codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
2017-04-26 13:00
543 查看
题目传送门
D. Mike and distribution
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Mike has always been thinking about the harshness of social inequality. He's so obsessed with it that sometimes it even affects him while solving problems. At the moment, Mike has two sequences of positive integers A = [a1, a2, ..., an] and B = [b1, b2, ..., bn] of
length neach which he uses to ask people some quite peculiar questions.
To test you on how good are you at spotting inequality in life, he wants you to find an "unfair" subset of the original sequence. To be more precise, he wants you to select k numbers P = [p1, p2, ..., pk] such
that 1 ≤ pi ≤ n for 1 ≤ i ≤ k and
elements in P are distinct. Sequence P will
represent indices of elements that you'll select from both sequences. He calls such a subset P "unfair" if
and only if the following conditions are satisfied: 2·(ap1 + ... + apk) is greater than
the sum of all elements from sequence A, and 2·(bp1 + ... + bpk) is greater than
the sum of all elements from the sequence B. Also, k should
be smaller or equal to
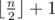
because
it will be to easy to find sequence P if he allowed you to select too many elements!
Mike guarantees you that a solution will always exist given the conditions described above, so please help him satisfy his curiosity!
Input
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105)
— the number of elements in the sequences.
On the second line there are n space-separated integers a1, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109)
— elements of sequence A.
On the third line there are also n space-separated integers b1, ..., bn (1 ≤ bi ≤ 109)
— elements of sequence B.
Output
On the first line output an integer k which represents the size of the found subset. k should
be less or equal to
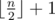
.
On the next line print k integers p1, p2, ..., pk (1 ≤ pi ≤ n)
— the elements of sequence P. You can print the numbers in any order you want. Elements in sequence P should
be distinct.
Example
input
output
题意:一个a数组,b数组,求一个序号数组p使得2*a[1-p]>a数组的总和,2*b[1-p]>b数组的总和
p<=(n/2)+1
例:8 7 4 8 3 总和30 取a[1] a[4] a[5] 8 8 3==19 19*2=38 >30 同理b。
一看到这题一般会想到贪心,由于是二维的贪心,所以一定要想让一维有序,所以可以按照a先排一下序。
得到排序后的数组a',先加上a'然后在依次两两选择b大的加上。
另外种想法。用随机数。总会随机到满足条件的嘛 23333
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
//using namespace __gnu_pbds;
using namespace std;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define endl '\n'
#define me(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x));
#define foreach(it,a) for(__typeof((a).begin()) it=(a).begin();it!=(a).end();it++)
#define close() ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
#define rand() srand(time(0));
typedef long long LL;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LINF=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
//const int dx[]={-1,0,1,0,-1,-1,1,1};
//const int dy[]={0,1,0,-1,1,-1,1,-1};
const int maxn=1e3+5;
const int maxx=1e5+100;
const double EPS=1e-9;
const int MOD=1000000007;
#define mod(x) ((x)%MOD);
template<class T>inline T min(T a,T b,T c) { return min(min(a,b),c);}
template<class T>inline T max(T a,T b,T c) { return max(max(a,b),c);}
template<class T>inline T min(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return min(min(a,b),min(c,d));}
template<class T>inline T max(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return max(max(a,b),max(c,d));}
//typedef tree<pt,null_type,less< pt >,rb_tree_tag,tree_order_statistics_node_update> rbtree;
/*lch[root] = build(L1,p-1,L2+1,L2+cnt);
rch[root] = build(p+1,R1,L2+cnt+1,R2);中前*/
/*lch[root] = build(L1,p-1,L2,L2+cnt-1);
rch[root] = build(p+1,R1,L2+cnt,R2-1);中后*/
long long gcd(long long a , long long b){if(b==0) return a;a%=b;return gcd(b,a);}
int a[maxx],b[maxx],c[maxx];
int main()
{
rand();
int n;
cin>>n;
LL sum1=0,sum2=0;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
c[i]=i;
sum1+=a[i];
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
{
cin>>b[i];
sum2+=b[i];
}
int k=n/2+1;
cout<<k<<endl;
for(;;)
{
random_shuffle(c+1,c+n+1);
LL fa=0,fb=0;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)
{
fa+=a[c[i]];
fb+=b[c[i]];
}
if(2*fa>sum1&&2*fb>sum2)
{
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)
printf("%d ",c[i]);
return 0;
}
}
}
D. Mike and distribution
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Mike has always been thinking about the harshness of social inequality. He's so obsessed with it that sometimes it even affects him while solving problems. At the moment, Mike has two sequences of positive integers A = [a1, a2, ..., an] and B = [b1, b2, ..., bn] of
length neach which he uses to ask people some quite peculiar questions.
To test you on how good are you at spotting inequality in life, he wants you to find an "unfair" subset of the original sequence. To be more precise, he wants you to select k numbers P = [p1, p2, ..., pk] such
that 1 ≤ pi ≤ n for 1 ≤ i ≤ k and
elements in P are distinct. Sequence P will
represent indices of elements that you'll select from both sequences. He calls such a subset P "unfair" if
and only if the following conditions are satisfied: 2·(ap1 + ... + apk) is greater than
the sum of all elements from sequence A, and 2·(bp1 + ... + bpk) is greater than
the sum of all elements from the sequence B. Also, k should
be smaller or equal to
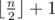
because
it will be to easy to find sequence P if he allowed you to select too many elements!
Mike guarantees you that a solution will always exist given the conditions described above, so please help him satisfy his curiosity!
Input
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105)
— the number of elements in the sequences.
On the second line there are n space-separated integers a1, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109)
— elements of sequence A.
On the third line there are also n space-separated integers b1, ..., bn (1 ≤ bi ≤ 109)
— elements of sequence B.
