并查集详解
2017-04-17 19:03
204 查看
并查集的概念
并查集顾名思义就是合并和查找,问题在于合并什么,查找什么。这里有一种朴素的思想来解释这两个问题。就是把这个想成一棵树。合并什么?就是把不在这棵树里的节点合并到该树中,而查找的是该棵树的根节点。大家可以想象有一棵树,如下: 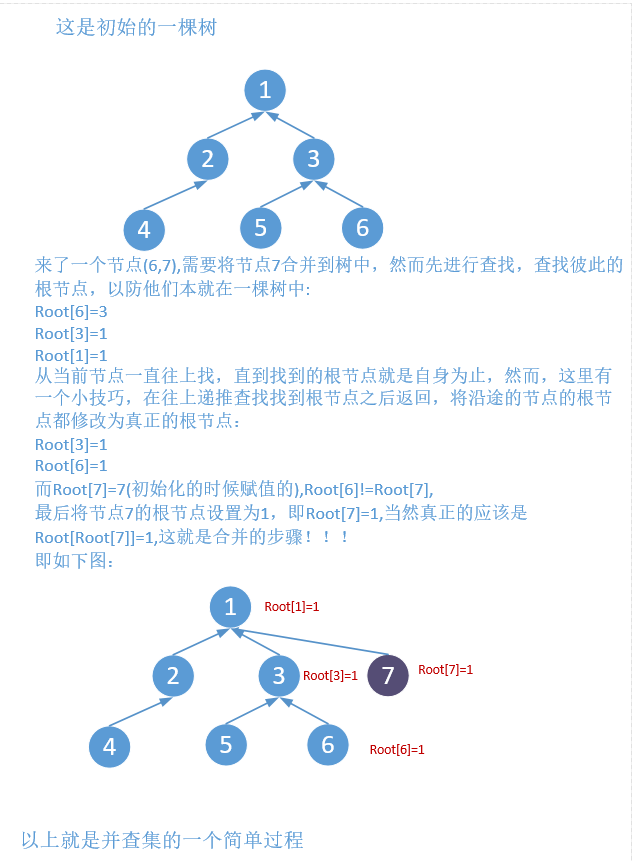
从上面可以看出并查集的特点,连通和分类。因此,并查集在算法中的运用很灵活也很广泛,比如朋友圈算法(朋友的朋友是朋友),团伙问题(朋友的朋友是朋友,敌人的敌人是朋友),连通图,最近公共祖先等等。下面将对几种典型的算法进行讲解。
朋友圈
题目描述:假如已知有n个人和m对好友关系(存于数字r)。如果两个人是直接或间接的好友(好友的好友的好友...),则认为他们属于同一个朋友圈,请写程序求出这n个人里一共有多少个朋友圈。
输入
输入包含多个测试用例,每个测试用例的第一行包含两个正整数 n、m,1=<n,m<=100000。接下来有m行,每行分别输入两个人的编号f,t(1=<f,t<=n),表示f和t是好友。 当n为0时,输入结束,该用例不被处理。 对应每个测试用例,输出在这n个人里一共有多少个朋友圈。
样例输入
5 3
1 2
2 3
4 5
3 3
1 2
1 3
2 3
0
样例输出:
2
1
来源:
小米2013年校园招聘笔试题
思路
这题是基本并查集概念的运用。从题中可以看出,关系组只有两种,一种是朋友,一种是陌生人。说白了,这就是用并查集来分类。同一棵树中就是同一个朋友圈,分居两棵树,就是不同的两个朋友圈。代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N;
while((N = sc.nextInt())!=0){
int M = sc.nextInt();
int root[] = new int[N+1];
for(int i=1;i<N+1;i++){//初始化根节点为自己,即各个自为一棵只有一个节点的树
root[i]=i;
}
while(M-->0){
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
union(root,x,y);//合并两棵树
}
int sum = 0;
for(int i=1;i<N+1;i++){
if(root[i]==i){//根节点为自己,表示是当前朋友圈的根节点,如果不是,则表示该节点属于某个根节点的朋友圈
sum++;
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
//合并的过程
private static void union(int[] root, int x, int y) {
int rootx = find(root,x);//递推寻找根节点
int rooty = find(root,y);
if(rootx==rooty){//如果根节点不等,说明两节点不在同一棵树中
return;
}
root[rootx]=rooty;//将x节点所在的树合并到y所在的树中(注:谁合并谁都无所谓)
}
//查找合并过程
private static int find(int[] root, int x) {
if(root[x]!=x){//如果没找到根节点就继续往上找,找到根节点之后返回,并沿路修改每个节点的根节点
root[x]=find(root,root[x]);
}
return root[x];
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
团伙问题
题目描述 整个组织有n个人,任何两个认识的人不是朋友就是敌人,而且满足:①我朋友的朋友是我的朋友;②我敌人的敌人是我的朋友。所有是朋友的人组成一个团伙。现在,警方委派你协助调查,拥有关于这n个人的m条信息(即某两个人是朋友,或某两个人是敌人),请你计算出这个城市最多可能有多少个团伙。 数据范围:2≤N≤1000,1≤M≤1000。
输入数据:
第一行包含一个整数N,第二行包含一个整数M,接下来M行描述M条信息,内容为以下两者之一:“x y 1”表示x与y是朋友;“x y 0”表示x与y是敌人(1≤x≤y≤N)。 0为输入结束。
输出数据:包含一个整数,即可能的最大团伙数。
样例输入:
6 4
1 4 1
3 5 1
4 6 0
1 2 0
0
样例输出:
3
思路
该题是上面朋友圈的升级版,唯一不同就是多了一种关系–敌人,所以一共有三种关系:朋友,敌人,陌生人。该题解题的关键点在于要能明白:x的敌人y与x之前的敌人是一个朋友圈,y的敌人与x是朋友。假设e[]表示敌人朋友圈,则e[x]与y是同一个朋友圈,或者说e[y]与x是同一个朋友圈,因此便转换为朋友圈问题。这个一点能明白,解题就很容易了。代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N;
while((N = sc.nextInt())!=0){
int M = sc.nextInt();
int root[] = new int[N+1];
int e[] = new int[N+1];//存放敌人
for(int i=1;i<N+1;i++){
root[i]=i;//根节点为自身
e[i]=0;//初始化,每个人都没有敌人
}
while(M-->0){
