构建生产者与消费者的单链表模式
2017-03-30 11:59
225 查看
1、在linux环境下实现一个单链表
代码:
运行结果如图所示:
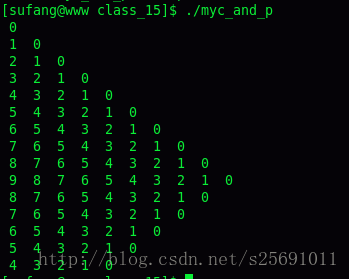
条件变量:函数pthread_cond_init()
pthread_cond_wait()—获得某种资源的执行流的等待的方式
pthread_cond_signal();—唤醒在该条件下等待的执行流
条件变量总是和Mutex搭配使⽤。
⼀个线程可以调⽤用pthread_cond_wait在一个Condition Variable上阻塞等待,这个函数做以下三步操作:
1. 释放Mutex
2. 阻塞等待
3. 当被唤醒时,重新获得Mutex并返回
构建一个生产者与一个消费者模式,创建两个线程在主函数中,代码如下:
生产者-消费者,生产者生产⼀一个结构体串在链表的表头上,消费者 从表头取⾛走结构体,代码如下:
运行结果:
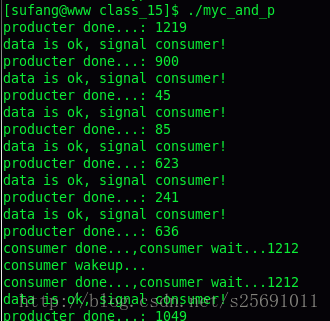
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<unistd.h>
typedef struct _node{
int data;
struct _node *next;
}node_t, *node_p, **node_pp;
static node_p alloc_node(int _d)
{
node_p _n = (node_p)malloc(sizeof(node_t));
if (NULL == _n){
perror("malloc");
exit(1);
}
_n->data = _d;
_n->next = NULL;
}
static int is_empty(node_p _h)
{
assert(_h);
return _h->next == NULL? 1:0;
}
void init_list(node_pp _h)
{
*_h = alloc_node(0);
}
void delete_node(node_p _tmp)
{
if (_tmp){
free(_tmp);
}
}
void destroy_list(node_p _h)
{
assert(_h);
int data;
while ( !is_empty(_h)){
pop_list(_h, &data);
}
delete_node(_h);
}
void push_list(node_p _h, int _d)
{
assert(_h);
node_p _n = alloc_node(_d);
_n->next = _h->next;
_h->next = _n;
}
void pop_list(node_p _h, int *_o)
{
assert(_h);
assert(_o);
if (!is_empty(_h)){
node_p _tmp = _h->next;
_h->next = _tmp->next;
*_o = _tmp->data;
delete_node(_tmp);
}
}
void show_list(node_p _h)
{
assert(_h);
node_p p = _h->next;
while (p != NULL){
printf(" %d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
node_p head = NULL;
init_list(&head);
int i = 0;
for (; i<10; i++){
push_list(head, i);
show_list(head);
sleep(1);
}
int data = 0;
for (; i>5; i--){
pop_list(head, &data);
show_list(head);
sleep(1);
}
destroy_list(head);
return 0;
}运行结果如图所示:

条件变量:函数pthread_cond_init()
pthread_cond_wait()—获得某种资源的执行流的等待的方式
pthread_cond_signal();—唤醒在该条件下等待的执行流
条件变量总是和Mutex搭配使⽤。
⼀个线程可以调⽤用pthread_cond_wait在一个Condition Variable上阻塞等待,这个函数做以下三步操作:
1. 释放Mutex
2. 阻塞等待
3. 当被唤醒时,重新获得Mutex并返回
构建一个生产者与一个消费者模式,创建两个线程在主函数中,代码如下:
pthread_t id1, id2; pthread_create(&id1, NULL, consumer, head); pthread_create(&id2, NULL, producter, head); pthread_join(id1, NULL); pthread_join(id2, NULL);
生产者-消费者,生产者生产⼀一个结构体串在链表的表头上,消费者 从表头取⾛走结构体,代码如下:
static pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
static pthread_cond_t needproduct = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
static void *con
a5e8
sumer(void *arg)
{
node_p h = (node_p)arg;
for ( ; ; ){
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
int data = rand()%1234;
while (! is_empty(h)){
printf("consumer done...,consumer wait...%d\n", data);
pthread_cond_wait(&needproduct,&lock);
printf("consumer wakeup...\n");
}
pop_list(h, &data);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
}
}
static void *producter(void *arg)
{
node_p h = (node_p)arg;
for( ; ; ){
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
int data = rand()%1234;
push_list(h, &data);
printf("producter done...: %d\n", data);
sleep(1);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
pthread_cond_signal(&needproduct);
printf("data is ok, signal consumer!\n");
}
}运行结果:

相关文章推荐
- 单生产者+单消费者模式下的双向循环链表之无锁结构
- 构建生产者,消费者模式的队列
- 生产者—消费者模式
- 阻塞队列和生产者-消费者模式
- 架构设计:生产者/消费者模式 第3页:队列缓冲区
- 生产者/消费者模式2:如何确定数据单元?
- 生产者/消费者模式1:概述
- 同步线程--生产者与消费者模式
- 多线程---使用ManualResetEvent来控制线程间的同步(实现了消费者和生产者模式)
- 架构设计:生产者/消费者模式 第1页:“生产者/消费者模式”介绍
- 架构设计:生产者/消费者模式
- 用ACE实现的生产者和消费者模式
- 老紫竹JAVA提高教程-信号量(Semaphore)在生产者和消费者模式的使用
- 生产者-消费者模式
- 架构设计:生产者/消费者模式[4]:双缓冲区
- 架构设计:生产者/消费者模式 第2页:如何确定数据单元
- Java线程间同步实现生产者-消费者模式
- 架构设计:生产者/消费者模式[0]:概述
- 消费者与生产者模式
- 架构设计:生产者/消费者模式 第5页:环形缓冲区
