DHCP服务器的搭建
2017-04-02 11:16
253 查看
dhcp笔记整理: http://services.linuxpanda.tech/DHCP/index.html
1 dhcp简介
当DHCP客户机第一次登录网络的时候(也就是客户机上没有任何IP地址数据时),它会通过UDP
67端口向网络上发出一个DHCPDISCOVER数据包(包中包含客户机的MAC地址和计算机名等信息)。因为客户机还不知道自己属于哪一个网络,所以封包的源地址为0.0.0.0,目标地址为255.255.255.255,然后再附上DHCP
discover的信息,向网络进行广播。
网络上每一台安装了TCP/IP协议的主机都会接收这个广播信息,但只有DHCP服务器才会做出响应。
DHCP Server分配IP地址
当DHCP Server监听到客户机发出的DHCP
discover广播后,它会从那些还没有租出去的地址中,选择最前面的空置IP,连同其它TCP/IP设定,通过UDP
68端口响应给客户机一个DHCP OFFER数据包(包中包含IP地址、子网掩码、地址租期等信息)。此时还是使用广播进行通讯,源IP地址为DHCP
Server的IP地址,目标地址为255.255.255.255。同时,DHCP
Server为此客户保留它提供的IP地址,从而不会为其他DHCP客户分配此IP地址(预留ip)。
由于客户机在开始的时候还没有IP地址,所以在其DHCP discover封包内会带有其MAC地址信息,并且有一个XID编号来辨别该封包,DHCP Server响应的DHCP OFFER封包则会根据这些资料传递给要求租约的客户。
DHCP Client接受IP租约
如果客户机收到网络上多台DHCP服务器的响应,只会挑选其中一个DHCP OFFER(一般是最先到达的那个),并且会向网络发送一个DHCP
REQUEST广播数据包(包中包含客户端的MAC地址、接受的租约中的IP地址、提供此租约的DHCP服务器地址等),告诉所有DHCP
Server它将接受哪一台服务器提供的IP地址,所有其他的DHCP服务器撤销它们的提供以便将IP地址提供给下一次IP租用请求。此时,由于还没有得到DHCP
Server的最后确认,客户端仍然使用0.0.0.0为源IP地址,255.255.255.255为目标地址进行广播。
事实上,并不是所有DHCP客户机都会无条件接受DHCP
Server的OFFER,特别是如果这些主机上安装有其它TCP/IP相关的客户机软件。客户机也可以用DHCP
REQUEST向服务器提出DHCP选择,这些选择会以不同的号码填写在DHCP Option
Field里面。客户机可以保留自己的一些TCP/IP设定。
租约确认
当DHCP Server接收到客户机的DHCP REQUEST之后,会广播返回给客户机一个DHCP ACK消息包,表明已经接受客户机的选择,并将这一IP地址的合法租用以及其他的配置信息都放入该广播包发给客户机。
客户机在接收到DHCP
ACK广播后,会向网络发送三个针对此IP地址的ARP解析请求以执行冲突检测,查询网络上有没有其它机器使用该IP地址;如果发现该IP地址已经被使用,客户机会发出一个DHCP
DECLINE数据包给DHCP Server,拒绝此IP地址租约,并重新发送DHCP
discover信息。此时,在DHCP服务器管理控制台中,会显示此IP地址为BAD_ADDRESS。
如果网络上没有其它主机使用此IP地址,则客户机的TCP/IP使用租约中提供的IP地址完成初始化,从而可以和其他网络中的主机进行通讯。
DHCP Client重新登录
以后DHCP客户端每次重新登录网络时,就不需要再发送DHCP discover发现信息了,而是直接发送包含前一次所分配的IP地址的DHCP
request请求信息。当DHCP服务器收到这一信息后,它会尝试让DHCP客户机继续使用原来的IP地址,并回答一个DHCP
ack确认信息。如果此IP地址已无法再分配给原来的DHCP客户机使用时,则DHCP服务器给DHCP客户机回答一个DHCP
nack否认信息。当原来的DHCP客户机收到此DHCP nack否认信息后,它就必须重新发送DHCPdiscover发现信息来请求新的IP地址。
更新租约
DHCP服务器向DHCP客户机出租的IP地址一般都有一个租借期限,期满后DHCP服务器便会收回出租的IP地址。如果DHCP客户机要延长其IP租约,则必须更新其IP租约。DHCP客户机启动时和IP租约期限过一半时,DHCP客户机都会自动向DHCP服务器发送更新其IP租约的信息。
这种方法指定了一个用来动态的提供给第一个访问网络的DHCP客户端的IP地址池(有时也称作区域或范围)。当DHCP客户端离开网络超过一定时间后,IP地址就会被回收到地址池以供其它DHCP客户端使用。
