Android N Phone进程启动流程
2017-04-24 17:20
267 查看
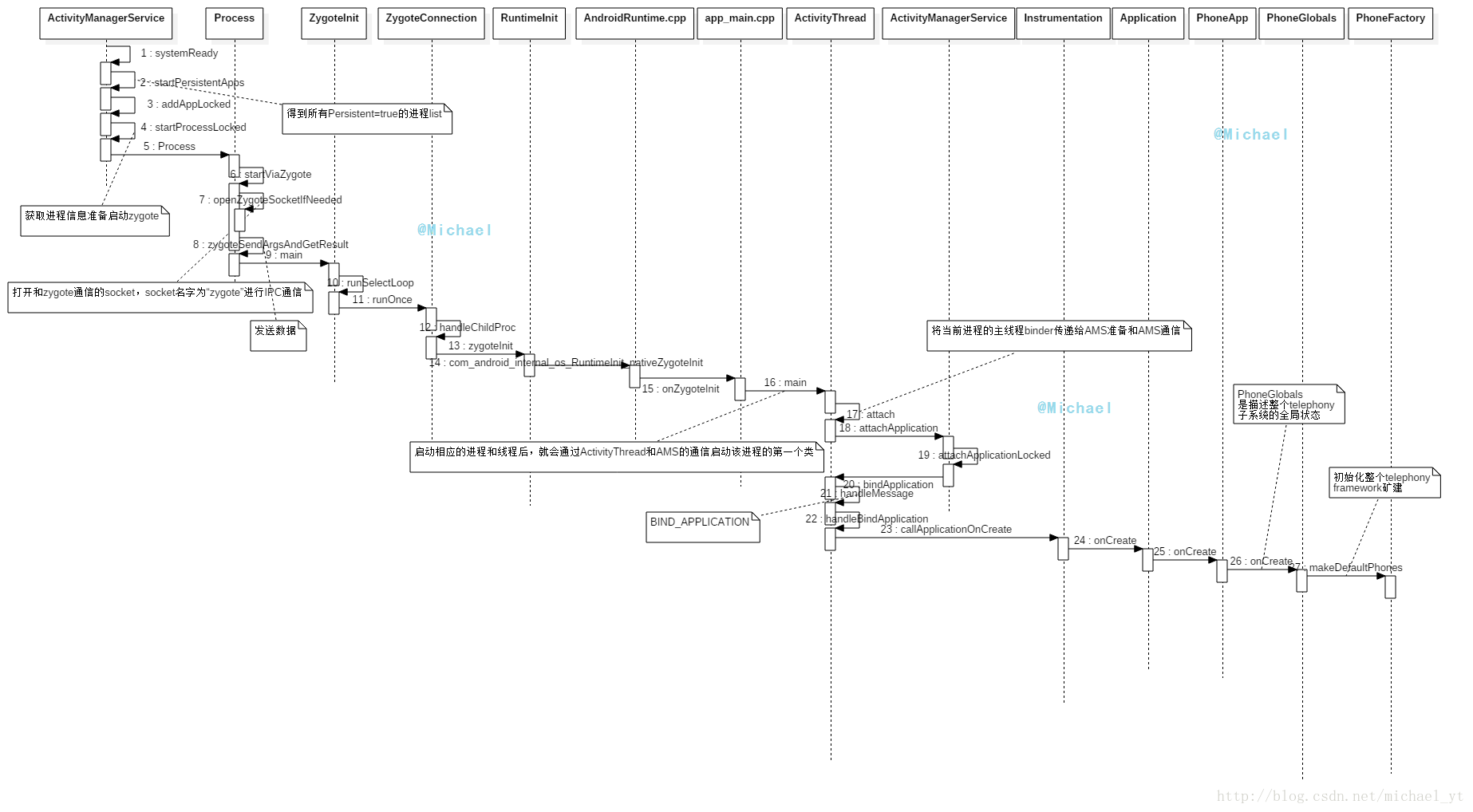
本流程图基于MTK平台 Android 7.0,本流程只作为沟通学习使用
从字面上理解就是常驻进程,当这个属性为true时,该进程应该在系统启动之后由AMS启动,那这个属性值和我们的Phone进程有什么关系呢?
