嵌入式 Linux根文件系统移植(一)——Linux文件系统简介
2017-03-26 12:43
330 查看
嵌入式 Linux根文件系统移植(一)——Linux文件系统简介
本文对文件系统分析的代码来源于linux 2.6.35.7版本。一、文件系统的体系结构
文件系统是对存储设备上的数据和元数据进行组织的机制,便于用户和操作系统的交互。Linux支持多种文件系统,文件系统接口实现为分层的体系结构,将用户接口层、文件系统实现和操作存储设备的驱动程序分隔开。Linux文件系统的体系结构如下: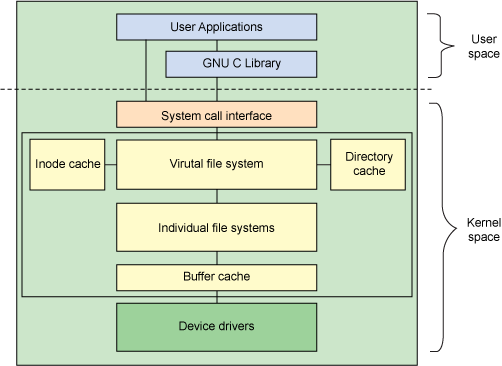
用户空间包含一些应用程序(例如,文件系统的使用者)和 GNU C库(glibc),为文件系统调用(打开、读取、写和关闭)提供用户接口。系统调用接口的作用就像是交换器,将系统调用从用户空间发送到内核空间中的适当端点。
VFS 是底层文件系统的主要接口,会导出一组接口,抽象到各个文件系统。有两个针对文件系统对象的缓存(inode 和 dentry),用于缓存最近使用过的文件系统对象。
每个文件系统的实现(比如 ext2、yaffs2等等)导出一组通用接口,供VFS使用。缓冲区缓存会缓存文件系统和相关块设备之间的请求。例如,对底层设备驱动程序的读写请求会通过缓冲区缓存来传递,允许在缓冲区缓存请求,减少访问物理设备的次数,加快访问速度。以最近使用(LRU)列表的形式管理缓冲区缓存。但是,可以使用sync命令将缓冲区缓存中的请求发送到存储媒体(迫使所有未写的数据发送到设备驱动程序,进而发送到存储设备)。
二、虚拟文件系统层
VFS 作为文件系统接口的根层。VFS 记录当前支持的文件系统以及当前挂装的文件系统。VFS并不是一种实际的文件系统,只存在于内存中,不存在于任何外存空间。VFS在系统启动时建立,在系统关闭时消亡。可以使用一组注册函数在Linux中动态地添加或删除文件系统。kernel保存当前支持的文件系统的列表,可以通过 /proc 文件系统在用户空间中查看这个列表。proc虚拟文件系统还显示当前与所支持文件系统相关联的设备。在Linux中添加新文件系统的方法是调用register_filesystem,函数的参数定义一个文件系统结构(file_system_type)的引用,文件系统结构定义了文件系统的名称、一组属性和两个超级块函数。register_filesystem函数也可以注销文件系统。
在注册新的文件系统时,会把要注册的新文件系统及其相关信息添加到 file_systems链表中(linux/include/linux/fs.h)。file_systems列表定义可以支持的文件系统。在命令行上输入cat /proc/filesystems,就可以查看当前linux系统支持的文件系统类型。
[code=cpp;toolbar:false">int register_filesystem(struct file_system_type * fs){int res = 0;struct file_system_type ** p; BUG_ON(strchr(fs->name, '.'));if (fs->next)return -EBUSY;INIT_LIST_HEAD(&fs->fs_supers);write_lock(&file_systems_lock);p = find_filesystem(fs->name, strlen(fs->name));if (*p)res = -EBUSY;else*p = fs;write_unlock(&file_systems_lock);return res;}
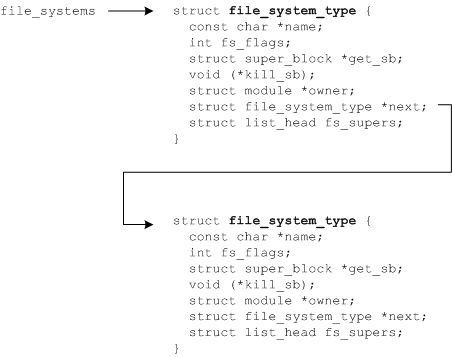
struct file_system_type {const char *name;int fs_flags;int (*get_sb) (struct file_system_type *, int, const char *, void *, struct vfsmount *);void (*kill_sb) (struct super_block *);struct module *owner;struct file_system_type * next;struct list_head fs_supers;struct lock_class_key s_lock_key;struct lock_class_key s_umount_key;struct lock_class_key s_vfs_rename_key;struct lock_class_key i_lock_key;struct lock_class_key i_mutex_key;struct lock_class_key i_mutex_dir_key;struct lock_class_key i_alloc_sem_key;};struct super_block {struct list_heads_list;/* Keep this first */dev_ts_dev;/* search index; _not_ kdev_t */unsigned chars_dirt;unsigned chars_blocksize_bits;unsigned longs_blocksize;loff_ts_maxbytes;/* Max file size */struct file_system_type*s_type;const struct super_operations*s_op;const struct dquot_operations*dq_op;const struct quotactl_ops*s_qcop;const struct export_operations *s_export_op;unsigned longs_flags;unsigned longs_magic;struct dentry*s_root;struct rw_semaphores_umount;struct mutexs_lock;ints_count;atomic_ts_active;#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITYvoid *s_security;#endifconst struct xattr_handler **s_xattr;struct list_heads_inodes;/* all inodes */struct hlist_heads_anon;/* anonymous dentries for (nfs) exporting */struct list_heads_files;struct list_heads_dentry_lru;/* unused dentry lru */ints_nr_dentry_unused;/* # of dentry on lru */struct block_device*s_bdev;struct backing_dev_info *s_bdi;struct mtd_info*s_mtd;struct list_heads_instances;struct quota_infos_dquot;/* Diskquota specific options */ints_frozen;wait_queue_head_ts_wait_unfrozen;char s_id[32];/* Informational name */void *s_fs_info;/* Filesystem private info */fmode_ts_mode;u32 s_time_gran;struct mutex s_vfs_rename_mutex;/* Kludge */char *s_subtype;char *s_options;};struct inode {struct hlist_nodei_hash;struct list_headi_list;/* backing dev IO list */struct list_headi_sb_list;struct list_headi_dentry;unsigned