MAC地址:
这种方法强制使用DHCP来区别每一块连接上网络的网卡的硬件地址,之后这块网卡每次连上网络请求DHCP服务时都为它提供这个固定的IP地址。
2 测试环境介绍
我这是使用vmware模拟环境,一台centos7用于dhcp服务器,一台rhel6(用户dhcp客户机)。 本身vmware有dhcp的功能, 这里我们给我们的测试机器定义到一个网络中去。使用下vmware的特定虚拟网络。这样我们的服务器和客户机就在同一个网络内部了。具体设置见下图:

同样把dhcp的客户机器也放置到vmware特定的网络中去。
3.安装dhcp
4.配置dhcp
5.重启dhcp服务
6.客户机器测试
6.1修改客户机的ip获取方式为dhcp
6.2重启客户端网卡查看分配的ip

6.3 给固定的mac地址分配固定的ip
我们这里修改dhcp服务器配置文件
在测试机器上使用dhcpclient -d命令再次获取
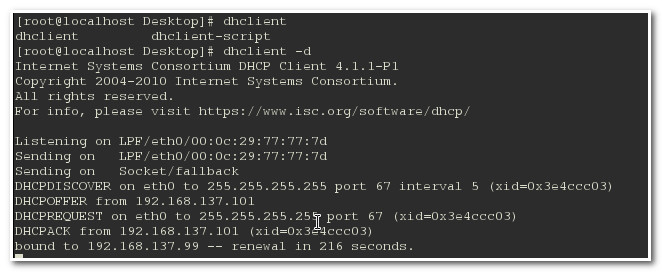
上图可以看到, 我们获取到的ip就是192.168.137.99这个IP地址。
1 dhcp简介
DHCP原理
动态主机配置协议(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol,DHCP)是用于对多个客户计算机集中分配IP地址以及IP地址相关的信息的协议,这样就能将IP地址和TCP/IP的设置统一管理起来,而避免不必要的地址冲突的问题。工作流程
寻找DHCP Server。当DHCP客户机第一次登录网络的时候(也就是客户机上没有任何IP地址数据时),它会通过UDP
67端口向网络上发出一个DHCPDISCOVER数据包(包中包含客户机的MAC地址和计算机名等信息)。因为客户机还不知道自己属于哪一个网络,所以封包的源地址为0.0.0.0,目标地址为255.255.255.255,然后再附上DHCP
discover的信息,向网络进行广播。
网络上每一台安装了TCP/IP协议的主机都会接收这个广播信息,但只有DHCP服务器才会做出响应。
DHCP Server分配IP地址
当DHCP Server监听到客户机发出的DHCP
discover广播后,它会从那些还没有租出去的地址中,选择最前面的空置IP,连同其它TCP/IP设定,通过UDP
68端口响应给客户机一个DHCP OFFER数据包(包中包含IP地址、子网掩码、地址租期等信息)。此时还是使用广播进行通讯,源IP地址为DHCP
Server的IP地址,目标地址为255.255.255.255。同时,DHCP
Server为此客户保留它提供的IP地址,从而不会为其他DHCP客户分配此IP地址(预留ip)。
由于客户机在开始的时候还没有IP地址,所以在其DHCP discover封包内会带有其MAC地址信息,并且有一个XID编号来辨别该封包,DHCP Server响应的DHCP OFFER封包则会根据这些资料传递给要求租约的客户。
DHCP Client接受IP租约
如果客户机收到网络上多台DHCP服务器的响应,只会挑选其中一个DHCP OFFER(一般是最先到达的那个),并且会向网络发送一个DHCP
REQUEST广播数据包(包中包含客户端的MAC地址、接受的租约中的IP地址、提供此租约的DHCP服务器地址等),告诉所有DHCP
Server它将接受哪一台服务器提供的IP地址,所有其他的DHCP服务器撤销它们的提供以便将IP地址提供给下一次IP租用请求。此时,由于还没有得到DHCP
Server的最后确认,客户端仍然使用0.0.0.0为源IP地址,255.255.255.255为目标地址进行广播。
事实上,并不是所有DHCP客户机都会无条件接受DHCP
Server的OFFER,特别是如果这些主机上安装有其它TCP/IP相关的客户机软件。客户机也可以用DHCP
REQUEST向服务器提出DHCP选择,这些选择会以不同的号码填写在DHCP Option
Field里面。客户机可以保留自己的一些TCP/IP设定。
租约确认
当DHCP Server接收到客户机的DHCP REQUEST之后,会广播返回给客户机一个DHCP ACK消息包,表明已经接受客户机的选择,并将这一IP地址的合法租用以及其他的配置信息都放入该广播包发给客户机。
客户机在接收到DHCP
ACK广播后,会向网络发送三个针对此IP地址的ARP解析请求以执行冲突检测,查询网络上有没有其它机器使用该IP地址;如果发现该IP地址已经被使用,客户机会发出一个DHCP
DECLINE数据包给DHCP Server,拒绝此IP地址租约,并重新发送DHCP
discover信息。此时,在DHCP服务器管理控制台中,会显示此IP地址为BAD_ADDRESS。
