Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2) C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons(DFS 邻接表 数据结构)
2017-03-07 20:36
531 查看
C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons
time limit per test2 seconds
memory limit per test256 megabytes
inputstandard input
outputstandard output
Andryusha goes through a park each day. The squares and paths between them look boring to Andryusha, so he decided to decorate them.
The park consists of n squares connected with (n - 1) bidirectional paths in such a way that any square is reachable from any other using these paths. Andryusha decided to hang a colored balloon at each of the squares. The baloons’ colors are described by positive integers, starting from 1. In order to make the park varicolored, Andryusha wants to choose the colors in a special way. More precisely, he wants to use such colors that if a, b and c are distinct squares that a and b have a direct path between them, and b and c have a direct path between them, then balloon colors on these three squares are distinct.
Andryusha wants to use as little different colors as possible. Help him to choose the colors!
Input
The first line contains single integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — the number of squares in the park.
Each of the next (n - 1) lines contains two integers x and y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n) — the indices of two squares directly connected by a path.
It is guaranteed that any square is reachable from any other using the paths.
Output
In the first line print single integer k — the minimum number of colors Andryusha has to use.
In the second line print n integers, the i-th of them should be equal to the balloon color on the i-th square. Each of these numbers should be within range from 1 to k.
Examples
input
3
2 3
1 3
output
3
1 3 2
input
5
2 3
5 3
4 3
1 3
output
5
1 3 2 5 4
input
5
2 1
3 2
4 3
5 4
output
3
1 2 3 1 2
Note
In the first sample the park consists of three squares: 1 → 3 → 2. Thus, the balloon colors have to be distinct.
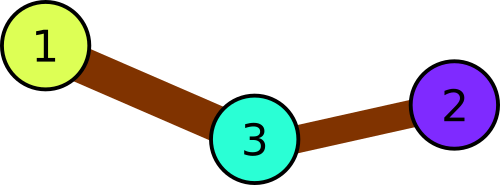
Illustration for the first sample.
In the second example there are following triples of consequently connected squares:
1 → 3 → 2
1 → 3 → 4
1 → 3 → 5
2 → 3 → 4
2 → 3 → 5
4 → 3 → 5
We can see that each pair of squares is encountered in some triple, so all colors have to be distinct.
Illustration for the second sample.
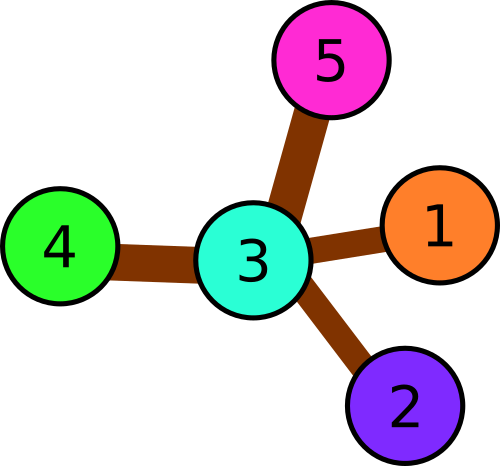
In the third example there are following triples:
1 → 2 → 3
2 → 3 → 4
3 → 4 → 5
We can see that one or two colors is not enough, but there is an answer that uses three colors only.
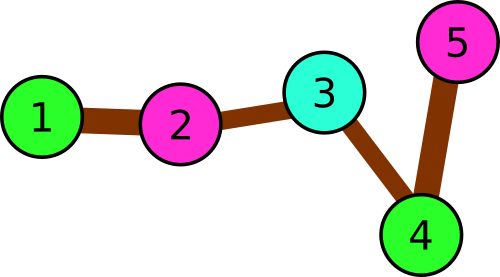
Illustration for the third sample.
题意:给定一颗N个结点N-1条边的连通图,连续相邻的三个结点颜色不能相同,输出做大所需颜色数量和每个结点的颜色。
思路:采用邻接表双向建图,深搜时根据当前结点找下一节点的颜色时还要照顾到上一节点的颜色。
代码
time limit per test2 seconds
memory limit per test256 megabytes
inputstandard input
outputstandard output
Andryusha goes through a park each day. The squares and paths between them look boring to Andryusha, so he decided to decorate them.
The park consists of n squares connected with (n - 1) bidirectional paths in such a way that any square is reachable from any other using these paths. Andryusha decided to hang a colored balloon at each of the squares. The baloons’ colors are described by positive integers, starting from 1. In order to make the park varicolored, Andryusha wants to choose the colors in a special way. More precisely, he wants to use such colors that if a, b and c are distinct squares that a and b have a direct path between them, and b and c have a direct path between them, then balloon colors on these three squares are distinct.
Andryusha wants to use as little different colors as possible. Help him to choose the colors!
Input
The first line contains single integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — the number of squares in the park.
Each of the next (n - 1) lines contains two integers x and y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n) — the indices of two squares directly connected by a path.
It is guaranteed that any square is reachable from any other using the paths.
Output
In the first line print single integer k — the minimum number of colors Andryusha has to use.
In the second line print n integers, the i-th of them should be equal to the balloon color on the i-th square. Each of these numbers should be within range from 1 to k.
Examples
input
3
2 3
1 3
output
3
1 3 2
input
5
2 3
5 3
4 3
1 3
output
5
1 3 2 5 4
input
5
2 1
3 2
4 3
5 4
output
3
1 2 3 1 2
Note
In the first sample the park consists of three squares: 1 → 3 → 2. Thus, the balloon colors have to be distinct.

