Uva 1590 IP Networks
2017-04-05 14:06
375 查看
Description

Alex is administrator of IP networks. His clients have a bunch of individual IP addresses and he decided to group all those IP addresses into the smallest possible IP network.
Each IP address is a 4-byte number that is written byte-by-byte in a decimal dot-separated notation ``byte0.byte1.byte2.byte3" (quotes are added for clarity). Each byte is written as a decimal number from 0
to 255 (inclusive) without extra leading zeroes.
IP network is described by two 4-byte numbers - network address and network mask. Both network address and network mask are written in the same notation as IP addresses.
In order to understand the meaning of network address and network mask you have to consider their binary representation. Binary representation of IP address, network address, and network mask consists of 32
bits: 8 bits for byte0 (most significant to least significant), followed by 8 bits for byte1, followed by 8 bits for byte2, and followed by 8 bits for byte3.
IP network contains a range of 2n IP addresses where 0
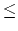
n
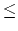
32 .
Network mask always has 32 - n first bits set to one, and n last bits set to zero in its binary representation. Network address has arbitrary 32 - n first
bits, and n last bits set to zero in its binary representation. IP network contains all IP addresses whose 32 - n first bits are equal to 32 - n first
bits of network address with arbitrary n last bits. We say that one IP network is smaller than the other IP network if it contains fewer IP addresses.
For example, IP network with network address 194.85.160.176 and network mask 255.255.255.248 contains 8 IP addresses from 194.85.160.176 to 194.85.160.183 (inclusive).
The first line of the input file contains a single integer number m(1
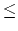
m
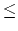
1000) .
The following m lines contain IP addresses, one address on a line. Each IP address may appear more than once in the input file.
on the second line.
Sample
Sample

Alex is administrator of IP networks. His clients have a bunch of individual IP addresses and he decided to group all those IP addresses into the smallest possible IP network.
Each IP address is a 4-byte number that is written byte-by-byte in a decimal dot-separated notation ``byte0.byte1.byte2.byte3" (quotes are added for clarity). Each byte is written as a decimal number from 0
to 255 (inclusive) without extra leading zeroes.
IP network is described by two 4-byte numbers - network address and network mask. Both network address and network mask are written in the same notation as IP addresses.
In order to understand the meaning of network address and network mask you have to consider their binary representation. Binary representation of IP address, network address, and network mask consists of 32
bits: 8 bits for byte0 (most significant to least significant), followed by 8 bits for byte1, followed by 8 bits for byte2, and followed by 8 bits for byte3.
IP network contains a range of 2n IP addresses where 0
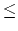
n
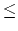
32 .
Network mask always has 32 - n first bits set to one, and n last bits set to zero in its binary representation. Network address has arbitrary 32 - n first
bits, and n last bits set to zero in its binary representation. IP network contains all IP addresses whose 32 - n first bits are equal to 32 - n first
bits of network address with arbitrary n last bits. We say that one IP network is smaller than the other IP network if it contains fewer IP addresses.
For example, IP network with network address 194.85.160.176 and network mask 255.255.255.248 contains 8 IP addresses from 194.85.160.176 to 194.85.160.183 (inclusive).
Input
The input file will contain several test cases, each of them as described below.The first line of the input file contains a single integer number m(1
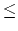
m
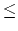
1000) .
The following m lines contain IP addresses, one address on a line. Each IP address may appear more than once in the input file.
Output
For each test case, write to the output file two lines that describe the smallest possible IP network that contains all IP addresses from the input file. Write network address on the first line and network maskon the second line.
Sample
Input
3 194.85.160.177 194.85.160.183 194.85.160.178
Sample
Output
930a 194.85.160.176 255.255.255.248
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int ip[4][10010];
int dist[9]={255,254,252,248,240,224,192,128,0};
int main()
{
int m;
while(~scanf("%d",&m))
{
memset(ip,0,sizeof(ip));
int dns[4];
int minip[4];
int i;
for(i=0;i<=m-1;i++)
{
scanf("%d.%d.%d.%d",&ip[0][i],&ip[1][i],&ip[2][i],&ip[3][i]);
}
for(i=0;i<=3;i++)
{
int dir=0;
int j;
sort(ip[i],ip[i]+m);//给四组分别排序
int p=ip[i][m-1];
int q=ip[i][0];
for(j=1;j<=8;j++)
{
if(p%2!=q%2) dir=j;
p/=2;
q/=2;
}//判断最后几位不同
dns[i]=dist[dir];
minip[i]=ip[i][0]&dns[i];//ip地址和子网掩码按位与运算得出最小ip地址
}
for(i=0;i<=3;i++)
{
if(dns[i]!=255)
{
for(i=i+1;i<=3;i++)
{
dns[i]=0;
minip[i]=0;
}
break;
}
}
printf("%d.%d.%d.%d\n",minip[0],minip[1],minip[2],minip[3]);
printf("%d.%d.%d.%d\n",dns[0],dns[1],dns[2],dns[3]);
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- UVA 1590 IP Networks(IP 网络)
- UVA 1590 IP Networks
- Uva 1590 IP Networks
- 小紫书 4-5 UVA 1590 IP Networks
- UVA 1590 - IP Networks
- UVA 1590 IP Networks
- UVA 1590 - IP Networks
- UVA 1590 IP Networks(暴力)
- UVALive3520 UVa1590 POJ2799 IP Networks【进制+位运算】
- UVA1590 IP网络(IP Networks)
- Uva 1590 IP Networks
- UVA 1590 IP Networks
- Uva-1590 - IP Networks-AC
- UVA 1590 IP Networks
- poj - 2799 UVA - 1590 IP Networks
- BFS:UVa1590-IP Networks (子网掩码相关知识)
- 算法竞赛入门经典第四章习题4-5 IP Networks UVA - 1590
- UVA 1590 IP Networks 位操作解题
- 4-5 UVA1590 IP网络(IP Networks)
- Uva1590——IP networks
