HDU1401 - Solitaire - 双向bfs+哈希状态压缩
2017-05-20 10:29
393 查看
1.题目描述:
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 4560 Accepted Submission(s): 1380
Problem Description
Solitaire is a game played on a chessboard 8x8. The rows and columns of the chessboard are numbered from 1 to 8, from the top to the bottom and from left to right respectively.
There are four identical pieces on the board. In one move it is allowed to:
> move a piece to an empty neighboring field (up, down, left or right),
> jump over one neighboring piece to an empty field (up, down, left or right).
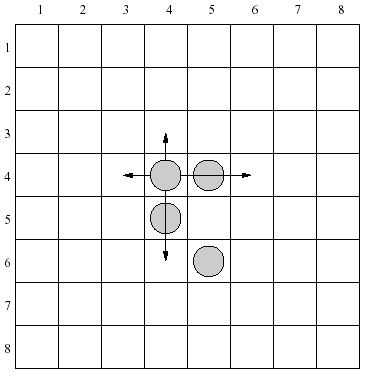
There are 4 moves allowed for each piece in the configuration shown above. As an example let's consider a piece placed in the row 4, column 4. It can be moved one row up, two rows down, one column left or two columns right.
Write a program that:
> reads two chessboard configurations from the standard input,
> verifies whether the second one is reachable from the first one in at most 8 moves,
> writes the result to the standard output.
Input
Each of two input lines contains 8 integers a1, a2, ..., a8 separated by single spaces and describes one configuration of pieces on the chessboard. Integers a2j-1 and a2j (1 <= j <= 4) describe the position of one piece - the row number and the column number
respectively. Process to the end of file.
Output
The output should contain one word for each test case - YES if a configuration described in the second input line is reachable from the configuration described in the first input line in at most 8 moves, or one word NO otherwise.
Sample Input
4 4 4 5 5 4 6 5
2 4 3 3 3 6 4 6
Sample Output
YES
Source
Southwestern Europe 2002
Recommend
Ignatius.L | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you: 1072 1372 1043 1044 1515
2.题意概述:
在8 * 8 的跳棋棋盘上,给你两个状态,每个状态4个点,判断一个状态8步内能否到达另一个状态。
3.解题思路:
给定了始末状态,很典型的双向广搜。从始末两个方向进行广度搜索,理想情况下可以减少二分之一的搜索量,从而提高搜索速度。问题的关键在于状态的保存,因为四个棋子是一样的,棋盘的0大小只有8*8,所以先按坐标排序之后,设定八个位置(四个坐标)的哈希,每次枚举当前的4个点和四个方向去判断,判断函数考虑用递归思路去判断那种有一个重棋子子的现象。而且限制条件为8步数,那么每次双向限制就是4步数。还有很多细节化的东西详见代码。
4.AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define maxn 100100
#define lson root << 1
#define rson root << 1 | 1
#define lent (t[root].r - t[root].l + 1)
#define lenl (t[lson].r - t[lson].l + 1)
#define lenr (t[rson].r - t[rson].l + 1)
#define N 1111
#define eps 1e-6
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define e exp(1.0)
using namespace std;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
char hs[8][8][8][8][8][8][8][8];
int dir[4][2] = { {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1} };
struct point
{
int x, y;
friend bool operator< (point a, point b)
{
if (a.x == b.x)
return a.y < b.y;
return a.x < b.x;
}
};
struct node
{
point p[4];
int step;
};
void sethash(node a, char k)
{
hs[a.p[0].x][a.p[0].y][a.p[1].x][a.p[1].y][a.p[2].x][a.p[2].y][a.p[3].x][a.p[3].y] = k;
}
char gethash(node a)
{
return hs[a.p[0].x][a.p[0].y][a.p[1].x][a.p[1].y][a.p[2].x][a.p[2].y][a.p[3].x][a.p[3].y];
}
bool judge(node &state, int i, int j, int m)
{
if (m == 1)
{
if (state.step >= 4)
return 0;
state.step++;
}
state.p[i].x += dir[j][0];
state.p[i].y += dir[j][1];