如果网络上没有其它主机使用此IP地址,则客户机的TCP/IP使用租约中提供的IP地址完成初始化,从而可以和其他网络中的主机进行通讯。
DHCP Client重新登录
以后DHCP客户端每次重新登录网络时,就不需要再发送DHCP discover发现信息了,而是直接发送包含前一次所分配的IP地址的DHCP
request请求信息。当DHCP服务器收到这一信息后,它会尝试让DHCP客户机继续使用原来的IP地址,并回答一个DHCP
ack确认信息。如果此IP地址已无法再分配给原来的DHCP客户机使用时,则DHCP服务器给DHCP客户机回答一个DHCP
nack否认信息。当原来的DHCP客户机收到此DHCP nack否认信息后,它就必须重新发送DHCPdiscover发现信息来请求新的IP地址。
更新租约
DHCP服务器向DHCP客户机出租的IP地址一般都有一个租借期限,期满后DHCP服务器便会收回出租的IP地址。如果DHCP客户机要延长其IP租约,则必须更新其IP租约。DHCP客户机启动时和IP租约期限过一半时,DHCP客户机都会自动向DHCP服务器发送更新其IP租约的信息。
DHCP服务器提供以下两种配置方法
地址池:这种方法指定了一个用来动态的提供给第一个访问网络的DHCP客户端的IP地址池(有时也称作区域或范围)。当DHCP客户端离开网络超过一定时间后,IP地址就会被回收到地址池以供其它DHCP客户端使用。
MAC地址:
这种方法强制使用DHCP来区别每一块连接上网络的网卡的硬件地址,之后这块网卡每次连上网络请求DHCP服务时都为它提供这个固定的IP地址。
2 测试环境介绍
我这是使用vmware模拟环境,一台centos7用于dhcp服务器,一台rhel6(用户dhcp客户机)。 本身vmware有dhcp的功能, 这里我们给我们的测试机器定义到一个网络中去。使用下vmware的特定虚拟网络。这样我们的服务器和客户机就在同一个网络内部了。具体设置见下图:

同样把dhcp的客户机器也放置到vmware特定的网络中去。
3.安装dhcp
[root@mail yum.repos.d]# yum list all |grep dhcp #查看相关dhcp安装情况 dhcp.x86_64 12:4.2.5-47.el7.centos @cdrom dhcp-common.x86_64 12:4.2.5-47.el7.centos @anaconda dhcp-devel.x86_64 12:4.2.5-47.el7.centos @cdrom dhcp-libs.x86_64 12:4.2.5-47.el7.centos @anaconda dhcp-devel.i686 12:4.2.5-47.el7.centos cdrom dhcp-libs.i686 12:4.2.5-47.el7.centos cdrom [root@mail yum.repos.d]# yum install dhcp dhcp-common dhcp-libs #安装dhcp
4.配置dhcp
[root@mail dhcp]# cd /etc/dhcp #进入dhcp目录 [root@mail dhcp]# ls #查看文件 dhcpd6.conf dhcpd.conf [root@mail dhcp]# cat dhcpd.conf #查看下默认配置文件, 这里发现配置文件全是注释, 只是提示了我们可以从其他文件中获取样例。 # # DHCP Server Configuration file. # see /usr/share/doc/dhcp*/dhcpd.conf.example # see dhcpd.conf(5) man page # root@mail dhcp]# cp /usr/share/doc/dhcp-4.2.5/dhcpd.conf.example dhcpd.conf cp: overwrite ‘dhcpd.conf’? y
[root@mail dhcp]# cat dhcpd.conf #查看样例的配置
# dhcpd.conf
#
# Sample configuration file for ISC dhcpd
#
# option definitions common to all supported networks...
option domain-name "example.org";
option domain-name-servers ns1.example.org, ns2.example.org;
default-lease-time 600;
max-lease-time 7200;
# Use this to enble / disable dynamic dns updates globally.
#ddns-update-style none;