longi_ino;atomic_ti_count;unsigned inti_nlink;uid_ti_uid;gid_ti_gid;dev_ti_rdev;unsigned inti_blkbits;u64i_version;loff_ti_size;#ifdef __NEED_I_SIZE_ORDEREDseqcount_ti_size_seqcount;#endifstruct timespeci_atime;struct timespeci_mtime;struct timespeci_ctime;blkcnt_ti_blocks;unsigned short i_bytes;umode_ti_mode;spinlock_ti_lock;/* i_blocks, i_bytes, maybe i_size */struct mutexi_mutex;struct rw_semaphorei_alloc_sem;const struct inode_operations*i_op;const struct file_operations*i_fop;/* former ->i_op->default_file_ops */struct super_block*i_sb;struct file_lock*i_flock;struct address_space*i_mapping;struct address_spacei_data;#ifdef CONFIG_QUOTAstruct dquot*i_dquot[MAXQUOTAS];#endifstruct list_headi_devices;union {struct pipe_inode_info*i_pipe;struct block_device*i_bdev;struct cdev*i_cdev;};__u32i_generation;#ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY__u32i_fsnotify_mask; /* all events this inode cares about */struct hlist_headi_fsnotify_mark_entries; /* fsnotify mark entries */#endif#ifdef CONFIG_INOTIFYstruct list_headinotify_watches; /* watches on this inode */struct mutexinotify_mutex;/* protects the watches list */#endifunsigned longi_state;unsigned longdirtied_when;/* jiffies of first dirtying */unsigned inti_flags;atomic_ti_writecount;#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITYvoid*i_security;#endif#ifdef CONFIG_FS_POSIX_ACLstruct posix_acl*i_acl;struct posix_acl*i_default_acl;#endifvoid*i_private; /* fs or device private pointer */}; struct inode_operations {int (*create) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,int, struct nameidata *);struct dentry * (*lookup) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, struct nameidata *);int (*link) (struct dentry *,struct inode *,struct dentry *);int (*unlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);int (*symlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,const char *);int (*mkdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,int);int (*rmdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);int (*mknod) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,int,dev_t);int (*rename) (struct inode *, struct dentry *,struct inode *, struct dentry *);int (*readlink) (struct dentry *, char __user *,int);void * (*follow_link) (struct dentry *, struct nameidata *);void (*put_link) (struct dentry *, struct nameidata *, void *);void (*truncate) (struct inode *);int (*permission) (struct inode *, int);int (*check_acl)(struct inode *, int);int (*setattr) (struct dentry *, struct iattr *);int (*getattr) (struct vfsmount *mnt, struct dentry *, struct kstat *);int (*setxattr) (struct dentry *, const char *,const void *,size_t,int);ssize_t (*getxattr) (struct dentry *, const char *, void *, size_t);ssize_t (*listxattr) (struct dentry *, char *, size_t);int (*removexattr) (struct dentry *, const char *);void (*truncate_range)(struct inode *, loff_t, loff_t);long (*fallocate)(struct inode *inode, int mode, loff_t offset, loff_t len);int (*fiemap)(struct inode *, struct fiemap_extent_info *, u64 start, u64 len);};[title3]
相关文章推荐
- 嵌入式 Linux根文件系统移植(二)——根文件系统简介
- 嵌入式 Linux根文件系统移植(二)——根文件系统简介
- 嵌入式 Linux根文件系统移植(三)——根文件系统构建
- 嵌入式根文件系统的移植和制作(一)
- 移植yaffs2文件系统到mini2440 嵌入式 yaffs2文件系统的移植
- 嵌入式根文件系统的移植和制作详解
- 嵌入式学习笔记(3)---YAFFS文件系统的制作移植
- 嵌入式根文件系统的移植和制作详解
- 嵌入式根文件系统的移植和制作(二)
- 嵌入式根文件系统的移植和制作详解
- 嵌入式根文件系统的移植和制作详解
- 嵌入式根文件系统的移植和制作详解
- Linux嵌入式移植之——(2)文件系统制作, initramfs
- 移植yaffs2文件系统到mini2440 嵌入式 yaffs2文件系统的移植
- 嵌入式根文件系统的移植和制作详解
- 嵌入式文件系统简介
- 嵌入式Linux文件系统简介
- 嵌入式根文件系统的定制及移植(一) 推荐
- 嵌入式根文件系统的定制及移植(二)
- 嵌入式linux文件系统简介
