二叉树的各种概念以及代码操作
2017-03-18 12:26
501 查看
二叉树的各种概念以及代码操作
一、基本概念* 每个结点最多有两棵子树,左子树和右子树,次序不可以颠倒。
性质:
1. 非空二叉树的第n层上至多有2^(n-1)个元素。
2. 深度为h的二叉树至多有2^h-1个结点。
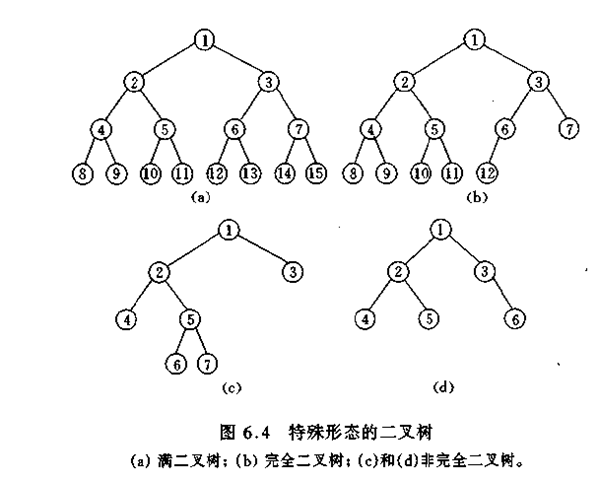
* 满二叉树:所有终端都在同一层次,且非终端结点的度数为2。
在满二叉树中若其深度为h,则其所包含的结点数必为2^h-1。
* 完全二叉树:只有最下面的两层结点度能够小于2,并且最下面一层的结点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置的二叉树。
* 图样
树的三种遍历方式
前序遍历:根节点->左子树->右子树中序遍历:左子树->根节点->右子树
后序遍历:左子树->右子树->根节点
例如:求下面树的三种遍历
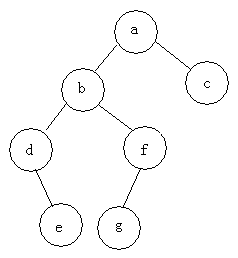
前序遍历:abdefgc
中序遍历:debgfac
后序遍历:edgfbca
最优二叉树
又名哈夫曼树,定义:给定n个权值作为n个叶子结点,构造一棵二叉树,若带权路径长度达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树,也称为哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)。哈夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的结点离根较近。二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree)
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),(又:二叉搜索树,二叉排序树)它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值; 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值; 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树。二叉查找树的插入:从根节点进行对比,小于根节点,在根节点左子树进行对比;大于根节点,在根节点右子树进行对比。一直重复上述过程,当找到节点为空的地方插入。
二叉树的删除
被删除节点没有子树的情况,直接删除,并修改对应父节点的指针为空。
对于只有一个子树的情况,考虑将其子树作为其父节点的子树,关于是左还是右,根据被删除的节点确定。
最复杂的是有两个子数的情况,可以考虑两种方法,都是同样的思想:用被删除节点A的左子树的最右节点或者A的右子树的最左节点作为替代A的节点,并修改相应的最左或最右节点的父节点的指针,修改方法类似2 。
图样
各种二叉树操作代码算法
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 高远</n>
* 邮箱 wgyscsf@163.com</n>
* 编写日期 2017-3-17下午2:31:24</n>
* </n>
*/
public class MyBinaryTreeList {
BinaryTree root;
// 定义二叉树
class BinaryTree {
BinaryTree left;
BinaryTree right;
int value;
public BinaryTree(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public BinaryTree() {
root = null;
}
}
// 向二叉查找树插入数据
boolean add(BinaryTree binaryTree,int value) {
if (root == null) {
root = new BinaryTree(value);
} else {
if (value < binaryTree.value) {
if (binaryTree.left == null) {
binaryTree.left = new BinaryTree(value);
} else {
add(binaryTree.left, value);
}
} else {
if (binaryTree.right == null) {
binaryTree.right = new BinaryTree(value);
} else {
add(binaryTree.right, value);
}
}
}
return true;
}
// 前序遍历
void preScanner(BinaryTree binaryTree) {
if (binaryTree == null)
return;
System.out.print(binaryTree.value + ",");
preScanner(binaryTree.left);
preScanner(binaryTree.right);
}
// 中序遍历
void midScanner(BinaryTree binaryTree) {
if (binaryTree == null)
return;
midScanner(binaryTree.left);
System.out.print(binaryTree.value + ",");
midScanner(binaryTree.right);
}
// 后序遍历
void finScanner(BinaryTree binaryTree) {
if (binaryTree == null)
return;
finScanner(binaryTree.left);
finScanner(binaryTree.right);
System.out.print(binaryTree.value + ",");
}
// 递归求树的深度