Output
On the first line output an integer k which represents the size of the found subset. k should
be less or equal to
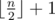
.
On the next line print k integers p1, p2, ..., pk (1 ≤ pi ≤ n)
— the elements of sequence P. You can print the numbers in any order you want. Elements in sequence P should
be distinct.
Example
input
5 8 7 4 8 3 4 2 5 3 7
output
3 1 4 5
题意:一个a数组,b数组,求一个序号数组p使得2*a[1-p]>a数组的总和,2*b[1-p]>b数组的总和
p<=(n/2)+1
例:8 7 4 8 3 总和30 取a[1] a[4] a[5] 8 8 3==19 19*2=38 >30 同理b。
一看到这题一般会想到贪心,由于是二维的贪心,所以一定要想让一维有序,所以可以按照a先排一下序。
得到排序后的数组a',先加上a'然后在依次两两选择b大的加上。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
//using namespace __gnu_pbds;
using namespace std;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define endl '\n'
#define me(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x));
#define foreach(it,a) for(__typeof((a).begin()) it=(a).begin();it!=(a).end();it++)
#define close() ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
typedef long long LL;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LINF=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
//const int dx[]={-1,0,1,0,-1,-1,1,1};
//const int dy[]={0,1,0,-1,1,-1,1,-1};
const int maxn=1e3+5;
const int maxx=1e5+100;
const double EPS=1e-9;
const int MOD=1000000007;
#define mod(x) ((x)%MOD);
template<class T>inline T min(T a,T b,T c) { return min(min(a,b),c);}
template<class T>inline T max(T a,T b,T c) { return max(max(a,b),c);}
template<class T>inline T min(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return min(min(a,b),min(c,d));}
template<class T>inline T max(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return max(max(a,b),max(c,d));}
//typedef tree<pt,null_type,less< pt >,rb_tree_tag,tree_order_statistics_node_update> rbtree;
/*lch[root] = build(L1,p-1,L2+1,L2+cnt);
rch[root] = build(p+1,R1,L2+cnt+1,R2);中前*/
/*lch[root] = build(L1,p-1,L2,L2+cnt-1);
rch[root] = build(p+1,R1,L2+cnt,R2-1);中后*/
long long gcd(long long a , long long b){if(b==0) return a;a%=b;return gcd(b,a);}
struct node
{
int x,y,id;
}Q[maxx];
bool cmp(node a,node b)
{
return a.x>b.x;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
{
cin >> Q[i].x;
Q[i].id = i;
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
cin >> Q[i].y;
sort(Q+1,Q+n+1,cmp);
cout << n / 2 + 1 << endl;
cout <<Q[1].id;
if(n % 2 == 0)
{
for(int i=2;i<n-1;i+=2)
{
if(Q[i].y<Q[i+1].y)
printf(" %d",Q[i+1].id);
else printf(" %d",Q[i].id);
}
printf(" %d",Q
.id);
}
else
{
for(int i=2;i<n;i+=2)
{
if(Q[i].y<Q[i+1].y)
printf(" %d",Q[i+1].id);
else printf(" %d",Q[i].id);
}
}
}另外种想法。用随机数。总会随机到满足条件的嘛 23333
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
//using namespace __gnu_pbds;
using namespace std;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define endl '\n'
#define me(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x));
#define foreach(it,a) for(__typeof((a).begin()) it=(a).begin();it!=(a).end();it++)
#define close() ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
#define rand() srand(time(0));
typedef long long LL;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LINF=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
//const int dx[]={-1,0,1,0,-1,-1,1,1};
//const int dy[]={0,1,0,-1,1,-1,1,-1};
const int maxn=1e3+5;
const int maxx=1e5+100;
const double EPS=1e-9;
const int MOD=1000000007;
#define mod(x) ((x)%MOD);
template<class T>inline T min(T a,T b,T c) { return min(min(a,b),c);}
template<class T>inline T max(T a,T b,T c) { return max(max(a,b),c);}
template<class T>inline T min(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return min(min(a,b),min(c,d));}
template<class T>inline T max(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return max(max(a,b),max(c,d));}
//typedef tree<pt,null_type,less< pt >,rb_tree_tag,tree_order_statistics_node_update> rbtree;
/*lch[root] = build(L1,p-1,L2+1,L2+cnt);
rch[root] = build(p+1,R1,L2+cnt+1,R2);中前*/
/*lch[root] = build(L1,p-1,L2,L2+cnt-1);
rch[root] = build(p+1,R1,L2+cnt,R2-1);中后*/
long long gcd(long long a , long long b){if(b==0) return a;a%=b;return gcd(b,a);}
int a[maxx],b[maxx],c[maxx];
int main()
{
rand();
int n;
cin>>n;
LL sum1=0,sum2=0;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
c[i]=i;
sum1+=a[i];
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
{
cin>>b[i];
sum2+=b[i];
}
int k=n/2+1;
cout<<k<<endl;
for(;;)
{
random_shuffle(c+1,c+n+1);
LL fa=0,fb=0;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)
{
fa+=a[c[i]];
fb+=b[c[i]];
}
if(2*fa>sum1&&2*fb>sum2)
{
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)
printf("%d ",c[i]);
return 0;
}
}
}
相关文章推荐
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
- Codeforces 798D:Mike and distribution
- 【codeforces 798D】Mike and distribution
- 【算法系列学习】codeforces D. Mike and distribution 二维贪心
- Codeforces 798C:Mike and gcd problem【数论+贪心】
- [CF798D] Mike and distribution(贪心,鸽笼原理,随机)
- Codeforces-798D. Mike and distribution
- Codeforces-798C-Mike and gcd problem(贪心+数论)
- Codeforces 798C:Mike and gcd problem