if (state.p[i].x >= 0 && state.p[i].x < 8 && state.p[i].y >= 0 && state.p[i].y < 8)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
if (i != k)
{
if (state.p[i].x == state.p[k].x && state.p[i].y == state.p[k].y)
{
if (m == 1)
return judge(state, i, j, 2);
return 0;
}
}
sort(state.p, state.p +
4000
4);
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
bool bfs2(node a, node b)
{
queue<node> q1, q2;
q1.push(a);
q2.push(b);
node pre;
while (!q1.empty() || !q2.empty())
{
if (!q1.empty())
{
pre = q1.front();
q1.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
node cur = pre;
if (judge(cur, i, j, 1))
{
char k = gethash(cur);
if (k == 2)
return 1;
if (k == 0)
{
sort(cur.p, cur.p + 4);
sethash(cur, 1);
q1.push(cur);
}
}
}
}
if (!q2.empty())
{
pre = q2.front();
q2.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
node cur = pre;
if (judge(cur, i, j, 1))
{
char k = gethash(cur);
if (k == 1)
return 1;
if (k == 0)
{
sort(cur.p, cur.p + 4);
sethash(cur, 2);
q2.push(cur);
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
long _begin_time = clock();
#endif
int x, y;
while (~scanf("%d%d", &x, &y))
{
memset(hs, 0, sizeof(hs));
node a, b;
a.p[0].x = --x;
a.p[0].y = --y;
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &a.p[i].x, &a.p[i].y);
a.p[i].x--;
a.p[i].y--;
}
sort(a.p, a.p + 4);
sethash(a, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &b.p[i].x, &b.p[i].y);
b.p[i].x--;
b.p[i].y--;
}
sort(b.p, b.p + 4);
sethash(b, 2);
a.step = b.step = 0;
if (bfs2(a, b))
puts("YES");
else
puts("NO");
}
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
long _end_time = clock();
printf("time = %ld ms.", _end_time - _begin_time);
#endif
return 0;
}
Solitaire
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 4560 Accepted Submission(s): 1380
Problem Description
Solitaire is a game played on a chessboard 8x8. The rows and columns of the chessboard are numbered from 1 to 8, from the top to the bottom and from left to right respectively.
There are four identical pieces on the board. In one move it is allowed to:
> move a piece to an empty neighboring field (up, down, left or right),
> jump over one neighboring piece to an empty field (up, down, left or right).

There are 4 moves allowed for each piece in the configuration shown above. As an example let's consider a piece placed in the row 4, column 4. It can be moved one row up, two rows down, one column left or two columns right.
Write a program that:
> reads two chessboard configurations from the standard input,
> verifies whether the second one is reachable from the first one in at most 8 moves,
> writes the result to the standard output.
Input
Each of two input lines contains 8 integers a1, a2, ..., a8 separated by single spaces and describes one configuration of pieces on the chessboard. Integers a2j-1 and a2j (1 <= j <= 4) describe the position of one piece - the row number and the column number
respectively. Process to the end of file.
Output
The output should contain one word for each test case - YES if a configuration described in the second input line is reachable from the configuration described in the first input line in at most 8 moves, or one word NO otherwise.