int treeDeepByRecursion(BinaryTree binaryTree) {
if (binaryTree == null)
return 0;
int leftDeep = treeDeepByRecursion(binaryTree.left);
int rightDeep = treeDeepByRecursion(binaryTree.right);
return leftDeep > rightDeep ? leftDeep + 1 : rightDeep + 1;
}
/*
* 非递归求树的深度,思路:
* 1.维护一个当前队列节点的长度a,在初始化一个长度为零的变量b。变量每次加一,取出一个数据,同时加入该节点的左右孩纸。当a=b,结束当前循环。
* 2. 结束循环前维护一个深度l,深度l++。 3. 重复1,2。当队列时结束。
*/
int treeDeepByNoRecursion(BinaryTree binaryTree) {
if (binaryTree == null)
return 0;
// 维护一个队列,
LinkedList<BinaryTree> binaryTreeList = new LinkedList<>();
binaryTreeList.offer(binaryTree);
int currentIndex;
int lastIndex;
BinaryTree currentBinaryTree;
//深度
int leval=0;
//结束条件
while(!binaryTreeList.isEmpty()){
currentIndex=0;
lastIndex=binaryTreeList.size();
while (currentIndex < lastIndex) {
// poll取出一个元素,并从原来队列删除;peek查询第一个数据。
currentBinaryTree = binaryTreeList.poll();
currentIndex++;
// 以下是将下一层加入队列,在下次循环中进行计算
if (currentBinaryTree.left != null) {
binaryTreeList.offer(currentBinaryTree.left);
}
if (currentBinaryTree.right != null) {
binaryTreeList.offer(currentBinaryTree.right);
}
}
leval++;
}
return leval;
}
// 求树的宽度。思路和非递归求树的深度相对应。
int treeWidth(BinaryTree binaryTree) {
LinkedList<BinaryTree> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.offer(binaryTree);
int currentIndex;// 当前位置节点。
int lastIndex;// 当前层最大节点的数量,即当前层树的宽度。
BinaryTree currentBinaryTree;// 当前取出的节点。
int maxLen = 0;// 最大层的值。
while (!linkedList.isEmpty()) {
currentIndex = 0;
lastIndex = linkedList.size();
while (currentIndex < lastIndex) {
currentBinaryTree = linkedList.poll();
currentIndex++;
// 以下是将下一层加入队列,在下次循环中进行计算
if (currentBinaryTree.left != null) {
linkedList.offer(currentBinaryTree.left);
}
if (currentBinaryTree.right != null) {
linkedList.offer(currentBinaryTree.right);
}
}
// 处理最大层的数量
if (lastIndex > maxLen) {
maxLen = lastIndex;
}
}
return maxLen;
}
// 找出二叉树的所有深度遍历路径
ArrayList<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> listList3 = new ArrayList<>();
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> getAllDeepPath(BinaryTree binaryTree) {
if (binaryTree == null)
return listList3;
list3.add(binaryTree.value);
if (binaryTree.left == null && binaryTree.right == null) {
// 这种写法不行,原因:@param c the collection whose elements are to be placed
// into this list
// listList3.add(list3);
listList3.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(list3));//
}
if (binaryTree.left != null)
getAllDeepPath(binaryTree.left);
if (binaryTree.right != null)
getAllDeepPath(binaryTree.right);
list3.remove(list3.size() - 1);
return listList3;
}
// 在二叉树中找出和为某一值的所有路径
List<Integer> list4 = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> allList4 = new ArrayList<>();