我们知道Phone进程的全称应该是: package=”com.android.phone” ,我们可以在 service 目录下的 Telephony 模块的 AndroidManifest 文件中看到他的定义,这个文件里面有一个名为“PhoneApp”的application,它的persistent的属性为: android:persistent=”true” ,我们通过上面的流程图可以知道,PhoneApp 通过它的 onCreate 方法,创建了PhoneGlobals,PhoneGlobals 则创建了我们的 phone,所以我们的 Phone 进程也是通过 persistent 属性来启动的。
上面主要介绍了从AMS到PhoneApp的流程,具体介绍了一下系统是如何启动persistent为true的进程的,后续会介绍Phone进程启动过程中的一些关键类和它们的作用。
整体流程图

部分关键点说明
persistent属性
以下来自官网介绍:https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/manifest/application-element.htmlandroid:persistent Whether or not the application should remain running at all times — "true" if it should, and "false" if not. The default value is "false". Applications should not normally set this flag; persistence mode is intended only for certain system applications.
从字面上理解就是常驻进程,当这个属性为true时,该进程应该在系统启动之后由AMS启动,那这个属性值和我们的Phone进程有什么关系呢?
我们知道Phone进程的全称应该是: package=”com.android.phone” ,我们可以在 service 目录下的 Telephony 模块的 AndroidManifest 文件中看到他的定义,这个文件里面有一个名为“PhoneApp”的application,它的persistent的属性为: android:persistent=”true” ,我们通过上面的流程图可以知道,PhoneApp 通过它的 onCreate 方法,创建了PhoneGlobals,PhoneGlobals 则创建了我们的 phone,所以我们的 Phone 进程也是通过 persistent 属性来启动的。
启动流程部分关键方法
遍历所有persistent为true的进程
//ActivityManagerService.java
private void startPersistentApps(int matchFlags) {
if (mFactoryTest == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) return;
synchronized (this) {
try {
final List<ApplicationInfo> apps = AppGlobals.getPackageManager()
.getPersistentApplications(STOCK_PM_FLAGS | matchFlags).getList(); //得到所有persistent为true的进程信息
for (ApplicationInfo app : apps) {
if (!"android".equals(app.packageName)) {
addAppLocked(app, false, null /* ABI override */);//逐一启动进程
}
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
}
}具体获取所有persistent为true的进程信息
//PackageManagerService.java
private @NonNull List<ApplicationInfo> getPersistentApplicationsInternal(int flags) {
final ArrayList<ApplicationInfo> finalList = new ArrayList<ApplicationInfo>();
// reader
synchronized (mPackages) {
final Iterator<PackageParser.Package> i = mPackages.values().iterator(); //拿到所有的package
final int userId = UserHandle.getCallingUserId();
while (i.hasNext()) { //遍历所有的package
final PackageParser.Package p = i.next();
if (p.applicationInfo == null) continue;
final boolean matchesUnaware = ((flags & MATCH_DIRECT_BOOT_UNAWARE) != 0)
&& !p.applicationInfo.isDirectBootAware();
final boolean matchesAware = ((flags & MATCH_DIRECT_BOOT_AWARE) != 0) //根据传入的flags赋值
&& p.applicationInfo.isDirectBootAware();
if ((p.applicationInfo.flags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_PERSISTENT) != 0
&& (!mSafeMode || isSystemApp(p))
&& (matchesUnaware || matchesAware)) {
PackageSetting ps = mSettings.mPackages.get(p.packageName);
if (ps != null) {
ApplicationInfo ai = PackageParser.generateApplicationInfo(p, flags, //拿到对应package 的信息
ps.readUserState(userId), userId);
if (ai != null) {
/// M: Add phone package at front
if (p.packageName.equals("com.android.phone")) { //MTK加的把phone进程放到第一个,加快启动
finalList.add(0, ai);
} else {
finalList.add(ai);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return finalList;
}通过 zygote 机制创建进程
//Process.java
/**
* Starts a new process via the zygote mechanism.
*
* @param processClass Class name whose static main() to run
* @param niceName 'nice' process name to appear in ps
* @param uid a POSIX uid that the new process should setuid() to
* @param gid a POSIX gid that the new process shuold setgid() to
* @param gids null-ok; a list of supplementary group IDs that the
* new process should setgroup() to.