Sample Input
4 4 4 5 5 4 6 5
2 4 3 3 3 6 4 6
Sample Output
YES
Source
Southwestern Europe 2002
Recommend
Ignatius.L | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you: 1072 1372 1043 1044 1515
2.题意概述:
在8 * 8 的跳棋棋盘上,给你两个状态,每个状态4个点,判断一个状态8步内能否到达另一个状态。
3.解题思路:
给定了始末状态,很典型的双向广搜。从始末两个方向进行广度搜索,理想情况下可以减少二分之一的搜索量,从而提高搜索速度。问题的关键在于状态的保存,因为四个棋子是一样的,棋盘的0大小只有8*8,所以先按坐标排序之后,设定八个位置(四个坐标)的哈希,每次枚举当前的4个点和四个方向去判断,判断函数考虑用递归思路去判断那种有一个重棋子子的现象。而且限制条件为8步数,那么每次双向限制就是4步数。还有很多细节化的东西详见代码。
4.AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define maxn 100100
#define lson root << 1
#define rson root << 1 | 1
#define lent (t[root].r - t[root].l + 1)
#define lenl (t[lson].r - t[lson].l + 1)
#define lenr (t[rson].r - t[rson].l + 1)
#define N 1111
#define eps 1e-6
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define e exp(1.0)
using namespace std;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
char hs[8][8][8][8][8][8][8][8];
int dir[4][2] = { {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1} };
struct point
{
int x, y;
friend bool operator< (point a, point b)
{
if (a.x == b.x)
return a.y < b.y;
return a.x < b.x;
}
};
struct node
{
point p[4];
int step;
};
void sethash(node a, char k)
{
hs[a.p[0].x][a.p[0].y][a.p[1].x][a.p[1].y][a.p[2].x][a.p[2].y][a.p[3].x][a.p[3].y] = k;
}
char gethash(node a)
{
return hs[a.p[0].x][a.p[0].y][a.p[1].x][a.p[1].y][a.p[2].x][a.p[2].y][a.p[3].x][a.p[3].y];
}
bool judge(node &state, int i, int j, int m)
{
if (m == 1)
{
if (state.step >= 4)
return 0;
state.step++;
}
state.p[i].x += dir[j][0];
state.p[i].y += dir[j][1];
if (state.p[i].x >= 0 && state.p[i].x < 8 && state.p[i].y >= 0 && state.p[i].y < 8)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
if (i != k)
{
if (state.p[i].x == state.p[k].x && state.p[i].y == state.p[k].y)
{
if (m == 1)
return judge(state, i, j, 2);
return 0;
}
}
sort(state.p, state.p +
4000
4);
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
bool bfs2(node a, node b)
{
queue<node> q1, q2;
q1.push(a);
q2.push(b);
node pre;
while (!q1.empty() || !q2.empty())
{
if (!q1.empty())
{
pre = q1.front();
q1.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
node cur = pre;
if (judge(cur, i, j, 1))
{
char k = gethash(cur);
if (k == 2)
return 1;
if (k == 0)
{
sort(cur.p, cur.p + 4);
sethash(cur, 1);
q1.push(cur);
}
}
}
}
if (!q2.empty())
{
pre = q2.front();
q2.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
node cur = pre;
if (judge(cur, i, j, 1))
{
char k = gethash(cur);
if (k == 1)
return 1;
if (k == 0)
{
sort(cur.p, cur.p + 4);
sethash(cur, 2);
q2.push(cur);
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
long _begin_time = clock();
#endif
int x, y;
while (~scanf("%d%d", &x, &y))
{
memset(hs, 0, sizeof(hs));
node a, b;
a.p[0].x = --x;
a.p[0].y = --y;
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &a.p[i].x, &a.p[i].y);
a.p[i].x--;
a.p[i].y--;
}
sort(a.p, a.p + 4);
sethash(a, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &b.p[i].x, &b.p[i].y);
b.p[i].x--;
b.p[i].y--;
}
sort(b.p, b.p + 4);
sethash(b, 2);
a.step = b.step = 0;
if (bfs2(a, b))
puts("YES");
else
puts("NO");
}
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
long _end_time = clock();
printf("time = %ld ms.", _end_time - _begin_time);
#endif
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- hdu1401 Solitaire (双向bfs)
- HDU1401-Solitaire
- HDU1401:Solitaire(BFS)
- hdu1401 Solitaire ----双向BFS
- Hdu1401-Solitaire(双向bfs)
- hdu1401 Solitaire【双广】
- Hdu1401 Solitaire
- HDU1401 Solitaire 双向搜索
- 【POJ1198 Solitaire 】 思路+解题报告+测试数据生成器
- UVa 10651 - Pebble Solitaire 状态压缩 dp
- HDOJ 1401 Solitaire
- uva10651 - Pebble Solitaire(记忆化搜索)
- HDU 1401 Solitaire
- HDU 1401 Solitaire 双向BFS
- UVa 10651 - Pebble Solitaire 状态压缩 dp
- uva10651 - Pebble Solitaire(dp)
- uva 10651 - Pebble Solitaire
- UVA 10651 Pebble Solitaire(bfs+hash)
- UVa 10651 Pebble Solitaire(状压DP)
- HDU - 1401 Solitaire
