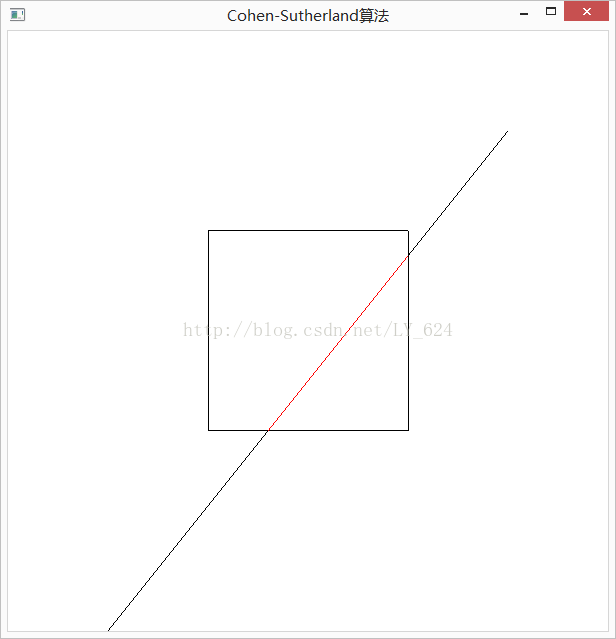
}运行结果:
相关文章推荐
- openGL-基于编码的剪裁算法Cohen-Sutherland
- [OpenGL]计算机图形学:直线裁剪算法中Cohen-Sutherland算法和Liang-Barsky算法
- Cohen-SutherLand算法(编码算法)
- Cohen-Sutherland算法裁剪线段
- Cohen-SutherLand算法(编码算法)
- Cohen-Sutherland线段裁剪算法
- 【裁剪】线段的裁剪——Cohen-Sutherland算法及代码实现
- Cohen-Sutherland线段裁剪算法
- Cohen-Sutherland裁剪算核心代码
- Cohen-SutherLand 裁剪算法 (vc++)
- Cohen Sutherland线段裁剪算法(C#实现)
- 计算机图形学 - 线段裁剪 - Cohen Sutherland算法
- Cohen-Sutherland线段裁剪算法
- OpenGL-2D(Cohen-Sutherland 裁线算法)
- opengl 直线裁剪Cohen-Sutherland算法
- 线段裁剪一:Cohen-Sutherland算法
- Cohen-Sutherland 窗口裁剪线段算法
- Cohen-Sutherland裁剪算法
- Cohen-Sutherland线段裁剪算法
- 计算机图形学Cohen_Sutherland算法裁剪线段