* @param debugFlags Additional flags.
* @param targetSdkVersion The target SDK version for the app.
* @param seInfo null-ok SELinux information for the new process.
* @param abi the ABI the process should use.
* @param instructionSet null-ok the instruction set to use.
* @param appDataDir null-ok the data directory of the app.
* @param extraArgs Additional arguments to supply to the zygote process.
* @return An object that describes the result of the attempt to start the process.
* @throws ZygoteStartFailedEx if process start failed for any reason
*/
private static ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
final int uid, final int gid,
final int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String[] extraArgs)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
synchronized(Process.class) {
ArrayList<String> argsForZygote = new ArrayList<String>();
// --runtime-args, --setuid=, --setgid=,
// and --setgroups= must go first
argsForZygote.add("--runtime-args");
argsForZygote.add("--setuid=" + uid);
argsForZygote.add("--setgid=" + gid);
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_JNI_LOGGING) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-jni-logging");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_SAFEMODE) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-safemode");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-debugger");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_CHECKJNI) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-checkjni");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_GENERATE_DEBUG_INFO) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--generate-debug-info");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ALWAYS_JIT) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--always-jit");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_NATIVE_DEBUGGABLE) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--native-debuggable");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_ASSERT) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-assert");
}
if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_DEFAULT) {
argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-default");
} else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_READ) {
argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-read");
} else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_WRITE) {
argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-write");
}
argsForZygote.add("--target-sdk-version=" + targetSdkVersion);
//TODO optionally enable debuger
//argsForZygote.add("--enable-debugger");
// --setgroups is a comma-separated list
if (gids != null && gids.length > 0) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("--setgroups=");
int sz = gids.length;
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
sb.append(',');
}
sb.append(gids[i]);
}
argsForZygote.add(sb.toString());
}
if (niceName != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--nice-name=" + niceName);
}
if (seInfo != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--seinfo=" + seInfo);
}
if (instructionSet != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--instruction-set=" + instructionSet);
}
if (appDataDir != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--app-data-dir=" + appDataDir);
}
argsForZygote.add(processClass);
if (extraArgs != null) {
for (String arg : extraArgs) {
argsForZygote.add(arg);
}
}
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi), argsForZygote);
}
}和AMS建立通信
//ActivityThread.java
private void attach(boolean system) {
sCurrentActivityThread = this;
mSystemThread = system;
if (!system) {
ViewRootImpl.addFirstDrawHandler(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ensureJitEnabled();
}
});
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("<pre-initialized>",
UserHandle.myUserId());
RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());//传入当前进程主线程的binder
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);//和AMS通过binder建立通信
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
//.............省略部分代码
}执行对应application的OnCreate方法
//ActivityThread.java
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
// Register the UI Thread as a sensitive thread to the runtime.
//......省略部分代码
try {
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);//执行application的OnCreate方法
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
} finally {
StrictMode.setThreadPolicy(savedPolicy);
}
}上面主要介绍了从AMS到PhoneApp的流程,具体介绍了一下系统是如何启动persistent为true的进程的,后续会介绍Phone进程启动过程中的一些关键类和它们的作用。
相关文章推荐
- Android O: init进程启动流程分析(阶段三)
- Android源码解析之(八)-->Zygote进程启动流程
- Android系统启动流程(一)解析init进程启动过程
- Android 应用进程启动流程
- Android源码(2) --- SystemServer进程启动流程
- Android6.0的phone应用源码分析(2)——phone相关进程启动分析
- Android在新进程中启动 Service 的流程原理分析
- Android app启动一个新进程流程
- Android源码基础解析之应用进程启动流程
- Android应用进程启动流程(Zygote进程与SystemServer进程)
- Android启动流程分析(四) init进程分析
- Android系统启动流程(一)解析init进程启动过程
- android N进程启动流程(一)(捕获输入事件、准备创建activity、焦点切换)
- Android Phone进程启动过程详解
- android init进程启动的大致流程
- android进程启动流程
- Android源码基础解析之Zygote进程启动流程
- Android源码基础解析之SystemServer进程启动流程
- Android源码解析之(九)-->SystemServer进程启动流程
- Android系统启动流程——init进程