# If this DHCP server is the official DHCP server for the local
# network, the authoritative directive should be uncommented.
#authoritative;
# Use this to send dhcp log messages to a different log file (you also
# have to hack syslog.conf to complete the redirection).
log-facility local7;
# No service will be given on this subnet, but declaring it helps the
# DHCP server to understand the network topology.
subnet 10.152.187.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
}
# This is a very basic subnet declaration.
subnet 10.254.239.0 netmask 255.255.255.224 {
range 10.254.239.10 10.254.239.20;
option routers rtr-239-0-1.example.org, rtr-239-0-2.example.org;
}
# This declaration allows BOOTP clients to get dynamic addresses,
# which we don't really recommend.
subnet 10.254.239.32 netmask 255.255.255.224 {
range dynamic-bootp 10.254.239.40 10.254.239.60;
option broadcast-address 10.254.239.31;
option routers rtr-239-32-1.example.org;
}
# A slightly different configuration for an internal subnet.
subnet 10.5.5.0 netmask 255.255.255.224 {
range 10.5.5.26 10.5.5.30;
option domain-name-servers ns1.internal.example.org;
option domain-name "internal.example.org";
option routers 10.5.5.1;
option broadcast-address 10.5.5.31;
default-lease-time 600;
max-lease-time 7200;
}
# Hosts which require special configuration options can be listed in
# host statements. If no address is specified, the address will be
# allocated dynamically (if possible), but the host-specific information
# will still come from the host declaration.
host passacaglia {
hardware ethernet 0:0:c0:5d:bd:95;
filename "vmunix.passacaglia";
server-name "toccata.fugue.com";
}
# Fixed IP addresses can also be specified for hosts. These addresses
# should not also be listed as being available for dynamic assignment.
# Hosts for which fixed IP addresses have been specified can boot using
# BOOTP or DHCP. Hosts for which no fixed address is specified can only
# be booted with DHCP, unless there is an address range on the subnet
# to which a BOOTP client is connected which has the dynamic-bootp flag
# set.
host fantasia {
hardware ethernet 08:00:07:26:c0:a5;
fixed-address fantasia.fugue.com;
}
# You can declare a class of clients and then do address allocation
# based on that. The example below shows a case where all clients
# in a certain class get addresses on the 10.17.224/24 subnet, and all
# other clients get addresses on the 10.0.29/24 subnet.
class "foo" {
match if substring (option vendor-class-identifier, 0, 4) = "SUNW";
}
shared-network 224-29 {
subnet 10.17.224.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers rtr-224.example.org;
}
subnet 10.0.29.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers rtr-29.example.org;
}
pool {
allow members of "foo";
range 10.17.224.10 10.17.224.250;
}
pool {
deny members of "foo";
range 10.0.29.10 10.0.29.230;
}
}[root@mail dhcp]# cat dhcpd.conf #修改文件内容如下。 这里的137网段和我的本机是ip是在同一网段的。
option domain-name "test.org";
option domain-name-servers 192.168.137.1, 192.168.137.2;
default-lease-time 600;
max-lease-time 7200;
log-facility local7;
subnet 192.168.137.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 192.168.137.50 192.168.137.100;
}
host fantasia {
#hardware ethernet 08:00:07:26:c0:a5;
#fixed-address fantasia.fugue.com;
}5.重启dhcp服务
[root@mail dhcp]# systemctl restart dhcpd.service
6.客户机器测试
6.1修改客户机的ip获取方式为dhcp
[root@localhost ~] # cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ [root@localhost ~] # vim /ifcfg-eth0 注释IPADDR,NETMASK,GATEWAY行, 修改BOOTPROTO值为dhcp [root@localhost ~] systemctl restart network.service
6.2重启客户端网卡查看分配的ip

6.3 给固定的mac地址分配固定的ip
我们这里修改dhcp服务器配置文件
option domain-name "test.org";
option domain-name-servers 192.168.137.1, 192.168.137.2;
default-lease-time 600;
max-lease-time 7200;
log-facility local7;
subnet 192.168.137.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 192.168.137.50 192.168.137.100;
}
host fantasia {
hardware ethernet 00:0C:29:77:77:7D; #这里的mac地址是客户机的mac地址
fixed-address 192.168.137.99;
}在测试机器上使用dhcpclient -d命令再次获取

上图可以看到, 我们获取到的ip就是192.168.137.99这个IP地址。
相关文章推荐
- quidway secpath下搭建DHCP服务器02
- 在Windows Server2003系统下搭建DHCP服务器
- DHCP服务器的搭建
- 如何在redhat 4中搭建DHCP服务器
- 三层交换机的配置和DHCP服务器的搭建
- 解决在DHCP环境下私自指定IP和私自搭建DHCP服务器的方法
- DHCP服务器的搭建
- Windows下搭建DHCP服务器之定义用户类别
- Windows 网络服务架构系列课程详解(一) ----DHCP服务器的搭建与配置
- Linux下搭建DHCP服务器
- 第一章 搭建DHCP服务器操作要点
- 用Linux系统搭建DHCP服务器及DHCP中继代理
- 菜鸟学Linux之二:DHCP服务器中继代理的搭建和部署
- 解决在DHCP环境下私自指定IP和私自搭建DHCP服务器的方法
- DHCP服务器的搭建及抓包分析DHCP的实现
- DHCP服务器的搭建
- Linux下搭建DHCP服务器
- DHCP服务器中继代理的搭建和部署
- DHCP服务器的搭建