Illustration for the first sample.
In the second example there are following triples of consequently connected squares:
1 → 3 → 2
1 → 3 → 4
1 → 3 → 5
2 → 3 → 4
2 → 3 → 5
4 → 3 → 5
We can see that each pair of squares is encountered in some triple, so all colors have to be distinct.
Illustration for the second sample.

In the third example there are following triples:
1 → 2 → 3
2 → 3 → 4
3 → 4 → 5
We can see that one or two colors is not enough, but there is an answer that uses three colors only.

Illustration for the third sample.
题意:给定一颗N个结点N-1条边的连通图,连续相邻的三个结点颜色不能相同,输出做大所需颜色数量和每个结点的颜色。
思路:采用邻接表双向建图,深搜时根据当前结点找下一节点的颜色时还要照顾到上一节点的颜色。
代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string.h>
#include<string>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=400005;
int u[maxn];
int v[maxn];
int first[maxn];
int nextt[maxn];
int color[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
int N;
int max_color_num=1;
void DFS(int last,int now)
{
if(now==-1)
return;
int color_num=1;
for(int i=first[now]; i!=-1; i=nextt[i])
{
if(vis[v[i]]==false)
{
if(last!=-1&&color[last]==color_num)
color_num++;
if(color[now]==color_num)
color_num++;
if(last!=-1&&color[last]==color_num)
color_num++;
color[v[i]]=color_num;
max_color_num=max(max_color_num,color[v[i]]);
vis[v[i]]=true;
DFS(now,v[i]);
color_num++;
}
}
return;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&N);
memset(u,-1,sizeof(u));
memset(v,-1,sizeof(v));
memset(first,-1,sizeof(first));
memset(nextt,-1,sizeof(nextt));
memset(color,-1,sizeof(color));
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=1; i<N; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&u[i],&v[i]);
nextt[i]=first[u[i]];
first[u[i]]=i;
//建立双向邻接表
u[i+N-1]=v[i];
v[i+N-1]=u[i];
nextt[i+N-1]=first[u[i+N-1]];
first[u[i+N-1]]=i+N-1;
}
color[1]=1;
vis[1]=true;
DFS(-1,1);
printf("%d\n%d",max_color_num,color[1]);
for(int i=2; i<=N; i++)
printf(" %d",color[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- #树上DFS# Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2) C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons
- 【贪心】【DFS】Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals) C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2)C Andryusha and Colored Balloons (dfs)
- CodeForces 780C Andryusha and Colored Balloons【DFS】
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2 C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons ( 树上染色问题
- CodeForces 780C Andryusha and Colored Balloons (DFS)
- Codeforces Round #403 C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons(DFS)
- 【Codeforces 781 A Andryusha and Colored Balloons】+ DFS
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2) C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons
- Codeforces 780C Andryusha and Colored Balloons 搜索dfs
- codeforces 780-C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons(dfs)
- Codeforces Round #403 div2 C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2) C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals) C Andryusha and Colored Balloons
- C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons
- Andryusha and Colored Balloons
- AC日记——Andryusha and Colored Balloons codeforces 780c
- C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons
- Codeforces Andryusha and Colored Balloons
- C. Andryusha and Colored Balloons