private List<List<Integer>> getSpDeepTree(BinaryTree binaryTree, int target) {
if (binaryTree == null)
return allList4;
list4.add(binaryTree.value);
target -= binaryTree.value;
if (target == 0 && binaryTree.left == null && binaryTree.right == null)
allList4.add(new ArrayList<>(list4));
if (binaryTree.left != null)
getSpDeepTree(binaryTree.left, target);
if (binaryTree.right != null)
getSpDeepTree(binaryTree.right, target);
list4.remove(list4.size() - 1);
return allList4;
}
// test
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[] { 5, 3, 4, 1, 7, 8, 2, 6, 0, 9 };
MyBinaryTreeList binaryTreeList = new MyBinaryTreeList();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
binaryTreeList.add(binaryTreeList.root, arr[i]);
}
System.out.println("前序遍历");
binaryTreeList.preScanner(binaryTreeList.root);
System.out.println("中序遍历");
binaryTreeList.midScanner(binaryTreeList.root);
System.out.println("后序遍历");
binaryTreeList.finScanner(binaryTreeList.root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("递归树的深度:"
+ binaryTreeList.treeDeepByRecursion(binaryTreeList.root));
System.out.println("非递归树的深度:"
+ binaryTreeList.treeDeepByNoRecursion(binaryTreeList.root));
System.out.println("递归树的宽度:"
+ binaryTreeList.treeWidth(binaryTreeList.root));
System.out.println("在二叉树中找所有路径2:");
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> findPath3 = binaryTreeList
.getAllDeepPath(binaryTreeList.root);
for (List<Integer> arrayList : findPath3) {
for (Integer integer : arrayList) {
System.out.print(integer + ",");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("在二叉树中找出和为某一值的所有路径2:");
List<List<Integer>> findPath4 = binaryTreeList.getSpDeepTree(
binaryTreeList.root, 12);
for (List<Integer> arrayList : findPath4) {
for (Integer integer : arrayList) {
System.out.print(integer + ",");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
相关文章推荐
- 【整理】二叉树概念以及代码实现
- Oracle数据库的概念(权限、角色)以及各种操作(创建表空间、创建表、查询、更新、删除、插入)和常用函数
- 二叉树的定义,节点的增删改查以及父节点、子节点的各种操作。
- 二叉树常见概念、性质、问题以及操作
- 队列的基本操作概念及各种实现方式的代码
- c# 流的概念以及一个操作文本文件的实例代码
- [emacs] Python代码补全的各种方法介绍以及对比
- 遍历二叉树的各种操作
- Java中各种文件类型操作的代码与详细文件IO讲解
- 一个WinForm记事本程序(包含主/下拉/弹出菜单/打开文件/保存文件/打印/页面设置/字体/颜色对话框/剪切版操作等等控件用法以及记事本菜单事件/按键事件的具体代码)
- Jquery选择器的概念以及选择器的学习一(基本、层级、简单,另有简单动画效果代码)
- Android中Exif的操作以及Camera应用中相关代码优化方案
- 一个WinForm记事本程序(包含主/下拉/弹出菜单/打开文件/保存文件/打印/页面设置/字体/颜色对话框/剪切版操作等等控件用法以及记事本菜单事件/按键事件的具体代码)
- 查找二叉树的基本操作以及层次遍历
- 带头结点和不带头结点的单链表的尾插法以及各种操作
- Android中对Group的各种操作示例代码
- 遍历二叉树的各种操作(非递归遍历)
- 二叉树实现(包括遍历等各种操作,递归与非递归)
- 一个WinForm记事本程序(包含主/下拉/弹出菜单/打开文件/保存文件/打印/页面设置/字体/颜色对话框/剪切版操作等等控件用法以及记事本菜单事件/按键事件的具体代码)
- 单词吸血鬼源代码 二叉树操作
