Webrtc delay-base-bwe代码分析(4): OveruseDetector模块
2017-05-22 19:35
1316 查看
@(webrtc)[webrtc, congestion control]
阈值自适应原因如下:
个人理解:
- 防止某些网络状态比较极端,使链路评估总是处于比较极端的情况。
- 由于基于RTT算法的公平性问题,在对抗基于丢包的拥塞控制算法衰减快,容易造成自身饿死,例如除了GCC外还有一条TCP流。

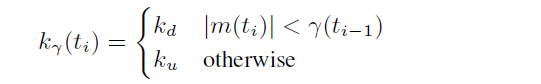
公式如上,delta_T为到达时间差,k为增益系数,m(ti)为ti时刻的延迟。
增益系数是自适应的,当本次延迟值在上一轮迭代的阈值范围内时,增益系数k会进行衰减,其他时候增益系数k将会增加。
参数选择是一个可以调优的过程,这里暂不讨论,webrtc中也开辟了对应的实验性接口可供配置。
Webrtc delay-base-bwe代码分析(4): OveruseDetector模块
0. 简介
这个模块主要是根据OveruseEstimator模块校正后的到达时间差来对链路使用状态进行评估,为有限自动状态机提供状态转换的条件,同时本模块还有GCC文档中提到的自适应阈值计算。阈值自适应原因如下:
个人理解:
- 防止某些网络状态比较极端,使链路评估总是处于比较极端的情况。
- 由于基于RTT算法的公平性问题,在对抗基于丢包的拥塞控制算法衰减快,容易造成自身饿死,例如除了GCC外还有一条TCP流。
We show that the threshold (ti), used by the over-use detector, must be made adaptive otherwise two issues can occur: 1) the delay-based control action may have no effect when the size of the bottleneck queue along the path is not sufficiently large and 2) the GCC flow may be starved by a concurrent loss-based TCP flow.
1. 原理

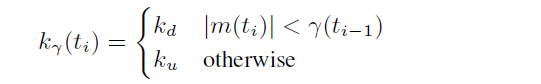
公式如上,delta_T为到达时间差,k为增益系数,m(ti)为ti时刻的延迟。
增益系数是自适应的,当本次延迟值在上一轮迭代的阈值范围内时,增益系数k会进行衰减,其他时候增益系数k将会增加。
参数选择是一个可以调优的过程,这里暂不讨论,webrtc中也开辟了对应的实验性接口可供配置。
2. 代码
代码实现比较简单明了,基本就是按照上述公式进行实现:BandwidthUsage OveruseDetector::Detect(double offset,
double ts_delta,
int num_of_deltas,
int64_t now_ms) {
if (num_of_deltas < 2) {
return kBwNormal;
}
const double prev_offset = prev_offset_;
prev_offset_ = offset;
// 更新delta T.
const double T = std::min(num_of_deltas, 60) * offset;
BWE_TEST_LOGGING_PLOT(1, "offset", now_ms, T);
BWE_TEST_LOGGING_PLOT(1, "threshold", now_ms, threshold_);
if (T > threshold_) {
// 过载,更新对应的过载时间,过载次数统计。
if (time_over_using_ == -1) {
// Initialize the timer. Assume that we've been
// over-using half of the time since the previous
// sample.
time_over_using_ = ts_delta / 2;
} else {
// Increment timer
time_over_using_ += ts_delta;
}
overuse_counter_++;
// 当且仅当总过载时间超过过载时间阈值,且其曲线仍成上升趋势(offset >= prev_offset),
// 进入过载状态
// 其他场景维持原状态。
// 判断具有一定容忍,防止因某些爆发式场景导致异常的过载判断影响网络吞吐量。
// 过载状态解除只有T降低至阈值之下。
if (time_over_using_ > overusing_time_threshold_ && overuse_counter_ > 1) {
if (offset >= prev_offset) {
time_over_using_ = 0;
overuse_counter_ = 0;
hypothesis_ = kBwOverusing;
}
}
}
// 清除过载相关参数
else if (T < -threshold_) {
// 低负载
time_over_using_ = -1;
overuse_counter_ = 0;
hypothesis_ = kBwUnderusing;
} else {
// 正常状态
time_over_using_ = -1;
overuse_counter_ = 0;
hypothesis_ = kBwNormal;
}
// 当过载发生时,T总是大于阈值,因此此时阈值增大。
// 当未发生过载时,T总是小于阈值,此时阈值缩小。
UpdateThreshold(T, now_ms);
return hypothesis_;
}
void OveruseDetector::UpdateThreshold(double modified_offset, int64_t now_ms) {
// 实验性质
if (!in_experiment_)
return;
// 初始化
if (last_update_ms_ == -1)
last_update_ms_ = now_ms;
// 修正值超过阈值可控制的最大范围,这里啥都不做,防止阈值过大。
if (fabs(modified_offset) > threshold_ + kMaxAdaptOffsetMs) {
// Avoid adapting the threshold to big latency spikes, caused e.g.,
// by a sudden capacity drop.
last_update_ms_ = now_ms;
return;
}
// 第二个公式,根据修正值的绝对值和当前阈值(即i - 1时刻)比较,计算增益系数
// 默认k_down_ = 0.00006, k_up_ = 0.004。
// 这里两个值虽然都是正的,
// 但是增长和减小的符号在第一个式子中的fabs(modified_offset) - threshold_
const double k = fabs(modified_offset) < threshold_ ? k_down_ : k_up_;
const int64_t kMaxTimeDeltaMs = 100;
int64_t time_delta_ms = std::min(now_ms - last_update_ms_, kMaxTimeDeltaMs);
// 公式一,阈值自适应,根据新的增益系数对阈值进行修正。
threshold_ +=
k * (fabs(modified_offset) - threshold_) * time_delta_ms;
// 阈值上下限内修正。
const double kMinThreshold = 6;
const double kMaxThreshold = 600;
threshold_ = std::min(std::max(threshold_, kMinThreshold), kMaxThreshold);
last_update_ms_ = now_ms;
}参考资料:
1 google congestion control相关文章推荐
- Webrtc delay-base-bwe代码分析(3): OveruseEstimator模块
- Webrtc delay-base-bwe代码分析(2): InterArrival模块
- Webrtc delay-base-bwe代码分析(5): AimdRateControl模块
- Webrtc delay-base-bwe代码分析(6): 整体分析
- Webrtc delay-base-bwe代码分析(1): RateStatistics模块
- 0.driverbase-自旋锁(SpinLock)wrk代码分析
- cocos2d-x 3.0 示例代码分析3:BaseTest
- wojilu系统的ORM代码解析-[源代码结构分析,ObjectBase基类分析]
- chrome代码中base::JSONReader类的阅读分析(一)
- C++卷积神经网络实例:tiny_cnn代码详解(10)——layer_base和layer类结构分析
- 结合代码分析--BaseServlet存在的意义(刚接触servlet的必看)
- python中BaseHTTPServer.py代码阅读分析
- 《linux 内核完全剖析》 由逻辑地址转换成线性地址代码分析 get_base get_limit 代码分析笔记
- OSChina App代码分析之BaseApplication
- osworkflow的config代码分析
- ORACLE常见错误代码的分析与解决(三)
- NT,2000,XP 的 CDROM 引导扇区代码分析
- XY52代码整理和分析
- 一个方向控制射击小游戏的代码分析!(AS1.0)
- little c原代码分析[一]