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
int type = sc.nextInt();
if(type==1){//如果是朋友,则合并朋友圈
union(root,x,y);
}else{//如果是敌人
if(e[x]==0){//如果没有敌人,则该次关系的敌人就是第一个敌人
e[x]=y;
}else{
union(root,e[x],y);//如果已存在敌人,则去合并敌人朋友圈
}
if(e[y]==0){//相互记录
e[y]=x;
}else{
union(root,e[y],x);
}
}
}
int sum = 0;
for(int i=1;i<N+1;i++){
if(root[i]==i){
sum++;
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
//合并朋友圈(敌人朋友圈)
private static void union(int[] root, int x, int y) {
int rootx = find(root,x);
int rooty = find(root,y);
if(rootx==rooty){
return;
}
root[rootx]=rooty;
}
//查找根节点
private static int find(int[] root, int x) {
if(root[x]!=x){
root[x]=find(root,root[x]);
}
return root[x];
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
连通图
题目描述: 现在有孤岛n个,孤岛从1开始标序一直到n,有道路m条(道路是双向的,如果有多条道路连通岛屿i,j则选择最短的那条),请你求出能够让所有孤岛都连通的最小道路总长度。
输入:
数据有多组输入。
每组第一行输入n(1<=n<=1000),m(0<=m<=10000)。
输出:
对每组输入输出一行,如果能连通,输出能连通所有岛屿的最小道路长度,否则请输出字符串”no”。
样例输入:
3 5
1 2 2
1 2 1
2 3 5
1 3 3
3 1 2
4 2
1 2 3
样例输出:
3
no
这题除了考并查集,其实也是对kruskal算法的运用。如果大家知道kruskal,就知道首先应该是按距离排序,然后每次选择最短路径连接,一点点成为树的合并,最后合成为一棵最小生成树。代码如下:
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Scanner;
//存储边的结构,u->v距离为len
class Edg{
int u;
int v;
int len;
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext()){
int N = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
int root[] = new int[N+1];
for(int i=1;i<N+1;i++){
root[i]=i;
}
Edg[] edg = new Edg[M];
//边的输入
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
edg[i] = new Edg();
edg[i].u = sc.nextInt();
edg[i].v = sc.nextInt();
edg[i].len = sc.nextInt();
}
//将边按路径排序
java.util.Arrays.sort(edg, new Comparator<Edg>() {
@Override
public int compare(Edg a, Edg b) {
if(a.len>b.len){
return 1;
}else if(a.len<b.len){
return -1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
});
int sum=0;
int eds = 0;//合并的生成树中的边树
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
//查看u/v根节点是否相等,如果相等表示他们已经连通。
int rootu = find(root,edg[i].u);
int rootv = find(root,edg[i].v);
if(rootu!=rootv){//不连通,则合并两棵树,其实也就是将u节点所在的树合并到v中
root[rootu]=rootv;
eds++;
sum+=edg[i].len;//最小生成树中的连通距离
}
//如果合成的生成树边树等于节点总数N-1,则已经是最小生成树。
if(eds==N-1){
break;
}
}
if(eds==N-1){
System.out.println(sum);
}else{
System.out.println("no");
}
}
}
private static int find(int[] root, int x) {
return root[x]==x?x:(root[x]=find(root,root[x]));
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
